Randomized Asymmetric Chain of LoRA: The First Meaningful Theoretical Framework for Low-Rank Adaptation
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2024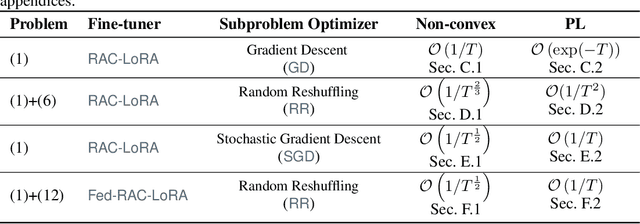
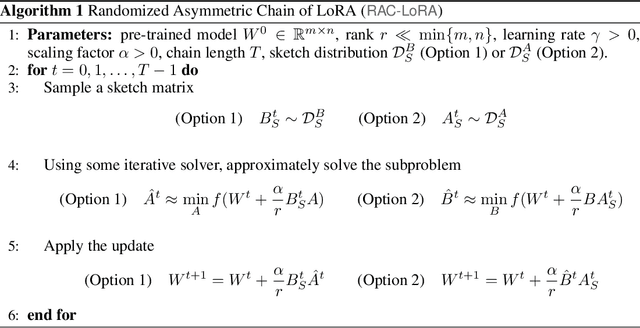
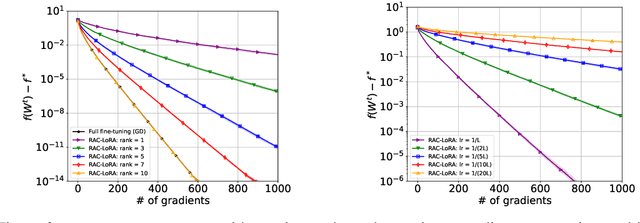
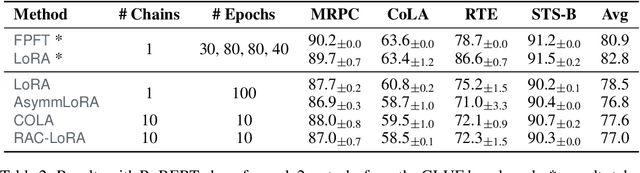
Fine-tuning has become a popular approach to adapting large foundational models to specific tasks. As the size of models and datasets grows, parameter-efficient fine-tuning techniques are increasingly important. One of the most widely used methods is Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), with adaptation update expressed as the product of two low-rank matrices. While LoRA was shown to possess strong performance in fine-tuning, it often under-performs when compared to full-parameter fine-tuning (FPFT). Although many variants of LoRA have been extensively studied empirically, their theoretical optimization analysis is heavily under-explored. The starting point of our work is a demonstration that LoRA and its two extensions, Asymmetric LoRA and Chain of LoRA, indeed encounter convergence issues. To address these issues, we propose Randomized Asymmetric Chain of LoRA (RAC-LoRA) -- a general optimization framework that rigorously analyzes the convergence rates of LoRA-based methods. Our approach inherits the empirical benefits of LoRA-style heuristics, but introduces several small but important algorithmic modifications which turn it into a provably convergent method. Our framework serves as a bridge between FPFT and low-rank adaptation. We provide provable guarantees of convergence to the same solution as FPFT, along with the rate of convergence. Additionally, we present a convergence analysis for smooth, non-convex loss functions, covering gradient descent, stochastic gradient descent, and federated learning settings. Our theoretical findings are supported by experimental results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge