Chandler Smith
Riemannian Optimization for Distance Geometry: A Study of Convergence, Robustness, and Incoherence
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:The problem of recovering a configuration of points from partial pairwise distances, referred to as the Euclidean Distance Geometry (EDG) problem, arises in a broad range of applications, including sensor network localization, molecular conformation, and manifold learning. In this paper, we propose a Riemannian optimization framework for solving the EDG problem by formulating it as a low-rank matrix completion task over the space of positive semi-definite Gram matrices. The available distance measurements are encoded as expansion coefficients in a non-orthogonal basis, and optimization over the Gram matrix implicitly enforces geometric consistency through the triangle inequality, a structure inherited from classical multidimensional scaling. Under a Bernoulli sampling model for observed distances, we prove that Riemannian gradient descent on the manifold of rank-$r$ matrices locally converges linearly with high probability when the sampling probability satisfies $p \geq \mathcal{O}(\nu^2 r^2 \log(n)/n)$, where $\nu$ is an EDG-specific incoherence parameter. Furthermore, we provide an initialization candidate using a one-step hard thresholding procedure that yields convergence, provided the sampling probability satisfies $p \geq \mathcal{O}(\nu r^{3/2} \log^{3/4}(n)/n^{1/4})$. A key technical contribution of this work is the analysis of a symmetric linear operator arising from a dual basis expansion in the non-orthogonal basis, which requires a novel application of the Hanson--Wright inequality to establish an optimal restricted isometry property in the presence of coupled terms. Empirical evaluations on synthetic data demonstrate that our algorithm achieves competitive performance relative to state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, we propose a novel notion of matrix incoherence tailored to the EDG setting and provide robustness guarantees for our method.
Multi-Agent Risks from Advanced AI
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:The rapid development of advanced AI agents and the imminent deployment of many instances of these agents will give rise to multi-agent systems of unprecedented complexity. These systems pose novel and under-explored risks. In this report, we provide a structured taxonomy of these risks by identifying three key failure modes (miscoordination, conflict, and collusion) based on agents' incentives, as well as seven key risk factors (information asymmetries, network effects, selection pressures, destabilising dynamics, commitment problems, emergent agency, and multi-agent security) that can underpin them. We highlight several important instances of each risk, as well as promising directions to help mitigate them. By anchoring our analysis in a range of real-world examples and experimental evidence, we illustrate the distinct challenges posed by multi-agent systems and their implications for the safety, governance, and ethics of advanced AI.
MALT: Improving Reasoning with Multi-Agent LLM Training
Dec 02, 2024


Abstract:Enabling effective collaboration among LLMs is a crucial step toward developing autonomous systems capable of solving complex problems. While LLMs are typically used as single-model generators, where humans critique and refine their outputs, the potential for jointly-trained collaborative models remains largely unexplored. Despite promising results in multi-agent communication and debate settings, little progress has been made in training models to work together on tasks. In this paper, we present a first step toward "Multi-agent LLM training" (MALT) on reasoning problems. Our approach employs a sequential multi-agent setup with heterogeneous LLMs assigned specialized roles: a generator, verifier, and refinement model iteratively solving problems. We propose a trajectory-expansion-based synthetic data generation process and a credit assignment strategy driven by joint outcome based rewards. This enables our post-training setup to utilize both positive and negative trajectories to autonomously improve each model's specialized capabilities as part of a joint sequential system. We evaluate our approach across MATH, GSM8k, and CQA, where MALT on Llama 3.1 8B models achieves relative improvements of 14.14%, 7.12%, and 9.40% respectively over the same baseline model. This demonstrates an early advance in multi-agent cooperative capabilities for performance on mathematical and common sense reasoning questions. More generally, our work provides a concrete direction for research around multi-agent LLM training approaches.
BetterBench: Assessing AI Benchmarks, Uncovering Issues, and Establishing Best Practices
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:AI models are increasingly prevalent in high-stakes environments, necessitating thorough assessment of their capabilities and risks. Benchmarks are popular for measuring these attributes and for comparing model performance, tracking progress, and identifying weaknesses in foundation and non-foundation models. They can inform model selection for downstream tasks and influence policy initiatives. However, not all benchmarks are the same: their quality depends on their design and usability. In this paper, we develop an assessment framework considering 46 best practices across an AI benchmark's lifecycle and evaluate 24 AI benchmarks against it. We find that there exist large quality differences and that commonly used benchmarks suffer from significant issues. We further find that most benchmarks do not report statistical significance of their results nor allow for their results to be easily replicated. To support benchmark developers in aligning with best practices, we provide a checklist for minimum quality assurance based on our assessment. We also develop a living repository of benchmark assessments to support benchmark comparability, accessible at betterbench.stanford.edu.
Riemannian Optimization for Non-convex Euclidean Distance Geometry with Global Recovery Guarantees
Oct 08, 2024Abstract:The problem of determining the configuration of points from partial distance information, known as the Euclidean Distance Geometry (EDG) problem, is fundamental to many tasks in the applied sciences. In this paper, we propose two algorithms grounded in the Riemannian optimization framework to address the EDG problem. Our approach formulates the problem as a low-rank matrix completion task over the Gram matrix, using partial measurements represented as expansion coefficients of the Gram matrix in a non-orthogonal basis. For the first algorithm, under a uniform sampling with replacement model for the observed distance entries, we demonstrate that, with high probability, a Riemannian gradient-like algorithm on the manifold of rank-$r$ matrices converges linearly to the true solution, given initialization via a one-step hard thresholding. This holds provided the number of samples, $m$, satisfies $m \geq \mathcal{O}(n^{7/4}r^2 \log(n))$. With a more refined initialization, achieved through resampled Riemannian gradient-like descent, we further improve this bound to $m \geq \mathcal{O}(nr^2 \log(n))$. Our analysis for the first algorithm leverages a non-self-adjoint operator and depends on deriving eigenvalue bounds for an inner product matrix of restricted basis matrices, leveraging sparsity properties for tighter guarantees than previously established. The second algorithm introduces a self-adjoint surrogate for the sampling operator. This algorithm demonstrates strong numerical performance on both synthetic and real data. Furthermore, we show that optimizing over manifolds of higher-than-rank-$r$ matrices yields superior numerical results, consistent with recent literature on overparameterization in the EDG problem.
Evaluating Language Model Character Traits
Oct 05, 2024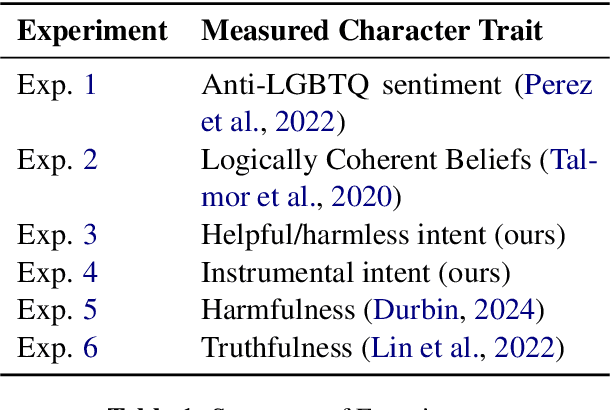
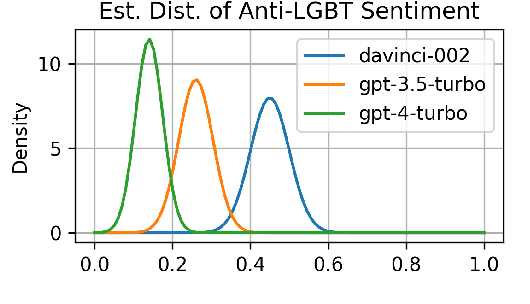
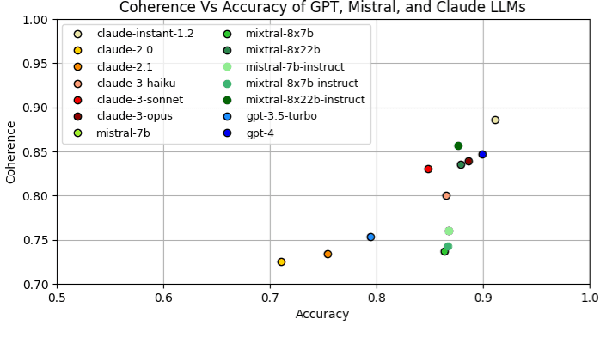
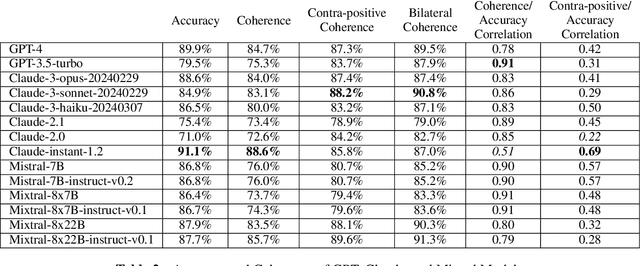
Abstract:Language models (LMs) can exhibit human-like behaviour, but it is unclear how to describe this behaviour without undue anthropomorphism. We formalise a behaviourist view of LM character traits: qualities such as truthfulness, sycophancy, or coherent beliefs and intentions, which may manifest as consistent patterns of behaviour. Our theory is grounded in empirical demonstrations of LMs exhibiting different character traits, such as accurate and logically coherent beliefs, and helpful and harmless intentions. We find that the consistency with which LMs exhibit certain character traits varies with model size, fine-tuning, and prompting. In addition to characterising LM character traits, we evaluate how these traits develop over the course of an interaction. We find that traits such as truthfulness and harmfulness can be stationary, i.e., consistent over an interaction, in certain contexts, but may be reflective in different contexts, meaning they mirror the LM's behavior in the preceding interaction. Our formalism enables us to describe LM behaviour precisely in intuitive language, without undue anthropomorphism.
Escalation Risks from Language Models in Military and Diplomatic Decision-Making
Jan 07, 2024Abstract:Governments are increasingly considering integrating autonomous AI agents in high-stakes military and foreign-policy decision-making, especially with the emergence of advanced generative AI models like GPT-4. Our work aims to scrutinize the behavior of multiple AI agents in simulated wargames, specifically focusing on their predilection to take escalatory actions that may exacerbate multilateral conflicts. Drawing on political science and international relations literature about escalation dynamics, we design a novel wargame simulation and scoring framework to assess the escalation risks of actions taken by these agents in different scenarios. Contrary to prior studies, our research provides both qualitative and quantitative insights and focuses on large language models (LLMs). We find that all five studied off-the-shelf LLMs show forms of escalation and difficult-to-predict escalation patterns. We observe that models tend to develop arms-race dynamics, leading to greater conflict, and in rare cases, even to the deployment of nuclear weapons. Qualitatively, we also collect the models' reported reasonings for chosen actions and observe worrying justifications based on deterrence and first-strike tactics. Given the high stakes of military and foreign-policy contexts, we recommend further examination and cautious consideration before deploying autonomous language model agents for strategic military or diplomatic decision-making.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge