Hung Yu Ling
SILK: Smooth InterpoLation frameworK for motion in-betweening A Simplified Computational Approach
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Motion in-betweening is a crucial tool for animators, enabling intricate control over pose-level details in each keyframe. Recent machine learning solutions for motion in-betweening rely on complex models, incorporating skeleton-aware architectures or requiring multiple modules and training steps. In this work, we introduce a simple yet effective Transformer-based framework, employing a single Transformer encoder to synthesize realistic motions for motion in-betweening tasks. We find that data modeling choices play a significant role in improving in-betweening performance. Among others, we show that increasing data volume can yield equivalent or improved motion transitions, that the choice of pose representation is vital for achieving high-quality results, and that incorporating velocity input features enhances animation performance. These findings challenge the assumption that model complexity is the primary determinant of animation quality and provide insights into a more data-centric approach to motion interpolation. Additional videos and supplementary material are available at https://silk-paper.github.io.
StableMotion: Training Motion Cleanup Models with Unpaired Corrupted Data
May 06, 2025
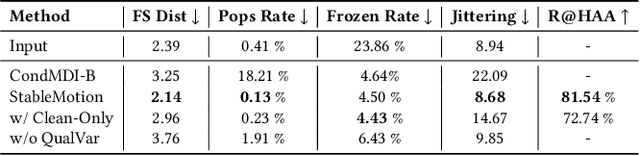
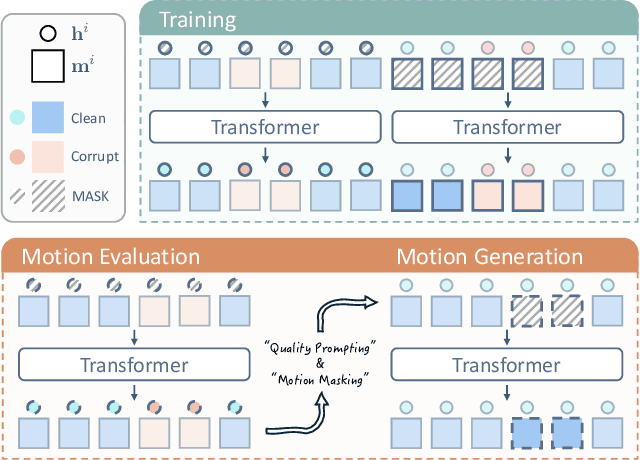
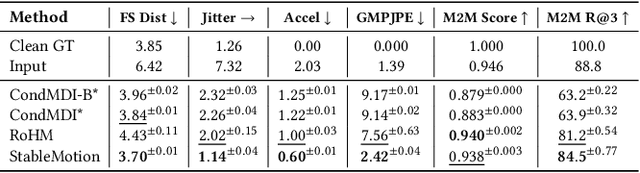
Abstract:Motion capture (mocap) data often exhibits visually jarring artifacts due to inaccurate sensors and post-processing. Cleaning this corrupted data can require substantial manual effort from human experts, which can be a costly and time-consuming process. Previous data-driven motion cleanup methods offer the promise of automating this cleanup process, but often require in-domain paired corrupted-to-clean training data. Constructing such paired datasets requires access to high-quality, relatively artifact-free motion clips, which often necessitates laborious manual cleanup. In this work, we present StableMotion, a simple yet effective method for training motion cleanup models directly from unpaired corrupted datasets that need cleanup. The core component of our method is the introduction of motion quality indicators, which can be easily annotated through manual labeling or heuristic algorithms and enable training of quality-aware motion generation models on raw motion data with mixed quality. At test time, the model can be prompted to generate high-quality motions using the quality indicators. Our method can be implemented through a simple diffusion-based framework, leading to a unified motion generate-discriminate model, which can be used to both identify and fix corrupted frames. We demonstrate that our proposed method is effective for training motion cleanup models on raw mocap data in production scenarios by applying StableMotion to SoccerMocap, a 245-hour soccer mocap dataset containing real-world motion artifacts. The trained model effectively corrects a wide range of motion artifacts, reducing motion pops and frozen frames by 68% and 81%, respectively. See https://youtu.be/3Y7MMAH02B4 for more results.
InterMimic: Towards Universal Whole-Body Control for Physics-Based Human-Object Interactions
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Achieving realistic simulations of humans interacting with a wide range of objects has long been a fundamental goal. Extending physics-based motion imitation to complex human-object interactions (HOIs) is challenging due to intricate human-object coupling, variability in object geometries, and artifacts in motion capture data, such as inaccurate contacts and limited hand detail. We introduce InterMimic, a framework that enables a single policy to robustly learn from hours of imperfect MoCap data covering diverse full-body interactions with dynamic and varied objects. Our key insight is to employ a curriculum strategy -- perfect first, then scale up. We first train subject-specific teacher policies to mimic, retarget, and refine motion capture data. Next, we distill these teachers into a student policy, with the teachers acting as online experts providing direct supervision, as well as high-quality references. Notably, we incorporate RL fine-tuning on the student policy to surpass mere demonstration replication and achieve higher-quality solutions. Our experiments demonstrate that InterMimic produces realistic and diverse interactions across multiple HOI datasets. The learned policy generalizes in a zero-shot manner and seamlessly integrates with kinematic generators, elevating the framework from mere imitation to generative modeling of complex human-object interactions.
Learning to Brachiate via Simplified Model Imitation
May 08, 2022


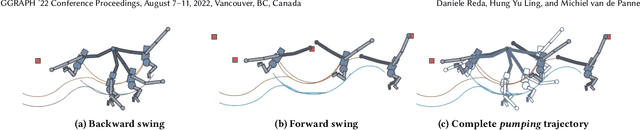
Abstract:Brachiation is the primary form of locomotion for gibbons and siamangs, in which these primates swing from tree limb to tree limb using only their arms. It is challenging to control because of the limited control authority, the required advance planning, and the precision of the required grasps. We present a novel approach to this problem using reinforcement learning, and as demonstrated on a finger-less 14-link planar model that learns to brachiate across challenging handhold sequences. Key to our method is the use of a simplified model, a point mass with a virtual arm, for which we first learn a policy that can brachiate across handhold sequences with a prescribed order. This facilitates the learning of the policy for the full model, for which it provides guidance by providing an overall center-of-mass trajectory to imitate, as well as for the timing of the holds. Lastly, the simplified model can also readily be used for planning suitable sequences of handholds in a given environment. Our results demonstrate brachiation motions with a variety of durations for the flight and hold phases, as well as emergent extra back-and-forth swings when this proves useful. The system is evaluated with a variety of ablations. The method enables future work towards more general 3D brachiation, as well as using simplified model imitation in other settings.
Character Controllers Using Motion VAEs
Mar 26, 2021



Abstract:A fundamental problem in computer animation is that of realizing purposeful and realistic human movement given a sufficiently-rich set of motion capture clips. We learn data-driven generative models of human movement using autoregressive conditional variational autoencoders, or Motion VAEs. The latent variables of the learned autoencoder define the action space for the movement and thereby govern its evolution over time. Planning or control algorithms can then use this action space to generate desired motions. In particular, we use deep reinforcement learning to learn controllers that achieve goal-directed movements. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach on multiple tasks. We further evaluate system-design choices and describe the current limitations of Motion VAEs.
ALLSTEPS: Curriculum-driven Learning of Stepping Stone Skills
May 09, 2020



Abstract:Humans are highly adept at walking in environments with foot placement constraints, including stepping-stone scenarios where the footstep locations are fully constrained. Finding good solutions to stepping-stone locomotion is a longstanding and fundamental challenge for animation and robotics. We present fully learned solutions to this difficult problem using reinforcement learning. We demonstrate the importance of a curriculum for efficient learning and evaluate four possible curriculum choices compared to a non-curriculum baseline. Results are presented for a simulated human character, a realistic bipedal robot simulation and a monster character, in each case producing robust, plausible motions for challenging stepping stone sequences and terrains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge