Cewu Lu
TacIPC: Intersection- and Inversion-free FEM-based Elastomer Simulation For Optical Tactile Sensors
Nov 10, 2023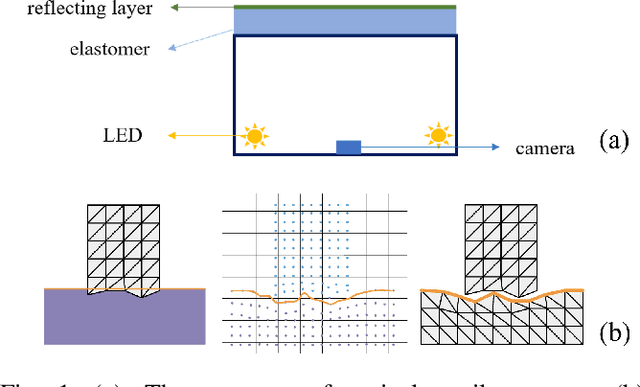
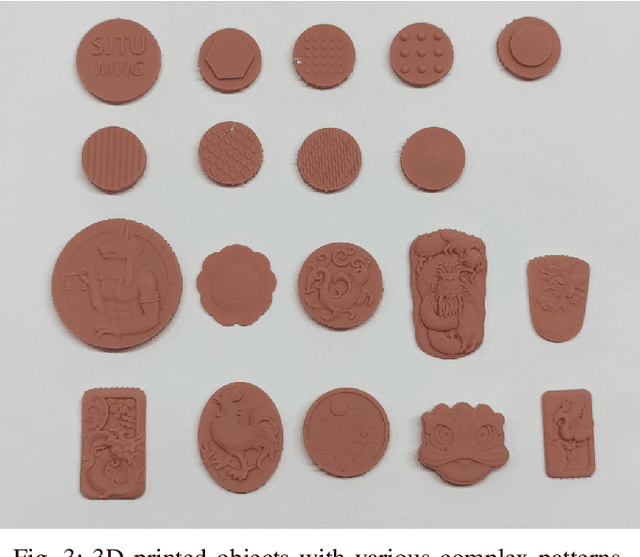
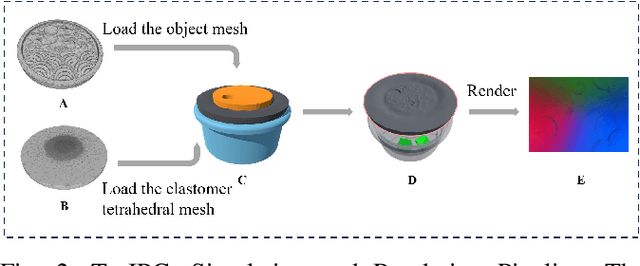

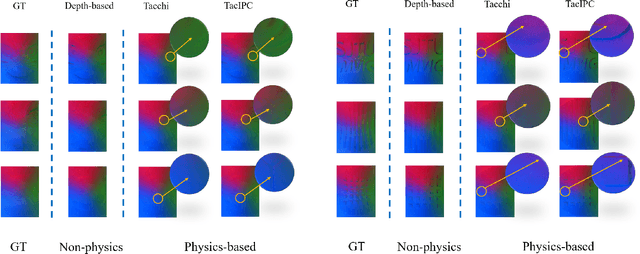
Abstract:Tactile perception stands as a critical sensory modality for human interaction with the environment. Among various tactile sensor techniques, optical sensor-based approaches have gained traction, notably for producing high-resolution tactile images. This work explores gel elastomer deformation simulation through a physics-based approach. While previous works in this direction usually adopt the explicit material point method (MPM), which has certain limitations in force simulation and rendering, we adopt the finite element method (FEM) and address the challenges in penetration and mesh distortion with incremental potential contact (IPC) method. As a result, we present a simulator named TacIPC, which can ensure numerically stable simulations while accommodating direct rendering and friction modeling. To evaluate TacIPC, we conduct three tasks: pseudo-image quality assessment, deformed geometry estimation, and marker displacement prediction. These tasks show its superior efficacy in reducing the sim-to-real gap. Our method can also seamlessly integrate with existing simulators. More experiments and videos can be found in the supplementary materials and on the website: https://sites.google.com/view/tac-ipc.
Intersection-free Robot Manipulation with Soft-Rigid Coupled Incremental Potential Contact
Nov 10, 2023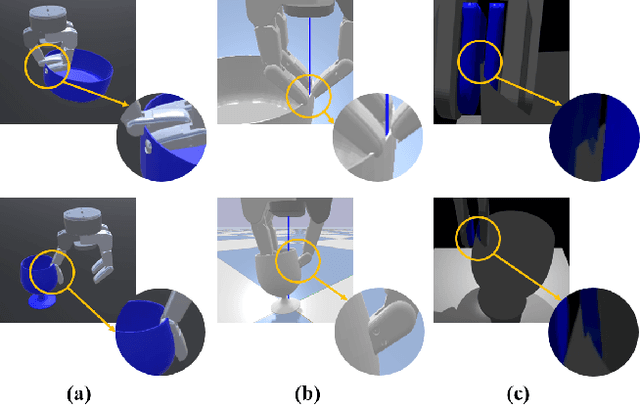

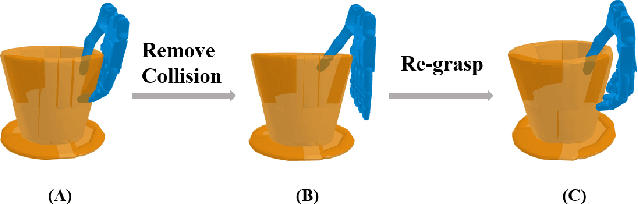
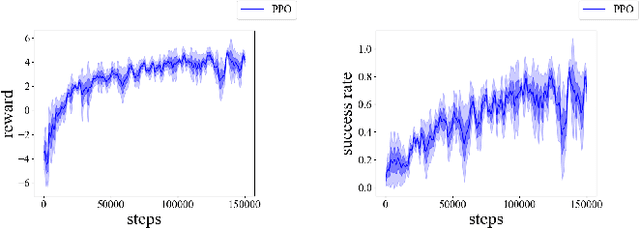
Abstract:This paper presents a novel simulation platform, ZeMa, designed for robotic manipulation tasks concerning soft objects. Such simulation ideally requires three properties: two-way soft-rigid coupling, intersection-free guarantees, and frictional contact modeling, with acceptable runtime suitable for deep and reinforcement learning tasks. Current simulators often satisfy only a subset of these needs, primarily focusing on distinct rigid-rigid or soft-soft interactions. The proposed ZeMa prioritizes physical accuracy and integrates the incremental potential contact method, offering unified dynamics simulation for both soft and rigid objects. It efficiently manages soft-rigid contact, operating 75x faster than baseline tools with similar methodologies like IPC-GraspSim. To demonstrate its applicability, we employ it for parallel grasp generation, penetrated grasp repair, and reinforcement learning for grasping, successfully transferring the trained RL policy to real-world scenarios.
Differentiable Fluid Physics Parameter Identification Via Stirring
Nov 09, 2023
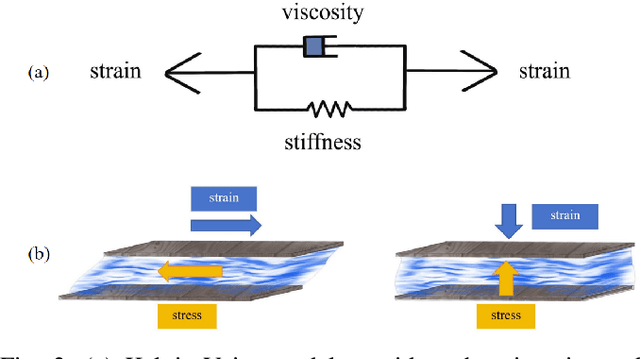


Abstract:Fluid interactions permeate daily human activities, with properties like density and viscosity playing pivotal roles in household tasks. While density estimation is straightforward through Archimedes' principle, viscosity poses a more intricate challenge, especially given the varied behaviors of Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids. These fluids, which differ in their stress-strain relationships, are delineated by specific constitutive models such as the Carreau, Cross, and Herschel-Bulkley models, each possessing unique viscosity parameters. This study introduces a novel differentiable fitting framework, DiffStir, tailored to identify key physics parameters via the common daily operation of stirring. By employing a robotic arm for stirring and harnessing a differentiable Material Point Method (diffMPM)-based simulator, the framework can determine fluid parameters by matching observations from both the simulator and the real world. Recognizing the distinct preferences of the aforementioned constitutive models for specific fluids, an online strategy was adopted to adaptively select the most fitting model based on real-world data. Additionally, we propose a refining neural network to bridge the sim-to-real gap and mitigate sensor noise-induced inaccuracies. Comprehensive experiments were conducted to validate the efficacy of DiffStir, showcasing its precision in parameter estimation when benchmarked against reported literature values. More experiments and videos can be found in the supplementary materials and on the website: https://sites.google.com/view/diffstir.
Differentiable Cloth Parameter Identification and State Estimation in Manipulation
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:In the realm of robotic cloth manipulation, accurately estimating the cloth state during or post-execution is imperative. However, the inherent complexities in a cloth's dynamic behavior and its near-infinite degrees of freedom (DoF) pose significant challenges. Traditional methods have been restricted to using keypoints or boundaries as cues for cloth state, which do not holistically capture the cloth's structure, especially during intricate tasks like folding. Additionally, the critical influence of cloth physics has often been overlooked in past research. Addressing these concerns, we introduce DiffCP, a novel differentiable pipeline that leverages the Anisotropic Elasto-Plastic (A-EP) constitutive model, tailored for differentiable computation and robotic tasks. DiffCP adopts a ``real-to-sim-to-real'' methodology. By observing real-world cloth states through an RGB-D camera and projecting this data into a differentiable simulator, the system identifies physics parameters by minimizing the geometric variance between observed and target states. Extensive experiments demonstrate DiffCP's ability and stability to determine physics parameters under varying manipulations, grasping points, and speeds. Additionally, its applications extend to cloth material identification, manipulation trajectory generation, and more notably, enhancing cloth pose estimation accuracy. More experiments and videos can be found in the supplementary materials and on the website: https://sites.google.com/view/diffcp.
Precise Robotic Needle-Threading with Tactile Perception and Reinforcement Learning
Nov 04, 2023Abstract:This work presents a novel tactile perception-based method, named T-NT, for performing the needle-threading task, an application of deformable linear object (DLO) manipulation. This task is divided into two main stages: Tail-end Finding and Tail-end Insertion. In the first stage, the agent traces the contour of the thread twice using vision-based tactile sensors mounted on the gripper fingers. The two-run tracing is to locate the tail-end of the thread. In the second stage, it employs a tactile-guided reinforcement learning (RL) model to drive the robot to insert the thread into the target needle eyelet. The RL model is trained in a Unity-based simulated environment. The simulation environment supports tactile rendering which can produce realistic tactile images and thread modeling. During insertion, the position of the poke point and the center of the eyelet are obtained through a pre-trained segmentation model, Grounded-SAM, which predicts the masks for both the needle eye and thread imprints. These positions are then fed into the reinforcement learning model, aiding in a smoother transition to real-world applications. Extensive experiments on real robots are conducted to demonstrate the efficacy of our method. More experiments and videos can be found in the supplementary materials and on the website: https://sites.google.com/view/tac-needlethreading.
UniFolding: Towards Sample-efficient, Scalable, and Generalizable Robotic Garment Folding
Nov 02, 2023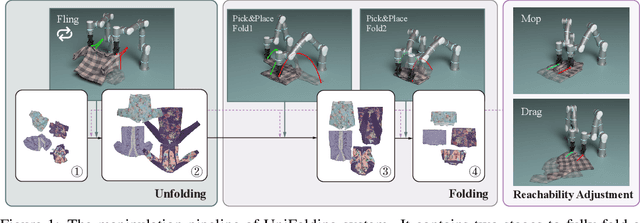
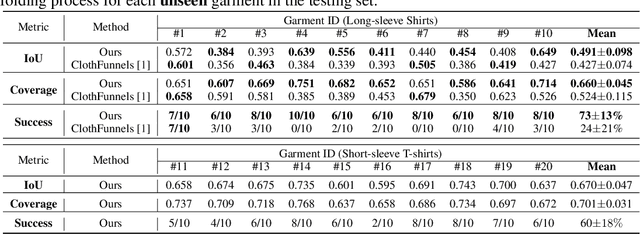
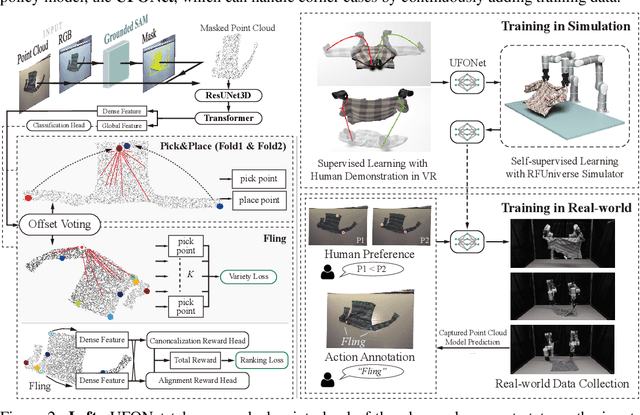
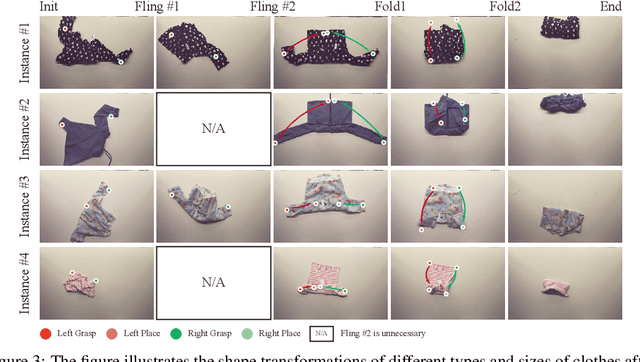
Abstract:This paper explores the development of UniFolding, a sample-efficient, scalable, and generalizable robotic system for unfolding and folding various garments. UniFolding employs the proposed UFONet neural network to integrate unfolding and folding decisions into a single policy model that is adaptable to different garment types and states. The design of UniFolding is based on a garment's partial point cloud, which aids in generalization and reduces sensitivity to variations in texture and shape. The training pipeline prioritizes low-cost, sample-efficient data collection. Training data is collected via a human-centric process with offline and online stages. The offline stage involves human unfolding and folding actions via Virtual Reality, while the online stage utilizes human-in-the-loop learning to fine-tune the model in a real-world setting. The system is tested on two garment types: long-sleeve and short-sleeve shirts. Performance is evaluated on 20 shirts with significant variations in textures, shapes, and materials. More experiments and videos can be found in the supplementary materials and on the website: https://unifolding.robotflow.ai
Open X-Embodiment: Robotic Learning Datasets and RT-X Models
Oct 17, 2023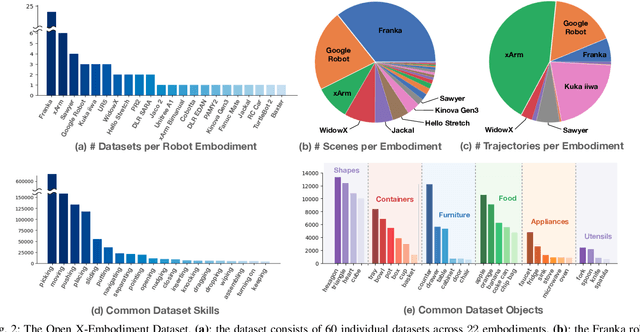
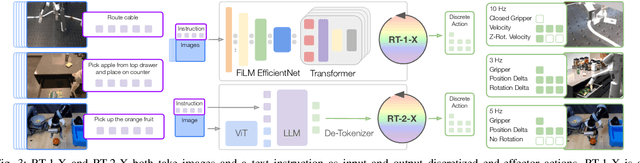
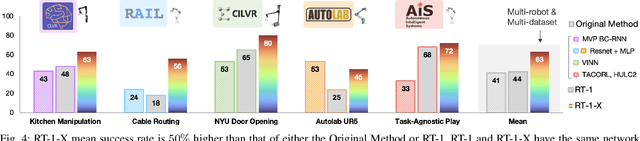
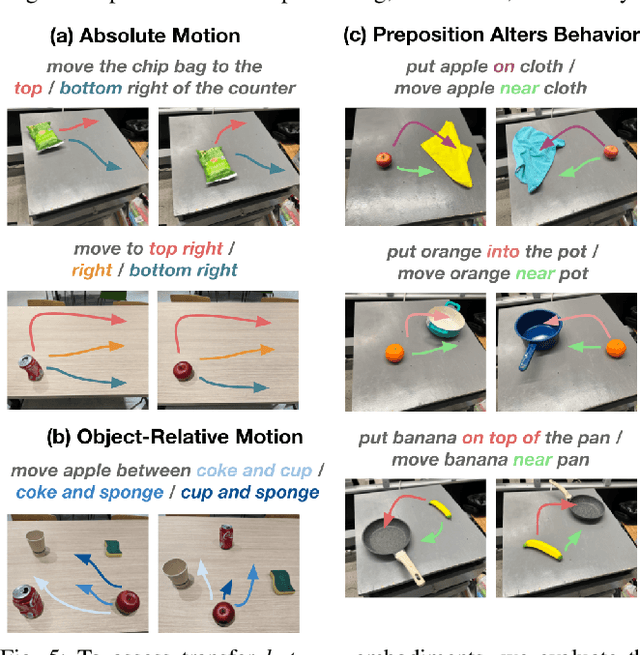
Abstract:Large, high-capacity models trained on diverse datasets have shown remarkable successes on efficiently tackling downstream applications. In domains from NLP to Computer Vision, this has led to a consolidation of pretrained models, with general pretrained backbones serving as a starting point for many applications. Can such a consolidation happen in robotics? Conventionally, robotic learning methods train a separate model for every application, every robot, and even every environment. Can we instead train generalist X-robot policy that can be adapted efficiently to new robots, tasks, and environments? In this paper, we provide datasets in standardized data formats and models to make it possible to explore this possibility in the context of robotic manipulation, alongside experimental results that provide an example of effective X-robot policies. We assemble a dataset from 22 different robots collected through a collaboration between 21 institutions, demonstrating 527 skills (160266 tasks). We show that a high-capacity model trained on this data, which we call RT-X, exhibits positive transfer and improves the capabilities of multiple robots by leveraging experience from other platforms. More details can be found on the project website $\href{https://robotics-transformer-x.github.io}{\text{robotics-transformer-x.github.io}}$.
Bridging the Gap between Human Motion and Action Semantics via Kinematic Phrases
Oct 11, 2023



Abstract:The goal of motion understanding is to establish a reliable mapping between motion and action semantics, while it is a challenging many-to-many problem. An abstract action semantic (i.e., walk forwards) could be conveyed by perceptually diverse motions (walk with arms up or swinging), while a motion could carry different semantics w.r.t. its context and intention. This makes an elegant mapping between them difficult. Previous attempts adopted direct-mapping paradigms with limited reliability. Also, current automatic metrics fail to provide reliable assessments of the consistency between motions and action semantics. We identify the source of these problems as the significant gap between the two modalities. To alleviate this gap, we propose Kinematic Phrases (KP) that take the objective kinematic facts of human motion with proper abstraction, interpretability, and generality characteristics. Based on KP as a mediator, we can unify a motion knowledge base and build a motion understanding system. Meanwhile, KP can be automatically converted from motions and to text descriptions with no subjective bias, inspiring Kinematic Prompt Generation (KPG) as a novel automatic motion generation benchmark. In extensive experiments, our approach shows superiority over other methods. Our code and data would be made publicly available at https://foruck.github.io/KP.
GAMMA: Generalizable Articulation Modeling and Manipulation for Articulated Objects
Oct 04, 2023Abstract:Articulated objects like cabinets and doors are widespread in daily life. However, directly manipulating 3D articulated objects is challenging because they have diverse geometrical shapes, semantic categories, and kinetic constraints. Prior works mostly focused on recognizing and manipulating articulated objects with specific joint types. They can either estimate the joint parameters or distinguish suitable grasp poses to facilitate trajectory planning. Although these approaches have succeeded in certain types of articulated objects, they lack generalizability to unseen objects, which significantly impedes their application in broader scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel framework of Generalizable Articulation Modeling and Manipulating for Articulated Objects (GAMMA), which learns both articulation modeling and grasp pose affordance from diverse articulated objects with different categories. In addition, GAMMA adopts adaptive manipulation to iteratively reduce the modeling errors and enhance manipulation performance. We train GAMMA with the PartNet-Mobility dataset and evaluate with comprehensive experiments in SAPIEN simulation and real-world Franka robot. Results show that GAMMA significantly outperforms SOTA articulation modeling and manipulation algorithms in unseen and cross-category articulated objects. We will open-source all codes and datasets in both simulation and real robots for reproduction in the final version. Images and videos are published on the project website at: http://sites.google.com/view/gamma-articulation
Low-Cost Exoskeletons for Learning Whole-Arm Manipulation in the Wild
Sep 26, 2023



Abstract:While humans can use parts of their arms other than the hands for manipulations like gathering and supporting, whether robots can effectively learn and perform the same type of operations remains relatively unexplored. As these manipulations require joint-level control to regulate the complete poses of the robots, we develop AirExo, a low-cost, adaptable, and portable dual-arm exoskeleton, for teleoperation and demonstration collection. As collecting teleoperated data is expensive and time-consuming, we further leverage AirExo to collect cheap in-the-wild demonstrations at scale. Under our in-the-wild learning framework, we show that with only 3 minutes of the teleoperated demonstrations, augmented by diverse and extensive in-the-wild data collected by AirExo, robots can learn a policy that is comparable to or even better than one learned from teleoperated demonstrations lasting over 20 minutes. Experiments demonstrate that our approach enables the model to learn a more general and robust policy across the various stages of the task, enhancing the success rates in task completion even with the presence of disturbances. Project website: https://airexo.github.io/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge