Alan Chan
Incident Analysis for AI Agents
Aug 19, 2025Abstract:As AI agents become more widely deployed, we are likely to see an increasing number of incidents: events involving AI agent use that directly or indirectly cause harm. For example, agents could be prompt-injected to exfiltrate private information or make unauthorized purchases. Structured information about such incidents (e.g., user prompts) can help us understand their causes and prevent future occurrences. However, existing incident reporting processes are not sufficient for understanding agent incidents. In particular, such processes are largely based on publicly available data, which excludes useful, but potentially sensitive, information such as an agent's chain of thought or browser history. To inform the development of new, emerging incident reporting processes, we propose an incident analysis framework for agents. Drawing on systems safety approaches, our framework proposes three types of factors that can cause incidents: system-related (e.g., CBRN training data), contextual (e.g., prompt injections), and cognitive (e.g., misunderstanding a user request). We also identify specific information that could help clarify which factors are relevant to a given incident: activity logs, system documentation and access, and information about the tools an agent uses. We provide recommendations for 1) what information incident reports should include and 2) what information developers and deployers should retain and make available to incident investigators upon request. As we transition to a world with more agents, understanding agent incidents will become increasingly crucial for managing risks.
Multi-Agent Risks from Advanced AI
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:The rapid development of advanced AI agents and the imminent deployment of many instances of these agents will give rise to multi-agent systems of unprecedented complexity. These systems pose novel and under-explored risks. In this report, we provide a structured taxonomy of these risks by identifying three key failure modes (miscoordination, conflict, and collusion) based on agents' incentives, as well as seven key risk factors (information asymmetries, network effects, selection pressures, destabilising dynamics, commitment problems, emergent agency, and multi-agent security) that can underpin them. We highlight several important instances of each risk, as well as promising directions to help mitigate them. By anchoring our analysis in a range of real-world examples and experimental evidence, we illustrate the distinct challenges posed by multi-agent systems and their implications for the safety, governance, and ethics of advanced AI.
Infrastructure for AI Agents
Jan 17, 2025



Abstract:Increasingly many AI systems can plan and execute interactions in open-ended environments, such as making phone calls or buying online goods. As developers grow the space of tasks that such AI agents can accomplish, we will need tools both to unlock their benefits and manage their risks. Current tools are largely insufficient because they are not designed to shape how agents interact with existing institutions (e.g., legal and economic systems) or actors (e.g., digital service providers, humans, other AI agents). For example, alignment techniques by nature do not assure counterparties that some human will be held accountable when a user instructs an agent to perform an illegal action. To fill this gap, we propose the concept of agent infrastructure: technical systems and shared protocols external to agents that are designed to mediate and influence their interactions with and impacts on their environments. Agent infrastructure comprises both new tools and reconfigurations or extensions of existing tools. For example, to facilitate accountability, protocols that tie users to agents could build upon existing systems for user authentication, such as OpenID. Just as the Internet relies on infrastructure like HTTPS, we argue that agent infrastructure will be similarly indispensable to ecosystems of agents. We identify three functions for agent infrastructure: 1) attributing actions, properties, and other information to specific agents, their users, or other actors; 2) shaping agents' interactions; and 3) detecting and remedying harmful actions from agents. We propose infrastructure that could help achieve each function, explaining use cases, adoption, limitations, and open questions. Making progress on agent infrastructure can prepare society for the adoption of more advanced agents.
Authenticated Delegation and Authorized AI Agents
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:The rapid deployment of autonomous AI agents creates urgent challenges around authorization, accountability, and access control in digital spaces. New standards are needed to know whom AI agents act on behalf of and guide their use appropriately, protecting online spaces while unlocking the value of task delegation to autonomous agents. We introduce a novel framework for authenticated, authorized, and auditable delegation of authority to AI agents, where human users can securely delegate and restrict the permissions and scope of agents while maintaining clear chains of accountability. This framework builds on existing identification and access management protocols, extending OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect with agent-specific credentials and metadata, maintaining compatibility with established authentication and web infrastructure. Further, we propose a framework for translating flexible, natural language permissions into auditable access control configurations, enabling robust scoping of AI agent capabilities across diverse interaction modalities. Taken together, this practical approach facilitates immediate deployment of AI agents while addressing key security and accountability concerns, working toward ensuring agentic AI systems perform only appropriate actions and providing a tool for digital service providers to enable AI agent interactions without risking harm from scalable interaction.
IDs for AI Systems
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:AI systems are increasingly pervasive, yet information needed to decide whether and how to engage with them may not exist or be accessible. A user may not be able to verify whether a system satisfies certain safety standards. An investigator may not know whom to investigate when a system causes an incident. A platform may find it difficult to penalize repeated negative interactions with the same system. Across a number of domains, IDs address analogous problems by identifying \textit{particular} entities (e.g., a particular Boeing 747) and providing information about other entities of the same class (e.g., some or all Boeing 747s). We propose a framework in which IDs are ascribed to \textbf{instances} of AI systems (e.g., a particular chat session with Claude 3), and associated information is accessible to parties seeking to interact with that system. We characterize IDs for AI systems, argue that there could be significant demand for IDs from key actors, analyze how those actors could incentivize ID adoption, explore potential implementations of our framework, and highlight limitations and risks. IDs seem most warranted in high-stakes settings, where certain actors (e.g., those that enable AI systems to make financial transactions) could experiment with incentives for ID use. Deployers of AI systems could experiment with developing ID implementations. With further study, IDs could help to manage a world where AI systems pervade society.
Foundational Challenges in Assuring Alignment and Safety of Large Language Models
Apr 15, 2024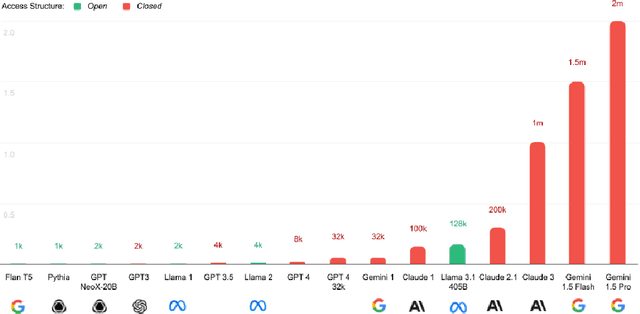


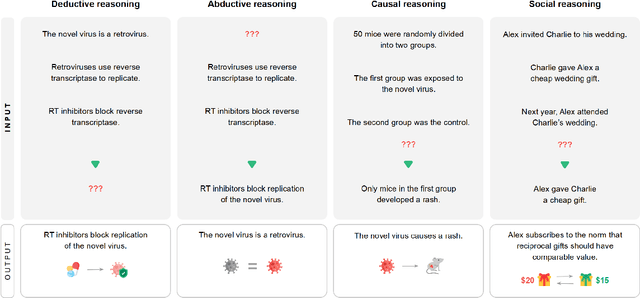
Abstract:This work identifies 18 foundational challenges in assuring the alignment and safety of large language models (LLMs). These challenges are organized into three different categories: scientific understanding of LLMs, development and deployment methods, and sociotechnical challenges. Based on the identified challenges, we pose $200+$ concrete research questions.
Visibility into AI Agents
Feb 04, 2024

Abstract:Increased delegation of commercial, scientific, governmental, and personal activities to AI agents -- systems capable of pursuing complex goals with limited supervision -- may exacerbate existing societal risks and introduce new risks. Understanding and mitigating these risks involves critically evaluating existing governance structures, revising and adapting these structures where needed, and ensuring accountability of key stakeholders. Information about where, why, how, and by whom certain AI agents are used, which we refer to as visibility, is critical to these objectives. In this paper, we assess three categories of measures to increase visibility into AI agents: agent identifiers, real-time monitoring, and activity logging. For each, we outline potential implementations that vary in intrusiveness and informativeness. We analyze how the measures apply across a spectrum of centralized through decentralized deployment contexts, accounting for various actors in the supply chain including hardware and software service providers. Finally, we discuss the implications of our measures for privacy and concentration of power. Further work into understanding the measures and mitigating their negative impacts can help to build a foundation for the governance of AI agents.
Black-Box Access is Insufficient for Rigorous AI Audits
Jan 25, 2024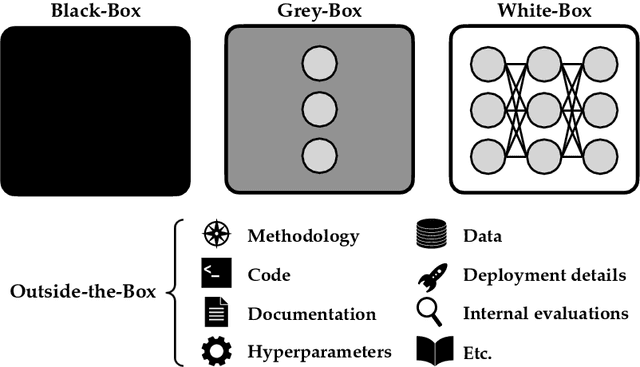
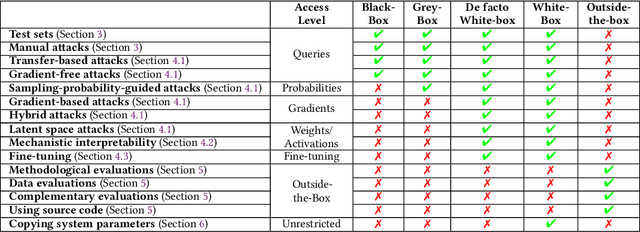
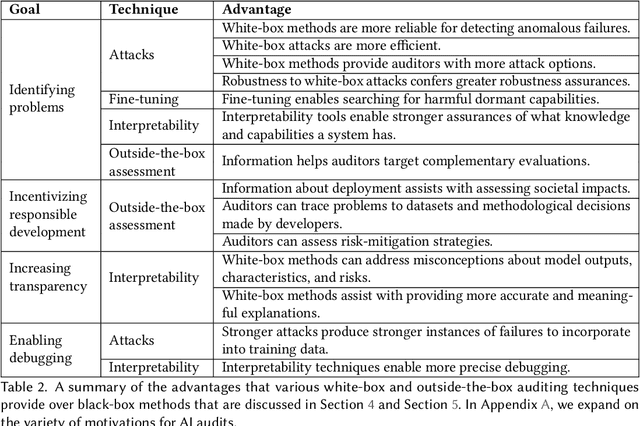
Abstract:External audits of AI systems are increasingly recognized as a key mechanism for AI governance. The effectiveness of an audit, however, depends on the degree of system access granted to auditors. Recent audits of state-of-the-art AI systems have primarily relied on black-box access, in which auditors can only query the system and observe its outputs. However, white-box access to the system's inner workings (e.g., weights, activations, gradients) allows an auditor to perform stronger attacks, more thoroughly interpret models, and conduct fine-tuning. Meanwhile, outside-the-box access to its training and deployment information (e.g., methodology, code, documentation, hyperparameters, data, deployment details, findings from internal evaluations) allows for auditors to scrutinize the development process and design more targeted evaluations. In this paper, we examine the limitations of black-box audits and the advantages of white- and outside-the-box audits. We also discuss technical, physical, and legal safeguards for performing these audits with minimal security risks. Given that different forms of access can lead to very different levels of evaluation, we conclude that (1) transparency regarding the access and methods used by auditors is necessary to properly interpret audit results, and (2) white- and outside-the-box access allow for substantially more scrutiny than black-box access alone.
Hazards from Increasingly Accessible Fine-Tuning of Downloadable Foundation Models
Dec 22, 2023
Abstract:Public release of the weights of pretrained foundation models, otherwise known as downloadable access \citep{solaiman_gradient_2023}, enables fine-tuning without the prohibitive expense of pretraining. Our work argues that increasingly accessible fine-tuning of downloadable models may increase hazards. First, we highlight research to improve the accessibility of fine-tuning. We split our discussion into research that A) reduces the computational cost of fine-tuning and B) improves the ability to share that cost across more actors. Second, we argue that increasingly accessible fine-tuning methods may increase hazard through facilitating malicious use and making oversight of models with potentially dangerous capabilities more difficult. Third, we discuss potential mitigatory measures, as well as benefits of more accessible fine-tuning. Given substantial remaining uncertainty about hazards, we conclude by emphasizing the urgent need for the development of mitigations.
An International Consortium for Evaluations of Societal-Scale Risks from Advanced AI
Nov 06, 2023



Abstract:Given rapid progress toward advanced AI and risks from frontier AI systems (advanced AI systems pushing the boundaries of the AI capabilities frontier), the creation and implementation of AI governance and regulatory schemes deserves prioritization and substantial investment. However, the status quo is untenable and, frankly, dangerous. A regulatory gap has permitted AI labs to conduct research, development, and deployment activities with minimal oversight. In response, frontier AI system evaluations have been proposed as a way of assessing risks from the development and deployment of frontier AI systems. Yet, the budding AI risk evaluation ecosystem faces significant coordination challenges, such as a limited diversity of evaluators, suboptimal allocation of effort, and perverse incentives. This paper proposes a solution in the form of an international consortium for AI risk evaluations, comprising both AI developers and third-party AI risk evaluators. Such a consortium could play a critical role in international efforts to mitigate societal-scale risks from advanced AI, including in managing responsible scaling policies and coordinated evaluation-based risk response. In this paper, we discuss the current evaluation ecosystem and its shortcomings, propose an international consortium for advanced AI risk evaluations, discuss issues regarding its implementation, discuss lessons that can be learnt from previous international institutions and existing proposals for international AI governance institutions, and, finally, we recommend concrete steps to advance the establishment of the proposed consortium: (i) solicit feedback from stakeholders, (ii) conduct additional research, (iii) conduct a workshop(s) for stakeholders, (iv) analyze feedback and create final proposal, (v) solicit funding, and (vi) create a consortium.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge