Vicente Ordonez
DeepSport: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Comprehensive Sports Video Reasoning via Agentic Reinforcement Learning
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Sports video understanding presents unique challenges, requiring models to perceive high-speed dynamics, comprehend complex rules, and reason over long temporal contexts. While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown promise in genral domains, the current state of research in sports remains narrowly focused: existing approaches are either single-sport centric, limited to specific tasks, or rely on training-free paradigms that lack robust, learned reasoning process. To address this gap, we introduce DeepSport, the first end-to-end trained MLLM framework designed for multi-task, multi-sport video understanding. DeepSport shifts the paradigm from passive frame processing to active, iterative reasoning, empowering the model to ``think with videos'' by dynamically interrogating content via a specialized frame-extraction tool. To enable this, we propose a data distillation pipeline that synthesizes high-quality Chain-of-Thought (CoT) trajectories from 10 diverse data source, creating a unified resource of 78k training data. We then employ a two-stage training strategy, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) followed by Reinforcement Learning (RL) with a novel gated tool-use reward, to optimize the model's reasoning process. Extensive experiments on the testing benchmark of 6.7k questions demonstrate that DeepSport achieves state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming baselines of both proprietary model and open-source models. Our work establishes a new foundation for domain-specific video reasoning to address the complexities of diverse sports.
SportR: A Benchmark for Multimodal Large Language Model Reasoning in Sports
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Deeply understanding sports requires an intricate blend of fine-grained visual perception and rule-based reasoning - a challenge that pushes the limits of current multimodal models. To succeed, models must master three critical capabilities: perceiving nuanced visual details, applying abstract sport rule knowledge, and grounding that knowledge in specific visual evidence. Current sports benchmarks either cover single sports or lack the detailed reasoning chains and precise visual grounding needed to robustly evaluate these core capabilities in a multi-sport context. To address this gap, we introduce SportR, the first multi-sports large-scale benchmark designed to train and evaluate MLLMs on the fundamental reasoning required for sports intelligence. Our benchmark provides a dataset of 5,017 images and 2,101 videos. To enable granular evaluation, we structure our benchmark around a progressive hierarchy of question-answer (QA) pairs designed to probe reasoning at increasing depths - from simple infraction identification to complex penalty prediction. For the most advanced tasks requiring multi-step reasoning, such as determining penalties or explaining tactics, we provide 7,118 high-quality, human-authored Chain of Thought (CoT) annotations. In addition, our benchmark incorporates both image and video modalities and provides manual bounding box annotations to test visual grounding in the image part directly. Extensive experiments demonstrate the profound difficulty of our benchmark. State-of-the-art baseline models perform poorly on our most challenging tasks. While training on our data via Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning improves these scores, they remain relatively low, highlighting a significant gap in current model capabilities. SportR presents a new challenge for the community, providing a critical resource to drive future research in multimodal sports reasoning.
NoiseShift: Resolution-Aware Noise Recalibration for Better Low-Resolution Image Generation
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models trained on a fixed set of resolutions often fail to generalize, even when asked to generate images at lower resolutions than those seen during training. High-resolution text-to-image generators are currently unable to easily offer an out-of-the-box budget-efficient alternative to their users who might not need high-resolution images. We identify a key technical insight in diffusion models that when addressed can help tackle this limitation: Noise schedulers have unequal perceptual effects across resolutions. The same level of noise removes disproportionately more signal from lower-resolution images than from high-resolution images, leading to a train-test mismatch. We propose NoiseShift, a training-free method that recalibrates the noise level of the denoiser conditioned on resolution size. NoiseShift requires no changes to model architecture or sampling schedule and is compatible with existing models. When applied to Stable Diffusion 3, Stable Diffusion 3.5, and Flux-Dev, quality at low resolutions is significantly improved. On LAION-COCO, NoiseShift improves SD3.5 by 15.89%, SD3 by 8.56%, and Flux-Dev by 2.44% in FID on average. On CelebA, NoiseShift improves SD3.5 by 10.36%, SD3 by 5.19%, and Flux-Dev by 3.02% in FID on average. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of NoiseShift in mitigating resolution-dependent artifacts and enhancing the quality of low-resolution image generation.
Improving Progressive Generation with Decomposable Flow Matching
Jun 24, 2025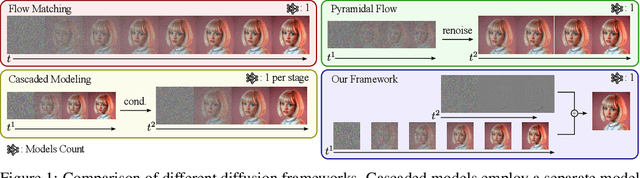
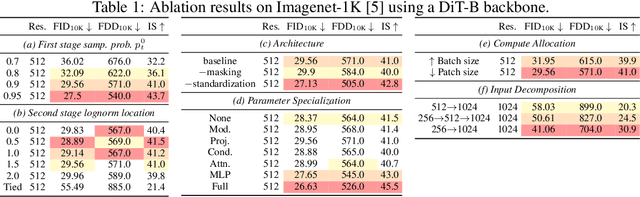
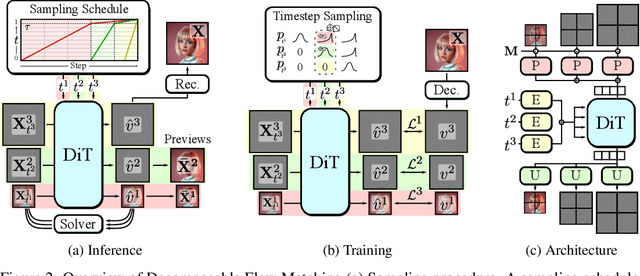
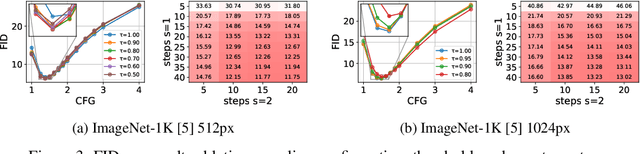
Abstract:Generating high-dimensional visual modalities is a computationally intensive task. A common solution is progressive generation, where the outputs are synthesized in a coarse-to-fine spectral autoregressive manner. While diffusion models benefit from the coarse-to-fine nature of denoising, explicit multi-stage architectures are rarely adopted. These architectures have increased the complexity of the overall approach, introducing the need for a custom diffusion formulation, decomposition-dependent stage transitions, add-hoc samplers, or a model cascade. Our contribution, Decomposable Flow Matching (DFM), is a simple and effective framework for the progressive generation of visual media. DFM applies Flow Matching independently at each level of a user-defined multi-scale representation (such as Laplacian pyramid). As shown by our experiments, our approach improves visual quality for both images and videos, featuring superior results compared to prior multistage frameworks. On Imagenet-1k 512px, DFM achieves 35.2% improvements in FDD scores over the base architecture and 26.4% over the best-performing baseline, under the same training compute. When applied to finetuning of large models, such as FLUX, DFM shows faster convergence speed to the training distribution. Crucially, all these advantages are achieved with a single model, architectural simplicity, and minimal modifications to existing training pipelines.
ProxyThinker: Test-Time Guidance through Small Visual Reasoners
May 30, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards have pushed the boundaries of the visual reasoning capabilities in large vision-language models (LVLMs). However, training LVLMs with reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) is computationally expensive, posing a significant challenge to scaling model size. In this work, we propose ProxyThinker, an inference-time technique that enables large models to inherit the visual reasoning capabilities from small, slow-thinking visual reasoners without any training. By subtracting the output distributions of base models from those of RFT reasoners, ProxyThinker modifies the decoding dynamics and successfully elicits the slow-thinking reasoning demonstrated by the emerged sophisticated behaviors such as self-verification and self-correction. ProxyThinker consistently boosts performance on challenging visual benchmarks on spatial, mathematical, and multi-disciplinary reasoning, enabling untuned base models to compete with the performance of their full-scale RFT counterparts. Furthermore, our implementation efficiently coordinates multiple language models with parallelism techniques and achieves up to 38 $\times$ faster inference compared to previous decoding-time methods, paving the way for the practical deployment of ProxyThinker. Code is available at https://github.com/MrZilinXiao/ProxyThinker.
LOCORE: Image Re-ranking with Long-Context Sequence Modeling
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:We introduce LOCORE, Long-Context Re-ranker, a model that takes as input local descriptors corresponding to an image query and a list of gallery images and outputs similarity scores between the query and each gallery image. This model is used for image retrieval, where typically a first ranking is performed with an efficient similarity measure, and then a shortlist of top-ranked images is re-ranked based on a more fine-grained similarity measure. Compared to existing methods that perform pair-wise similarity estimation with local descriptors or list-wise re-ranking with global descriptors, LOCORE is the first method to perform list-wise re-ranking with local descriptors. To achieve this, we leverage efficient long-context sequence models to effectively capture the dependencies between query and gallery images at the local-descriptor level. During testing, we process long shortlists with a sliding window strategy that is tailored to overcome the context size limitations of sequence models. Our approach achieves superior performance compared with other re-rankers on established image retrieval benchmarks of landmarks (ROxf and RPar), products (SOP), fashion items (In-Shop), and bird species (CUB-200) while having comparable latency to the pair-wise local descriptor re-rankers.
Evaluating Text-to-Image Synthesis with a Conditional Fréchet Distance
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:Evaluating text-to-image synthesis is challenging due to misalignment between established metrics and human preferences. We propose cFreD, a metric based on the notion of Conditional Fr\'echet Distance that explicitly accounts for both visual fidelity and text-prompt alignment. Existing metrics such as Inception Score (IS), Fr\'echet Inception Distance (FID) and CLIPScore assess either image quality or image-text alignment but not both which limits their correlation with human preferences. Scoring models explicitly trained to replicate human preferences require constant updates and may not generalize to novel generation techniques or out-of-domain inputs. Through extensive experiments across multiple recently proposed text-to-image models and diverse prompt datasets, we demonstrate that cFreD exhibits a higher correlation with human judgments compared to statistical metrics, including metrics trained with human preferences. Our findings validate cFreD as a robust, future-proof metric for the systematic evaluation of text-to-image models, standardizing benchmarking in this rapidly evolving field. We release our evaluation toolkit and benchmark in the appendix.
AV-Link: Temporally-Aligned Diffusion Features for Cross-Modal Audio-Video Generation
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:We propose AV-Link, a unified framework for Video-to-Audio and Audio-to-Video generation that leverages the activations of frozen video and audio diffusion models for temporally-aligned cross-modal conditioning. The key to our framework is a Fusion Block that enables bidirectional information exchange between our backbone video and audio diffusion models through a temporally-aligned self attention operation. Unlike prior work that uses feature extractors pretrained for other tasks for the conditioning signal, AV-Link can directly leverage features obtained by the complementary modality in a single framework i.e. video features to generate audio, or audio features to generate video. We extensively evaluate our design choices and demonstrate the ability of our method to achieve synchronized and high-quality audiovisual content, showcasing its potential for applications in immersive media generation. Project Page: snap-research.github.io/AVLink/
ParallelSpec: Parallel Drafter for Efficient Speculative Decoding
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Speculative decoding has proven to be an efficient solution to large language model (LLM) inference, where the small drafter predicts future tokens at a low cost, and the target model is leveraged to verify them in parallel. However, most existing works still draft tokens auto-regressively to maintain sequential dependency in language modeling, which we consider a huge computational burden in speculative decoding. We present ParallelSpec, an alternative to auto-regressive drafting strategies in state-of-the-art speculative decoding approaches. In contrast to auto-regressive drafting in the speculative stage, we train a parallel drafter to serve as an efficient speculative model. ParallelSpec learns to efficiently predict multiple future tokens in parallel using a single model, and it can be integrated into any speculative decoding framework that requires aligning the output distributions of the drafter and the target model with minimal training cost. Experimental results show that ParallelSpec accelerates baseline methods in latency up to 62% on text generation benchmarks from different domains, and it achieves 2.84X overall speedup on the Llama-2-13B model using third-party evaluation criteria.
Fairness and Bias Mitigation in Computer Vision: A Survey
Aug 05, 2024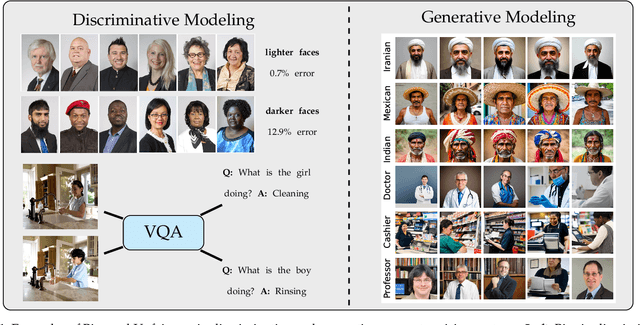
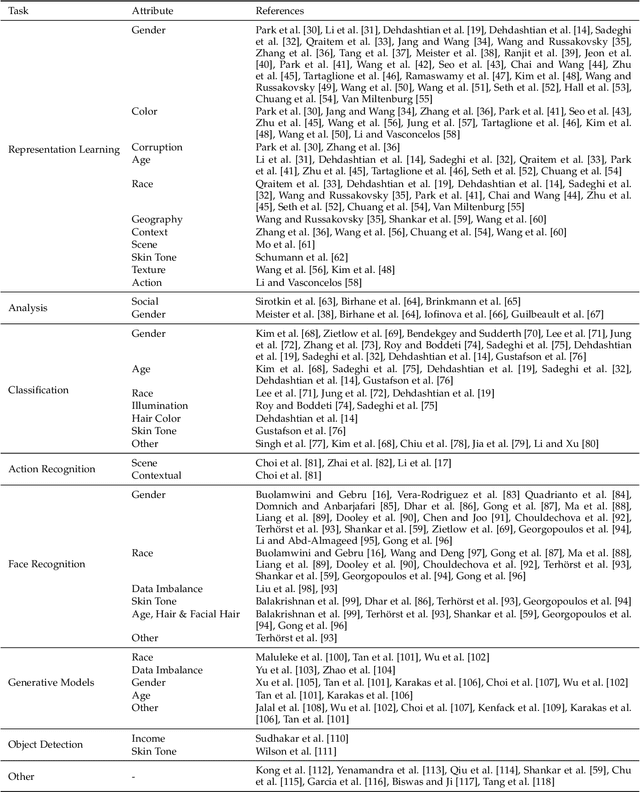
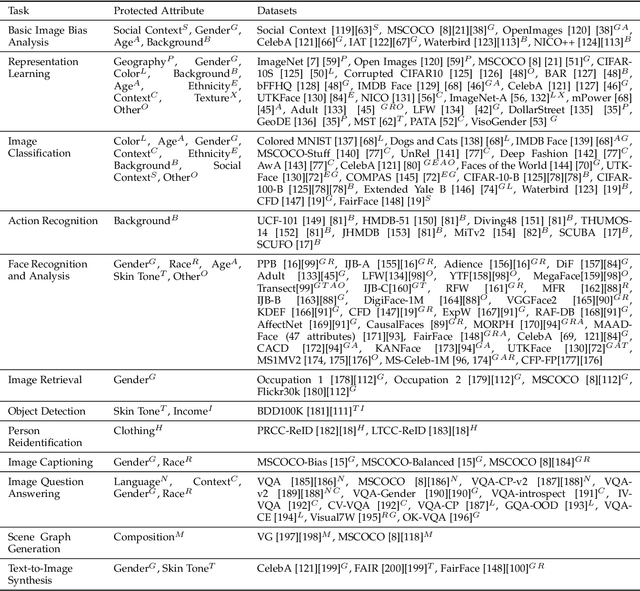
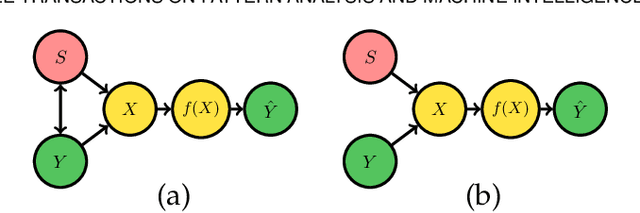
Abstract:Computer vision systems have witnessed rapid progress over the past two decades due to multiple advances in the field. As these systems are increasingly being deployed in high-stakes real-world applications, there is a dire need to ensure that they do not propagate or amplify any discriminatory tendencies in historical or human-curated data or inadvertently learn biases from spurious correlations. This paper presents a comprehensive survey on fairness that summarizes and sheds light on ongoing trends and successes in the context of computer vision. The topics we discuss include 1) The origin and technical definitions of fairness drawn from the wider fair machine learning literature and adjacent disciplines. 2) Work that sought to discover and analyze biases in computer vision systems. 3) A summary of methods proposed to mitigate bias in computer vision systems in recent years. 4) A comprehensive summary of resources and datasets produced by researchers to measure, analyze, and mitigate bias and enhance fairness. 5) Discussion of the field's success, continuing trends in the context of multimodal foundation and generative models, and gaps that still need to be addressed. The presented characterization should help researchers understand the importance of identifying and mitigating bias in computer vision and the state of the field and identify potential directions for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge