Hasan Abed Al Kader Hammoud
Unforgotten Safety: Preserving Safety Alignment of Large Language Models with Continual Learning
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:The safety alignment of large language models (LLMs) is becoming increasingly important with their democratization. In this paper, we study the safety degradation that comes with adapting LLMs to new tasks. We attribute this safety compromise to catastrophic forgetting and frame the problem of preserving safety when fine-tuning as a continual learning (CL) problem. We consider the fine-tuning-as-a-service setup where the user uploads their data to a service provider to get a customized model that excels on the user's selected task. We adapt several CL approaches from the literature and systematically evaluate their ability to mitigate safety degradation. These include regularization-based, memory-based, and model merging approaches. We consider two scenarios, (1) benign user data and (2) poisoned user data. Our results demonstrate that CL approaches consistently achieve lower attack success rates than standard fine-tuning. Among these, DER outperforms both other CL methods and existing safety-preserving baselines while maintaining task utility. These findings generalize across three downstream tasks (GSM8K, SST2, Code) and three model families (LLaMA2-7B, Mistral-7B, Gemma-2B), establishing CL as a practical solution to preserve safety.
AraLingBench A Human-Annotated Benchmark for Evaluating Arabic Linguistic Capabilities of Large Language Models
Nov 18, 2025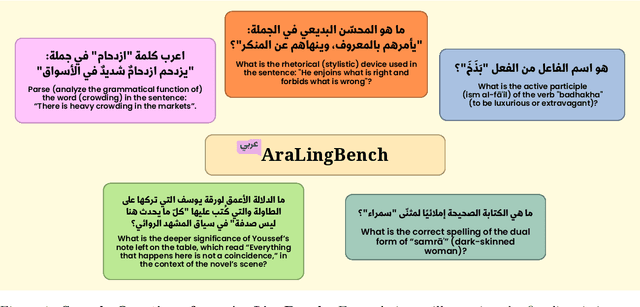
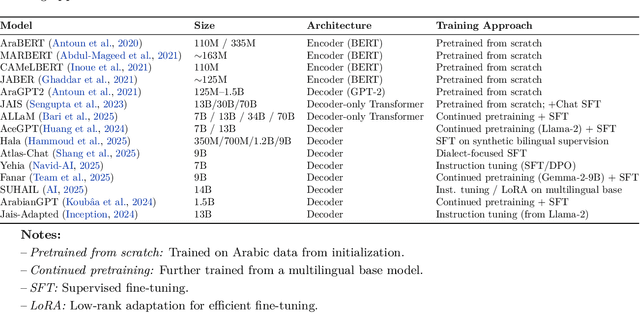
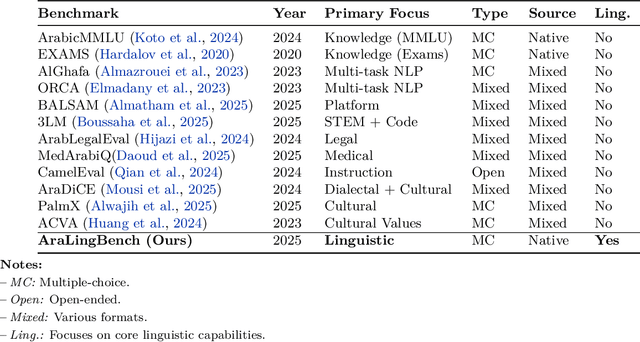
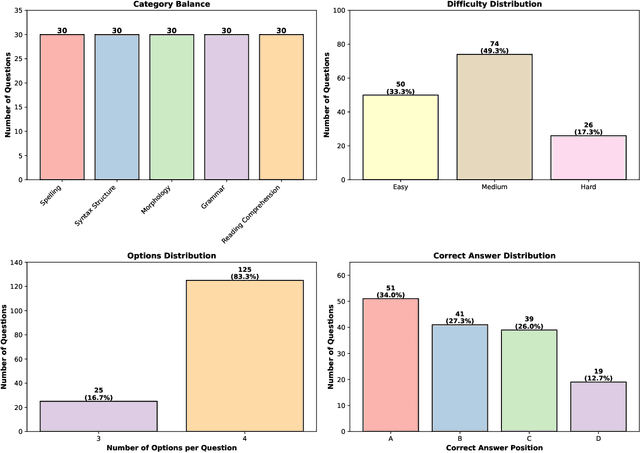
Abstract:We present AraLingBench: a fully human annotated benchmark for evaluating the Arabic linguistic competence of large language models (LLMs). The benchmark spans five core categories: grammar, morphology, spelling, reading comprehension, and syntax, through 150 expert-designed multiple choice questions that directly assess structural language understanding. Evaluating 35 Arabic and bilingual LLMs reveals that current models demonstrate strong surface level proficiency but struggle with deeper grammatical and syntactic reasoning. AraLingBench highlights a persistent gap between high scores on knowledge-based benchmarks and true linguistic mastery, showing that many models succeed through memorization or pattern recognition rather than authentic comprehension. By isolating and measuring fundamental linguistic skills, AraLingBench provides a diagnostic framework for developing Arabic LLMs. The full evaluation code is publicly available on GitHub.
Hala Technical Report: Building Arabic-Centric Instruction & Translation Models at Scale
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:We present Hala, a family of Arabic-centric instruction and translation models built with our translate-and-tune pipeline. We first compress a strong AR$\leftrightarrow$EN teacher to FP8 (yielding $\sim$2$\times$ higher throughput with no quality loss) and use it to create high-fidelity bilingual supervision. A lightweight language model LFM2-1.2B is then fine-tuned on this data and used to translate high-quality English instruction sets into Arabic, producing a million-scale corpus tailored to instruction following. We train Hala models at 350M, 700M, 1.2B, and 9B parameters, and apply slerp merging to balance Arabic specialization with base-model strengths. On Arabic-centric benchmarks, Hala achieves state-of-the-art results within both the "nano" ($\leq$2B) and "small" (7-9B) categories, outperforming their bases. We release models, data, evaluation, and recipes to accelerate research in Arabic NLP.
Turning the Spell Around: Lightweight Alignment Amplification via Rank-One Safety Injection
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Safety alignment in Large Language Models (LLMs) often involves mediating internal representations to refuse harmful requests. Recent research has demonstrated that these safety mechanisms can be bypassed by ablating or removing specific representational directions within the model. In this paper, we propose the opposite approach: Rank-One Safety Injection (ROSI), a white-box method that amplifies a model's safety alignment by permanently steering its activations toward the refusal-mediating subspace. ROSI operates as a simple, fine-tuning-free rank-one weight modification applied to all residual stream write matrices. The required safety direction can be computed from a small set of harmful and harmless instruction pairs. We show that ROSI consistently increases safety refusal rates - as evaluated by Llama Guard 3 - while preserving the utility of the model on standard benchmarks such as MMLU, HellaSwag, and Arc. Furthermore, we show that ROSI can also re-align 'uncensored' models by amplifying their own latent safety directions, demonstrating its utility as an effective last-mile safety procedure. Our results suggest that targeted, interpretable weight steering is a cheap and potent mechanism to improve LLM safety, complementing more resource-intensive fine-tuning paradigms.
Train Long, Think Short: Curriculum Learning for Efficient Reasoning
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Recent work on enhancing the reasoning abilities of large language models (LLMs) has introduced explicit length control as a means of constraining computational cost while preserving accuracy. However, existing approaches rely on fixed-length training budgets, which do not take advantage of the natural progression from exploration to compression during learning. In this work, we propose a curriculum learning strategy for length-controlled reasoning using Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). Our method starts with generous token budgets and gradually tightens them over training, encouraging models to first discover effective solution strategies and then distill them into more concise reasoning traces. We augment GRPO with a reward function that balances three signals: task correctness (via verifier feedback), length efficiency, and formatting adherence (via structural tags). Experiments on GSM8K, MATH500, SVAMP, College Math, and GSM+ demonstrate that curriculum-based training consistently outperforms fixed-budget baselines at the same final budget, achieving higher accuracy and significantly improved token efficiency. We further ablate the impact of reward weighting and decay schedule design, showing that progressive constraint serves as a powerful inductive bias for training efficient reasoning models. Our code and checkpoints are released at: https://github.com/hammoudhasan/curriculum_grpo.
An Embarrassingly Simple Defense Against LLM Abliteration Attacks
May 25, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are typically aligned to comply with safety guidelines by refusing harmful instructions. A recent attack, termed abliteration, isolates and suppresses the single latent direction most responsible for refusal behavior, enabling the model to generate unethical content. We propose a defense that modifies how models generate refusals. We construct an extended-refusal dataset that contains harmful prompts with a full response that justifies the reason for refusal. We then fine-tune Llama-2-7B-Chat and Qwen2.5-Instruct (1.5B and 3B parameters) on our extended-refusal dataset, and evaluate the resulting systems on a set of harmful prompts. In our experiments, extended-refusal models maintain high refusal rates, dropping at most by 10%, whereas baseline models' refusal rates drop by 70-80% after abliteration. A broad evaluation of safety and utility shows that extended-refusal fine-tuning neutralizes the abliteration attack while preserving general performance.
Beyond the Last Answer: Your Reasoning Trace Uncovers More than You Think
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) leverage step-by-step reasoning to solve complex problems. Standard evaluation practice involves generating a complete reasoning trace and assessing the correctness of the final answer presented at its conclusion. In this paper, we challenge the reliance on the final answer by posing the following two questions: Does the final answer reliably represent the model's optimal conclusion? Can alternative reasoning paths yield different results? To answer these questions, we analyze intermediate reasoning steps, termed subthoughts, and propose a method based on our findings. Our approach involves segmenting a reasoning trace into sequential subthoughts based on linguistic cues. We start by prompting the model to generate continuations from the end-point of each intermediate subthought. We extract a potential answer from every completed continuation originating from different subthoughts. We find that aggregating these answers by selecting the most frequent one (the mode) often yields significantly higher accuracy compared to relying solely on the answer derived from the original complete trace. Analyzing the consistency among the answers derived from different subthoughts reveals characteristics that correlate with the model's confidence and correctness, suggesting potential for identifying less reliable answers. Our experiments across various LLMs and challenging mathematical reasoning datasets (AIME2024 and AIME2025) show consistent accuracy improvements, with gains reaching up to 13\% and 10\% respectively. Implementation is available at: https://github.com/hammoudhasan/SubthoughtReasoner.
DiffCLIP: Differential Attention Meets CLIP
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:We propose DiffCLIP, a novel vision-language model that extends the differential attention mechanism to CLIP architectures. Differential attention was originally developed for large language models to amplify relevant context while canceling out noisy information. In this work, we integrate this mechanism into CLIP's dual encoder (image and text) framework. With minimal additional parameters, DiffCLIP achieves superior performance on image-text understanding tasks. Across zero-shot classification, retrieval, and robustness benchmarks, DiffCLIP consistently outperforms baseline CLIP models. Notably, these gains come with negligible computational overhead, demonstrating that differential attention can significantly enhance multi-modal representations without sacrificing efficiency. Code can be found at https://github.com/hammoudhasan/DiffCLIP.
Randomized Asymmetric Chain of LoRA: The First Meaningful Theoretical Framework for Low-Rank Adaptation
Oct 10, 2024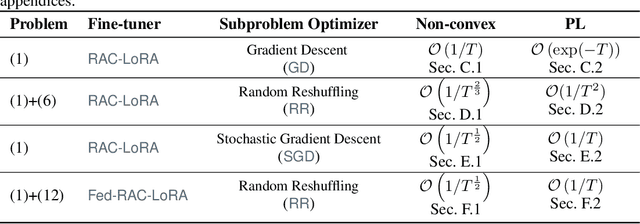
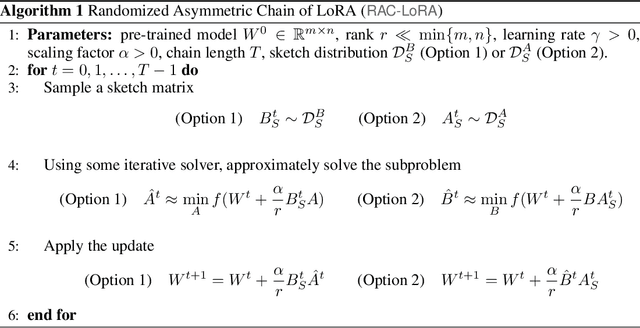
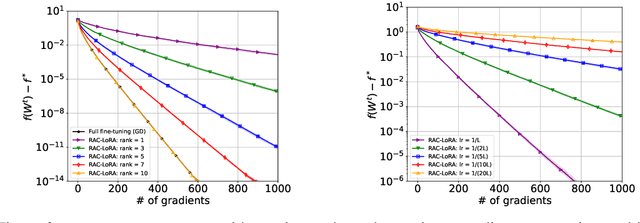
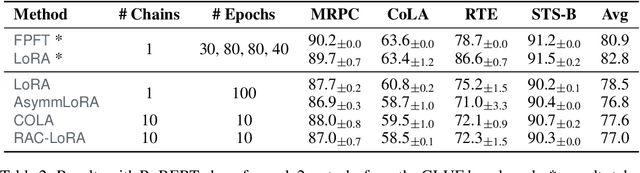
Abstract:Fine-tuning has become a popular approach to adapting large foundational models to specific tasks. As the size of models and datasets grows, parameter-efficient fine-tuning techniques are increasingly important. One of the most widely used methods is Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), with adaptation update expressed as the product of two low-rank matrices. While LoRA was shown to possess strong performance in fine-tuning, it often under-performs when compared to full-parameter fine-tuning (FPFT). Although many variants of LoRA have been extensively studied empirically, their theoretical optimization analysis is heavily under-explored. The starting point of our work is a demonstration that LoRA and its two extensions, Asymmetric LoRA and Chain of LoRA, indeed encounter convergence issues. To address these issues, we propose Randomized Asymmetric Chain of LoRA (RAC-LoRA) -- a general optimization framework that rigorously analyzes the convergence rates of LoRA-based methods. Our approach inherits the empirical benefits of LoRA-style heuristics, but introduces several small but important algorithmic modifications which turn it into a provably convergent method. Our framework serves as a bridge between FPFT and low-rank adaptation. We provide provable guarantees of convergence to the same solution as FPFT, along with the rate of convergence. Additionally, we present a convergence analysis for smooth, non-convex loss functions, covering gradient descent, stochastic gradient descent, and federated learning settings. Our theoretical findings are supported by experimental results.
Model Merging and Safety Alignment: One Bad Model Spoils the Bunch
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:Merging Large Language Models (LLMs) is a cost-effective technique for combining multiple expert LLMs into a single versatile model, retaining the expertise of the original ones. However, current approaches often overlook the importance of safety alignment during merging, leading to highly misaligned models. This work investigates the effects of model merging on alignment. We evaluate several popular model merging techniques, demonstrating that existing methods do not only transfer domain expertise but also propagate misalignment. We propose a simple two-step approach to address this problem: (i) generating synthetic safety and domain-specific data, and (ii) incorporating these generated data into the optimization process of existing data-aware model merging techniques. This allows us to treat alignment as a skill that can be maximized in the resulting merged LLM. Our experiments illustrate the effectiveness of integrating alignment-related data during merging, resulting in models that excel in both domain expertise and alignment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge