Sergey Tulyakov
Visual Personalization Turing Test
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:We introduce the Visual Personalization Turing Test (VPTT), a new paradigm for evaluating contextual visual personalization based on perceptual indistinguishability, rather than identity replication. A model passes the VPTT if its output (image, video, 3D asset, etc.) is indistinguishable to a human or calibrated VLM judge from content a given person might plausibly create or share. To operationalize VPTT, we present the VPTT Framework, integrating a 10k-persona benchmark (VPTT-Bench), a visual retrieval-augmented generator (VPRAG), and the VPTT Score, a text-only metric calibrated against human and VLM judgments. We show high correlation across human, VLM, and VPTT evaluations, validating the VPTT Score as a reliable perceptual proxy. Experiments demonstrate that VPRAG achieves the best alignment-originality balance, offering a scalable and privacy-safe foundation for personalized generative AI.
S2DiT: Sandwich Diffusion Transformer for Mobile Streaming Video Generation
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have recently improved video generation quality. However, their heavy computational cost makes real-time or on-device generation infeasible. In this work, we introduce S2DiT, a Streaming Sandwich Diffusion Transformer designed for efficient, high-fidelity, and streaming video generation on mobile hardware. S2DiT generates more tokens but maintains efficiency with novel efficient attentions: a mixture of LinConv Hybrid Attention (LCHA) and Stride Self-Attention (SSA). Based on this, we uncover the sandwich design via a budget-aware dynamic programming search, achieving superior quality and efficiency. We further propose a 2-in-1 distillation framework that transfers the capacity of large teacher models (e.g., Wan 2.2-14B) to the compact few-step sandwich model. Together, S2DiT achieves quality on par with state-of-the-art server video models, while streaming at over 10 FPS on an iPhone.
SnapGen++: Unleashing Diffusion Transformers for Efficient High-Fidelity Image Generation on Edge Devices
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion transformers (DiTs) have set new standards in image generation, yet remain impractical for on-device deployment due to their high computational and memory costs. In this work, we present an efficient DiT framework tailored for mobile and edge devices that achieves transformer-level generation quality under strict resource constraints. Our design combines three key components. First, we propose a compact DiT architecture with an adaptive global-local sparse attention mechanism that balances global context modeling and local detail preservation. Second, we propose an elastic training framework that jointly optimizes sub-DiTs of varying capacities within a unified supernetwork, allowing a single model to dynamically adjust for efficient inference across different hardware. Finally, we develop Knowledge-Guided Distribution Matching Distillation, a step-distillation pipeline that integrates the DMD objective with knowledge transfer from few-step teacher models, producing high-fidelity and low-latency generation (e.g., 4-step) suitable for real-time on-device use. Together, these contributions enable scalable, efficient, and high-quality diffusion models for deployment on diverse hardware.
Tuning-free Visual Effect Transfer across Videos
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:We present RefVFX, a new framework that transfers complex temporal effects from a reference video onto a target video or image in a feed-forward manner. While existing methods excel at prompt-based or keyframe-conditioned editing, they struggle with dynamic temporal effects such as dynamic lighting changes or character transformations, which are difficult to describe via text or static conditions. Transferring a video effect is challenging, as the model must integrate the new temporal dynamics with the input video's existing motion and appearance. % To address this, we introduce a large-scale dataset of triplets, where each triplet consists of a reference effect video, an input image or video, and a corresponding output video depicting the transferred effect. Creating this data is non-trivial, especially the video-to-video effect triplets, which do not exist naturally. To generate these, we propose a scalable automated pipeline that creates high-quality paired videos designed to preserve the input's motion and structure while transforming it based on some fixed, repeatable effect. We then augment this data with image-to-video effects derived from LoRA adapters and code-based temporal effects generated through programmatic composition. Building on our new dataset, we train our reference-conditioned model using recent text-to-video backbones. Experimental results demonstrate that RefVFX produces visually consistent and temporally coherent edits, generalizes across unseen effect categories, and outperforms prompt-only baselines in both quantitative metrics and human preference. See our website https://tuningfreevisualeffects-maker.github.io/Tuning-free-Visual-Effect-Transfer-across-Videos-Project-Page/
Diffusion-DRF: Differentiable Reward Flow for Video Diffusion Fine-Tuning
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has recently improved Text-to-Video (T2V) generation by enhancing visual fidelity and text alignment. However, current methods rely on non-differentiable preference signals from human annotations or learned reward models. This reliance makes training label-intensive, bias-prone, and easy-to-game, which often triggers reward hacking and unstable training. We propose Diffusion-DRF, a differentiable reward flow for fine-tuning video diffusion models using a frozen, off-the-shelf Vision-Language Model (VLM) as a training-free critic. Diffusion-DRF directly backpropagates VLM feedback through the diffusion denoising chain, converting logit-level responses into token-aware gradients for optimization. We propose an automated, aspect-structured prompting pipeline to obtain reliable multi-dimensional VLM feedback, while gradient checkpointing enables efficient updates through the final denoising steps. Diffusion-DRF improves video quality and semantic alignment while mitigating reward hacking and collapse -- without additional reward models or preference datasets. It is model-agnostic and readily generalizes to other diffusion-based generative tasks.
EasyV2V: A High-quality Instruction-based Video Editing Framework
Dec 18, 2025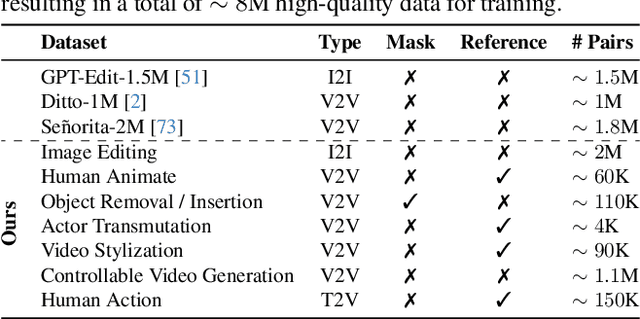

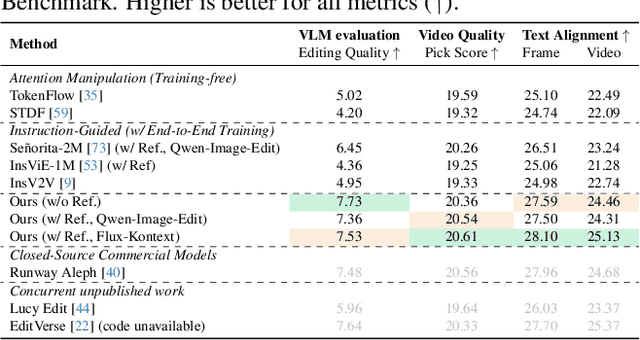
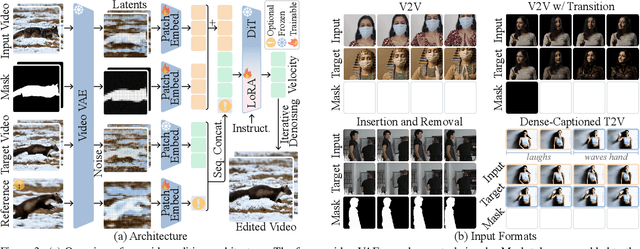
Abstract:While image editing has advanced rapidly, video editing remains less explored, facing challenges in consistency, control, and generalization. We study the design space of data, architecture, and control, and introduce \emph{EasyV2V}, a simple and effective framework for instruction-based video editing. On the data side, we compose existing experts with fast inverses to build diverse video pairs, lift image edit pairs into videos via single-frame supervision and pseudo pairs with shared affine motion, mine dense-captioned clips for video pairs, and add transition supervision to teach how edits unfold. On the model side, we observe that pretrained text-to-video models possess editing capability, motivating a simplified design. Simple sequence concatenation for conditioning with light LoRA fine-tuning suffices to train a strong model. For control, we unify spatiotemporal control via a single mask mechanism and support optional reference images. Overall, EasyV2V works with flexible inputs, e.g., video+text, video+mask+text, video+mask+reference+text, and achieves state-of-the-art video editing results, surpassing concurrent and commercial systems. Project page: https://snap-research.github.io/easyv2v/
AlcheMinT: Fine-grained Temporal Control for Multi-Reference Consistent Video Generation
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in subject-driven video generation with large diffusion models have enabled personalized content synthesis conditioned on user-provided subjects. However, existing methods lack fine-grained temporal control over subject appearance and disappearance, which are essential for applications such as compositional video synthesis, storyboarding, and controllable animation. We propose AlcheMinT, a unified framework that introduces explicit timestamps conditioning for subject-driven video generation. Our approach introduces a novel positional encoding mechanism that unlocks the encoding of temporal intervals, associated in our case with subject identities, while seamlessly integrating with the pretrained video generation model positional embeddings. Additionally, we incorporate subject-descriptive text tokens to strengthen binding between visual identity and video captions, mitigating ambiguity during generation. Through token-wise concatenation, AlcheMinT avoids any additional cross-attention modules and incurs negligible parameter overhead. We establish a benchmark evaluating multiple subject identity preservation, video fidelity, and temporal adherence. Experimental results demonstrate that AlcheMinT achieves visual quality matching state-of-the-art video personalization methods, while, for the first time, enabling precise temporal control over multi-subject generation within videos. Project page is at https://snap-research.github.io/Video-AlcheMinT
Omni-Attribute: Open-vocabulary Attribute Encoder for Visual Concept Personalization
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Visual concept personalization aims to transfer only specific image attributes, such as identity, expression, lighting, and style, into unseen contexts. However, existing methods rely on holistic embeddings from general-purpose image encoders, which entangle multiple visual factors and make it difficult to isolate a single attribute. This often leads to information leakage and incoherent synthesis. To address this limitation, we introduce Omni-Attribute, the first open-vocabulary image attribute encoder designed to learn high-fidelity, attribute-specific representations. Our approach jointly designs the data and model: (i) we curate semantically linked image pairs annotated with positive and negative attributes to explicitly teach the encoder what to preserve or suppress; and (ii) we adopt a dual-objective training paradigm that balances generative fidelity with contrastive disentanglement. The resulting embeddings prove effective for open-vocabulary attribute retrieval, personalization, and compositional generation, achieving state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks.
OmniView: An All-Seeing Diffusion Model for 3D and 4D View Synthesis
Dec 11, 2025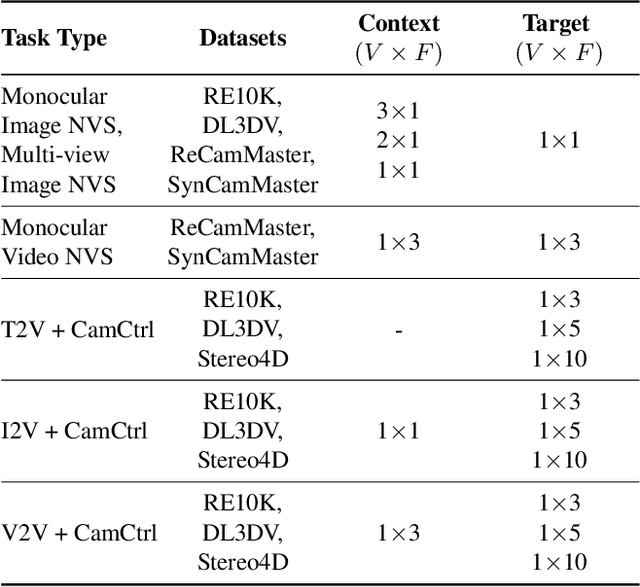
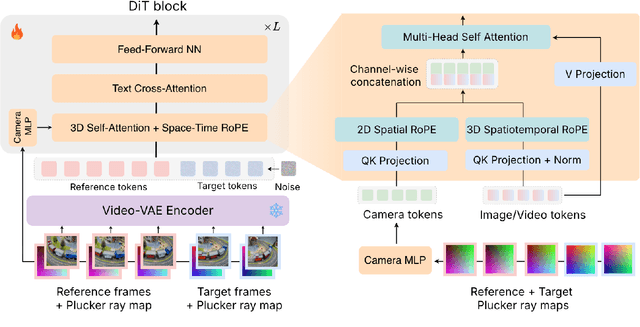
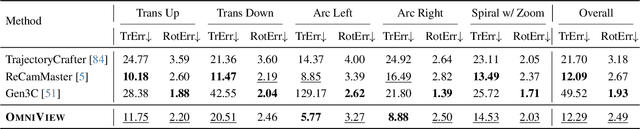

Abstract:Prior approaches injecting camera control into diffusion models have focused on specific subsets of 4D consistency tasks: novel view synthesis, text-to-video with camera control, image-to-video, amongst others. Therefore, these fragmented approaches are trained on disjoint slices of available 3D/4D data. We introduce OmniView, a unified framework that generalizes across a wide range of 4D consistency tasks. Our method separately represents space, time, and view conditions, enabling flexible combinations of these inputs. For example, OmniView can synthesize novel views from static, dynamic, and multiview inputs, extrapolate trajectories forward and backward in time, and create videos from text or image prompts with full camera control. OmniView is competitive with task-specific models across diverse benchmarks and metrics, improving image quality scores among camera-conditioned diffusion models by up to 33\% in multiview NVS LLFF dataset, 60\% in dynamic NVS Neural 3D Video benchmark, 20\% in static camera control on RE-10K, and reducing camera trajectory errors by 4x in text-conditioned video generation. With strong generalizability in one model, OmniView demonstrates the feasibility of a generalist 4D video model. Project page is available at https://snap-research.github.io/OmniView/
AlphaFlow: Understanding and Improving MeanFlow Models
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:MeanFlow has recently emerged as a powerful framework for few-step generative modeling trained from scratch, but its success is not yet fully understood. In this work, we show that the MeanFlow objective naturally decomposes into two parts: trajectory flow matching and trajectory consistency. Through gradient analysis, we find that these terms are strongly negatively correlated, causing optimization conflict and slow convergence. Motivated by these insights, we introduce $\alpha$-Flow, a broad family of objectives that unifies trajectory flow matching, Shortcut Model, and MeanFlow under one formulation. By adopting a curriculum strategy that smoothly anneals from trajectory flow matching to MeanFlow, $\alpha$-Flow disentangles the conflicting objectives, and achieves better convergence. When trained from scratch on class-conditional ImageNet-1K 256x256 with vanilla DiT backbones, $\alpha$-Flow consistently outperforms MeanFlow across scales and settings. Our largest $\alpha$-Flow-XL/2+ model achieves new state-of-the-art results using vanilla DiT backbones, with FID scores of 2.58 (1-NFE) and 2.15 (2-NFE).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge