Fabio Pizzati
BLAZER: Bootstrapping LLM-based Manipulation Agents with Zero-Shot Data Generation
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Scaling data and models has played a pivotal role in the remarkable progress of computer vision and language. Inspired by these domains, recent efforts in robotics have similarly focused on scaling both data and model size to develop more generalizable and robust policies. However, unlike vision and language, robotics lacks access to internet-scale demonstrations across diverse robotic tasks and environments. As a result, the scale of existing datasets typically suffers from the need for manual data collection and curation. To address this problem, here we propose BLAZER, a framework that learns manipulation policies from automatically generated training data. We build on the zero-shot capabilities of LLM planners and automatically generate demonstrations for diverse manipulation tasks in simulation. Successful examples are then used to finetune an LLM and to improve its planning capabilities without human supervision. Notably, while BLAZER training requires access to the simulator's state, we demonstrate direct transfer of acquired skills to sensor-based manipulation. Through extensive experiments, we show BLAZER to significantly improve zero-shot manipulation in both simulated and real environments. Moreover, BLAZER improves on tasks outside of its training pool and enables downscaling of LLM models. Our code and data will be made publicly available on the project page.
Learning to Generate Object Interactions with Physics-Guided Video Diffusion
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Recent models for video generation have achieved remarkable progress and are now deployed in film, social media production, and advertising. Beyond their creative potential, such models also hold promise as world simulators for robotics and embodied decision making. Despite strong advances, however, current approaches still struggle to generate physically plausible object interactions and lack physics-grounded control mechanisms. To address this limitation, we introduce KineMask, an approach for physics-guided video generation that enables realistic rigid body control, interactions, and effects. Given a single image and a specified object velocity, our method generates videos with inferred motions and future object interactions. We propose a two-stage training strategy that gradually removes future motion supervision via object masks. Using this strategy we train video diffusion models (VDMs) on synthetic scenes of simple interactions and demonstrate significant improvements of object interactions in real scenes. Furthermore, KineMask integrates low-level motion control with high-level textual conditioning via predictive scene descriptions, leading to effective support for synthesis of complex dynamical phenomena. Extensive experiments show that KineMask achieves strong improvements over recent models of comparable size. Ablation studies further highlight the complementary roles of low- and high-level conditioning in VDMs. Our code, model, and data will be made publicly available.
Towards Reliable Identification of Diffusion-based Image Manipulations
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Changing facial expressions, gestures, or background details may dramatically alter the meaning conveyed by an image. Notably, recent advances in diffusion models greatly improve the quality of image manipulation while also opening the door to misuse. Identifying changes made to authentic images, thus, becomes an important task, constantly challenged by new diffusion-based editing tools. To this end, we propose a novel approach for ReliAble iDentification of inpainted AReas (RADAR). RADAR builds on existing foundation models and combines features from different image modalities. It also incorporates an auxiliary contrastive loss that helps to isolate manipulated image patches. We demonstrate these techniques to significantly improve both the accuracy of our method and its generalisation to a large number of diffusion models. To support realistic evaluation, we further introduce BBC-PAIR, a new comprehensive benchmark, with images tampered by 28 diffusion models. Our experiments show that RADAR achieves excellent results, outperforming the state-of-the-art in detecting and localising image edits made by both seen and unseen diffusion models. Our code, data and models will be publicly available at alex-costanzino.github.io/radar.
PSyDUCK: Training-Free Steganography for Latent Diffusion
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in AI-generated steganography highlight its potential for safeguarding the privacy of vulnerable democratic actors, including aid workers, journalists, and whistleblowers operating in oppressive regimes. In this work, we address current limitations and establish the foundations for large-throughput generative steganography. We introduce a novel approach that enables secure and efficient steganography within latent diffusion models. We show empirically that our methods perform well across a variety of open-source latent diffusion models, particularly in generative image and video tasks.
SafetyDPO: Scalable Safety Alignment for Text-to-Image Generation
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-image (T2I) models have become widespread, but their limited safety guardrails expose end users to harmful content and potentially allow for model misuse. Current safety measures are typically limited to text-based filtering or concept removal strategies, able to remove just a few concepts from the model's generative capabilities. In this work, we introduce SafetyDPO, a method for safety alignment of T2I models through Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). We enable the application of DPO for safety purposes in T2I models by synthetically generating a dataset of harmful and safe image-text pairs, which we call CoProV2. Using a custom DPO strategy and this dataset, we train safety experts, in the form of low-rank adaptation (LoRA) matrices, able to guide the generation process away from specific safety-related concepts. Then, we merge the experts into a single LoRA using a novel merging strategy for optimal scaling performance. This expert-based approach enables scalability, allowing us to remove 7 times more harmful concepts from T2I models compared to baselines. SafetyDPO consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art on many benchmarks and establishes new practices for safety alignment in T2I networks. Code and data will be shared at https://safetydpo.github.io/.
Video Motion Transfer with Diffusion Transformers
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:We propose DiTFlow, a method for transferring the motion of a reference video to a newly synthesized one, designed specifically for Diffusion Transformers (DiT). We first process the reference video with a pre-trained DiT to analyze cross-frame attention maps and extract a patch-wise motion signal called the Attention Motion Flow (AMF). We guide the latent denoising process in an optimization-based, training-free, manner by optimizing latents with our AMF loss to generate videos reproducing the motion of the reference one. We also apply our optimization strategy to transformer positional embeddings, granting us a boost in zero-shot motion transfer capabilities. We evaluate DiTFlow against recently published methods, outperforming all across multiple metrics and human evaluation.
MALT: Improving Reasoning with Multi-Agent LLM Training
Dec 02, 2024


Abstract:Enabling effective collaboration among LLMs is a crucial step toward developing autonomous systems capable of solving complex problems. While LLMs are typically used as single-model generators, where humans critique and refine their outputs, the potential for jointly-trained collaborative models remains largely unexplored. Despite promising results in multi-agent communication and debate settings, little progress has been made in training models to work together on tasks. In this paper, we present a first step toward "Multi-agent LLM training" (MALT) on reasoning problems. Our approach employs a sequential multi-agent setup with heterogeneous LLMs assigned specialized roles: a generator, verifier, and refinement model iteratively solving problems. We propose a trajectory-expansion-based synthetic data generation process and a credit assignment strategy driven by joint outcome based rewards. This enables our post-training setup to utilize both positive and negative trajectories to autonomously improve each model's specialized capabilities as part of a joint sequential system. We evaluate our approach across MATH, GSM8k, and CQA, where MALT on Llama 3.1 8B models achieves relative improvements of 14.14%, 7.12%, and 9.40% respectively over the same baseline model. This demonstrates an early advance in multi-agent cooperative capabilities for performance on mathematical and common sense reasoning questions. More generally, our work provides a concrete direction for research around multi-agent LLM training approaches.
MatchDiffusion: Training-free Generation of Match-cuts
Nov 27, 2024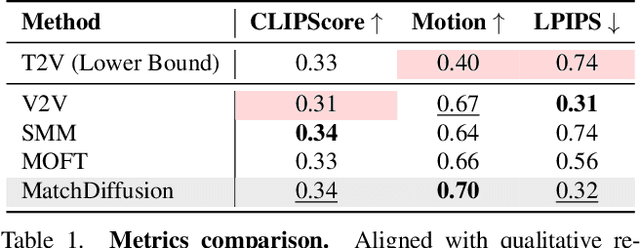

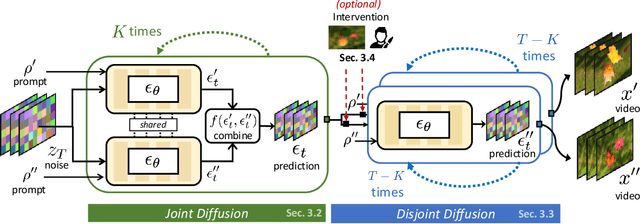
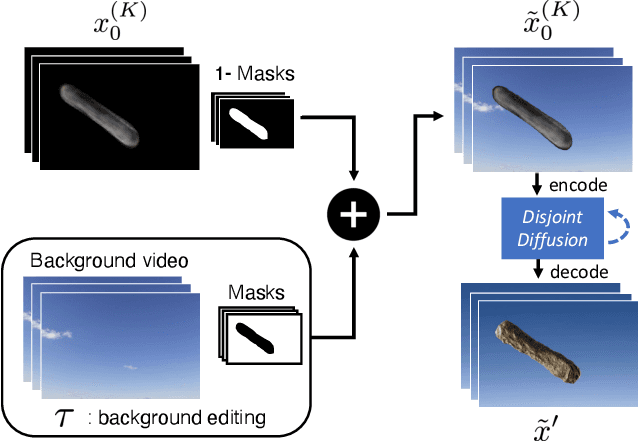
Abstract:Match-cuts are powerful cinematic tools that create seamless transitions between scenes, delivering strong visual and metaphorical connections. However, crafting match-cuts is a challenging, resource-intensive process requiring deliberate artistic planning. In MatchDiffusion, we present the first training-free method for match-cut generation using text-to-video diffusion models. MatchDiffusion leverages a key property of diffusion models: early denoising steps define the scene's broad structure, while later steps add details. Guided by this insight, MatchDiffusion employs "Joint Diffusion" to initialize generation for two prompts from shared noise, aligning structure and motion. It then applies "Disjoint Diffusion", allowing the videos to diverge and introduce unique details. This approach produces visually coherent videos suited for match-cuts. User studies and metrics demonstrate MatchDiffusion's effectiveness and potential to democratize match-cut creation.
Specify and Edit: Overcoming Ambiguity in Text-Based Image Editing
Jul 29, 2024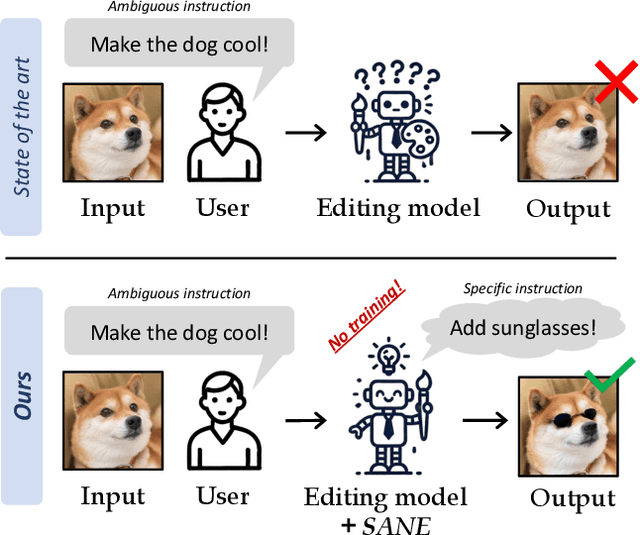
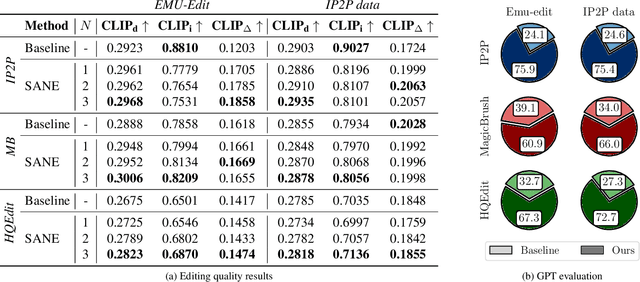
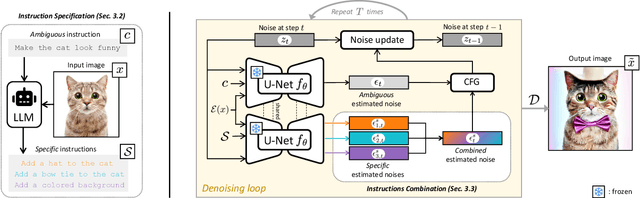

Abstract:Text-based editing diffusion models exhibit limited performance when the user's input instruction is ambiguous. To solve this problem, we propose $\textit{Specify ANd Edit}$ (SANE), a zero-shot inference pipeline for diffusion-based editing systems. We use a large language model (LLM) to decompose the input instruction into specific instructions, i.e. well-defined interventions to apply to the input image to satisfy the user's request. We benefit from the LLM-derived instructions along the original one, thanks to a novel denoising guidance strategy specifically designed for the task. Our experiments with three baselines and on two datasets demonstrate the benefits of SANE in all setups. Moreover, our pipeline improves the interpretability of editing models, and boosts the output diversity. We also demonstrate that our approach can be applied to any edit, whether ambiguous or not. Our code is public at https://github.com/fabvio/SANE.
Model Merging and Safety Alignment: One Bad Model Spoils the Bunch
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:Merging Large Language Models (LLMs) is a cost-effective technique for combining multiple expert LLMs into a single versatile model, retaining the expertise of the original ones. However, current approaches often overlook the importance of safety alignment during merging, leading to highly misaligned models. This work investigates the effects of model merging on alignment. We evaluate several popular model merging techniques, demonstrating that existing methods do not only transfer domain expertise but also propagate misalignment. We propose a simple two-step approach to address this problem: (i) generating synthetic safety and domain-specific data, and (ii) incorporating these generated data into the optimization process of existing data-aware model merging techniques. This allows us to treat alignment as a skill that can be maximized in the resulting merged LLM. Our experiments illustrate the effectiveness of integrating alignment-related data during merging, resulting in models that excel in both domain expertise and alignment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge