Ross Gruetzemacher
Strategic Insights from Simulation Gaming of AI Race Dynamics
Oct 04, 2024

Abstract:We present insights from "Intelligence Rising", a scenario exploration exercise about possible AI futures. Drawing on the experiences of facilitators who have overseen 43 games over a four-year period, we illuminate recurring patterns, strategies, and decision-making processes observed during gameplay. Our analysis reveals key strategic considerations about AI development trajectories in this simulated environment, including: the destabilising effects of AI races, the crucial role of international cooperation in mitigating catastrophic risks, the challenges of aligning corporate and national interests, and the potential for rapid, transformative change in AI capabilities. We highlight places where we believe the game has been effective in exposing participants to the complexities and uncertainties inherent in AI governance. Key recurring gameplay themes include the emergence of international agreements, challenges to the robustness of such agreements, the critical role of cybersecurity in AI development, and the potential for unexpected crises to dramatically alter AI trajectories. By documenting these insights, we aim to provide valuable foresight for policymakers, industry leaders, and researchers navigating the complex landscape of AI development and governance.
Implications for Governance in Public Perceptions of Societal-scale AI Risks
Jun 10, 2024

Abstract:Amid growing concerns over AI's societal risks--ranging from civilizational collapse to misinformation and systemic bias--this study explores the perceptions of AI experts and the general US registered voters on the likelihood and impact of 18 specific AI risks, alongside their policy preferences for managing these risks. While both groups favor international oversight over national or corporate governance, our survey reveals a discrepancy: voters perceive AI risks as both more likely and more impactful than experts, and also advocate for slower AI development. Specifically, our findings indicate that policy interventions may best assuage collective concerns if they attempt to more carefully balance mitigation efforts across all classes of societal-scale risks, effectively nullifying the near-vs-long-term debate over AI risks. More broadly, our results will serve not only to enable more substantive policy discussions for preventing and mitigating AI risks, but also to underscore the challenge of consensus building for effective policy implementation.
An International Consortium for Evaluations of Societal-Scale Risks from Advanced AI
Nov 06, 2023



Abstract:Given rapid progress toward advanced AI and risks from frontier AI systems (advanced AI systems pushing the boundaries of the AI capabilities frontier), the creation and implementation of AI governance and regulatory schemes deserves prioritization and substantial investment. However, the status quo is untenable and, frankly, dangerous. A regulatory gap has permitted AI labs to conduct research, development, and deployment activities with minimal oversight. In response, frontier AI system evaluations have been proposed as a way of assessing risks from the development and deployment of frontier AI systems. Yet, the budding AI risk evaluation ecosystem faces significant coordination challenges, such as a limited diversity of evaluators, suboptimal allocation of effort, and perverse incentives. This paper proposes a solution in the form of an international consortium for AI risk evaluations, comprising both AI developers and third-party AI risk evaluators. Such a consortium could play a critical role in international efforts to mitigate societal-scale risks from advanced AI, including in managing responsible scaling policies and coordinated evaluation-based risk response. In this paper, we discuss the current evaluation ecosystem and its shortcomings, propose an international consortium for advanced AI risk evaluations, discuss issues regarding its implementation, discuss lessons that can be learnt from previous international institutions and existing proposals for international AI governance institutions, and, finally, we recommend concrete steps to advance the establishment of the proposed consortium: (i) solicit feedback from stakeholders, (ii) conduct additional research, (iii) conduct a workshop(s) for stakeholders, (iv) analyze feedback and create final proposal, (v) solicit funding, and (vi) create a consortium.
Deep Transfer Learning & Beyond: Transformer Language Models in Information Systems Research
Oct 23, 2021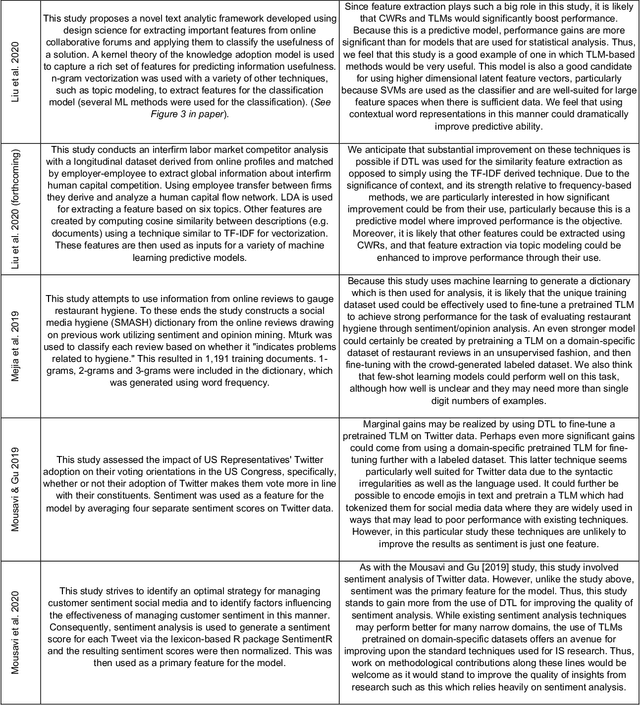
Abstract:AI is widely thought to be poised to transform business, yet current perceptions of the scope of this transformation may be myopic. Recent progress in natural language processing involving transformer language models (TLMs) offers a potential avenue for AI-driven business and societal transformation that is beyond the scope of what most currently foresee. We review this recent progress as well as recent literature utilizing text mining in top IS journals to develop an outline for how future IS research can benefit from these new techniques. Our review of existing IS literature reveals that suboptimal text mining techniques are prevalent and that the more advanced TLMs could be applied to enhance and increase IS research involving text data, and to enable new IS research topics, thus creating more value for the research community. This is possible because these techniques make it easier to develop very powerful custom systems and their performance is superior to existing methods for a wide range of tasks and applications. Further, multilingual language models make possible higher quality text analytics for research in multiple languages. We also identify new avenues for IS research, like language user interfaces, that may offer even greater potential for future IS research.
Forecasting AI Progress: A Research Agenda
Aug 04, 2020

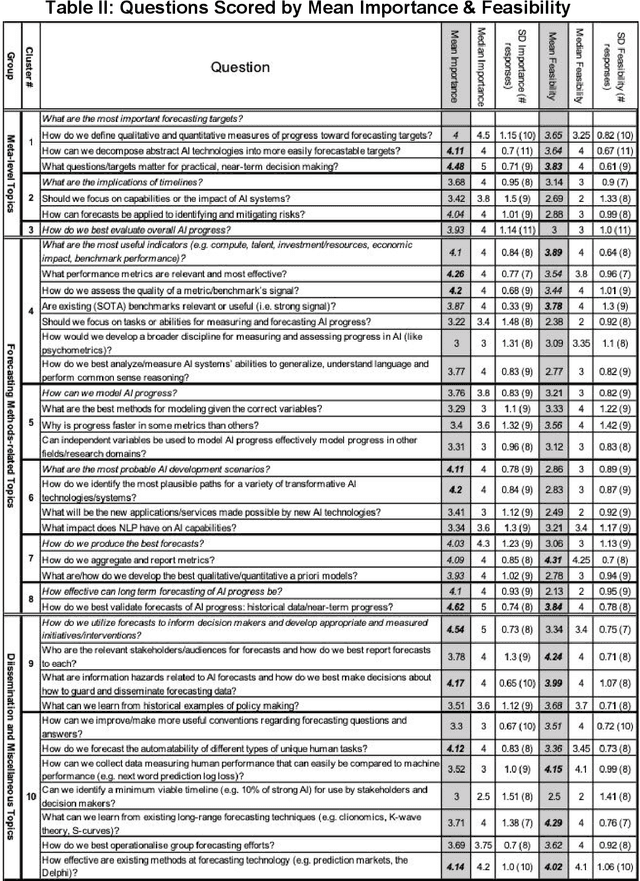
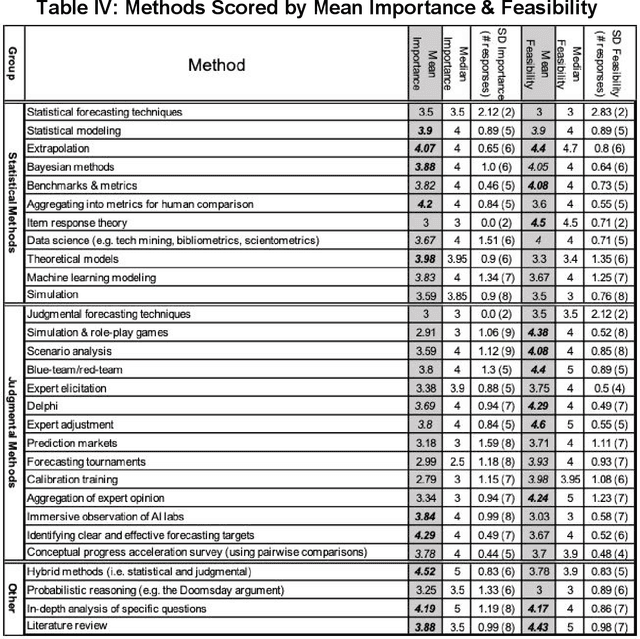
Abstract:Forecasting AI progress is essential to reducing uncertainty in order to appropriately plan for research efforts on AI safety and AI governance. While this is generally considered to be an important topic, little work has been conducted on it and there is no published document that gives and objective overview of the field. Moreover, the field is very diverse and there is no published consensus regarding its direction. This paper describes the development of a research agenda for forecasting AI progress which utilized the Delphi technique to elicit and aggregate experts' opinions on what questions and methods to prioritize. The results of the Delphi are presented; the remainder of the paper follow the structure of these results, briefly reviewing relevant literature and suggesting future work for each topic. Experts indicated that a wide variety of methods should be considered for forecasting AI progress. Moreover, experts identified salient questions that were both general and completely unique to the problem of forecasting AI progress. Some of the highest priority topics include the validation of (partially unresolved) forecasts, how to make forecasting action-guiding and the quality of different performance metrics. While statistical methods seem more promising, there is also recognition that supplementing judgmental techniques can be quite beneficial.
Exploring AI Futures Through Role Play
Dec 19, 2019

Abstract:We present an innovative methodology for studying and teaching the impacts of AI through a role play game. The game serves two primary purposes: 1) training AI developers and AI policy professionals to reflect on and prepare for future social and ethical challenges related to AI and 2) exploring possible futures involving AI technology development, deployment, social impacts, and governance. While the game currently focuses on the inter relations between short --, mid and long term impacts of AI, it has potential to be adapted for a broad range of scenarios, exploring in greater depths issues of AI policy research and affording training within organizations. The game presented here has undergone two years of development and has been tested through over 30 events involving between 3 and 70 participants. The game is under active development, but preliminary findings suggest that role play is a promising methodology for both exploring AI futures and training individuals and organizations in thinking about, and reflecting on, the impacts of AI and strategic mistakes that can be avoided today.
Defining and Unpacking Transformative AI
Nov 27, 2019


Abstract:Recently the concept of transformative AI (TAI) has begun to receive attention in the AI policy space. TAI is often framed as an alternative formulation to notions of strong AI (e.g. artificial general intelligence or superintelligence) and reflects increasing consensus that advanced AI which does not fit these definitions may nonetheless have extreme and long-lasting impacts on society. However, the term TAI is poorly defined and often used ambiguously. Some use the notion of TAI to describe levels of societal transformation associated with previous 'general purpose technologies' (GPTs) such as electricity or the internal combustion engine. Others use the term to refer to more drastic levels of transformation comparable to the agricultural or industrial revolutions. The notion has also been used much more loosely, with some implying that current AI systems are already having a transformative impact on society. This paper unpacks and analyses the notion of TAI, proposing a distinction between TAI and radically transformative AI (RTAI), roughly corresponding to societal change on the level of the agricultural or industrial revolutions. We describe some relevant dimensions associated with each and discuss what kinds of advances in capabilities they might require. We further consider the relationship between TAI and RTAI and whether we should necessarily expect a period of TAI to precede the emergence of RTAI. This analysis is important as it can help guide discussions among AI policy researchers about how to allocate resources towards mitigating the most extreme impacts of AI and it can bring attention to negative TAI scenarios that are currently neglected.
Alternative Techniques for Mapping Paths to HLAI
May 02, 2019
Abstract:The only systematic mapping of the HLAI technical landscape was conducted at a workshop in 2009 [Adams et al., 2012]. However, the results from it were not what organizers had hoped for [Goertzel 2014, 2016], merely just a series of milestones, up to 50% of which could be argued to have been completed already. We consider two more recent articles outlining paths to human-like intelligence [Mikolov et al., 2016; Lake et al., 2017]. These offer technical and more refined assessments of the requirements for HLAI rather than just milestones. While useful, they also have limitations. To address these limitations we propose the use of alternative techniques for an updated systematic mapping of the paths to HLAI. The newly proposed alternative techniques can model complex paths of future technologies using intricate directed graphs. Specifically, there are two classes of alternative techniques that we consider: scenario mapping methods and techniques for eliciting expert opinion through digital platforms and crowdsourcing. We assess the viability and utility of both the previous and alternative techniques, finding that the proposed alternative techniques could be very beneficial in advancing the existing body of knowledge on the plausible frameworks for creating HLAI. In conclusion, we encourage discussion and debate to initiate efforts to use these proposed techniques for mapping paths to HLAI.
Forecasting Transformative AI: An Expert Survey
Jan 24, 2019



Abstract:Transformative AI technologies have the potential to reshape critical aspects of society in the near future. However, in order to properly prepare policy initiatives for the arrival of such technologies accurate forecasts and timelines are necessary. A survey was administered to attendees of three AI conferences during the summer of 2018 (ICML, IJCAI and the HLAI conference). The survey included questions for estimating AI capabilities over the next decade, questions for forecasting five scenarios of transformative AI and questions concerning the impact of computational resources in AI research. Respondents indicated a median of 21.5% of human tasks (i.e., all tasks that humans are currently paid to do) can be feasibly automated now, and that this figure would rise to 40% in 5 years and 60% in 10 years. Median forecasts indicated a 50% probability of AI systems being capable of automating 90% of current human tasks in 25 years and 99% of current human tasks in 50 years. The conference of attendance was found to have a statistically significant impact on all forecasts, with attendees of HLAI providing more optimistic timelines with less uncertainty. These findings suggest that AI experts expect major advances in AI technology to continue over the next decade to a degree that will likely have profound transformative impacts on society.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge