Jefferson Hernandez
ProxyThinker: Test-Time Guidance through Small Visual Reasoners
May 30, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards have pushed the boundaries of the visual reasoning capabilities in large vision-language models (LVLMs). However, training LVLMs with reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) is computationally expensive, posing a significant challenge to scaling model size. In this work, we propose ProxyThinker, an inference-time technique that enables large models to inherit the visual reasoning capabilities from small, slow-thinking visual reasoners without any training. By subtracting the output distributions of base models from those of RFT reasoners, ProxyThinker modifies the decoding dynamics and successfully elicits the slow-thinking reasoning demonstrated by the emerged sophisticated behaviors such as self-verification and self-correction. ProxyThinker consistently boosts performance on challenging visual benchmarks on spatial, mathematical, and multi-disciplinary reasoning, enabling untuned base models to compete with the performance of their full-scale RFT counterparts. Furthermore, our implementation efficiently coordinates multiple language models with parallelism techniques and achieves up to 38 $\times$ faster inference compared to previous decoding-time methods, paving the way for the practical deployment of ProxyThinker. Code is available at https://github.com/MrZilinXiao/ProxyThinker.
Evaluating Text-to-Image Synthesis with a Conditional Fréchet Distance
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:Evaluating text-to-image synthesis is challenging due to misalignment between established metrics and human preferences. We propose cFreD, a metric based on the notion of Conditional Fr\'echet Distance that explicitly accounts for both visual fidelity and text-prompt alignment. Existing metrics such as Inception Score (IS), Fr\'echet Inception Distance (FID) and CLIPScore assess either image quality or image-text alignment but not both which limits their correlation with human preferences. Scoring models explicitly trained to replicate human preferences require constant updates and may not generalize to novel generation techniques or out-of-domain inputs. Through extensive experiments across multiple recently proposed text-to-image models and diverse prompt datasets, we demonstrate that cFreD exhibits a higher correlation with human judgments compared to statistical metrics, including metrics trained with human preferences. Our findings validate cFreD as a robust, future-proof metric for the systematic evaluation of text-to-image models, standardizing benchmarking in this rapidly evolving field. We release our evaluation toolkit and benchmark in the appendix.
Generative Visual Instruction Tuning
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:We propose to use machine-generated instruction-following data to improve the zero-shot capabilities of a large multimodal model with additional support for generative and image editing tasks. We achieve this by curating a new multimodal instruction-following set using GPT-4V and existing datasets for image generation and editing. Using this instruction set and the existing LLaVA-Finetune instruction set for visual understanding tasks, we produce GenLLaVA, a Generative Large Language, and Visual Assistant. GenLLaVA is built through a strategy that combines three types of large pre-trained models through instruction finetuning: LLaMA for language modeling, SigLIP for image-text matching, and StableDiffusion for text-to-image generation. Our model demonstrates visual understanding capabilities on par with LLaVA and additionally demonstrates competitive results with native multimodal models such as Unified-IO 2, paving the way for building advanced general-purpose visual assistants by effectively re-using existing multimodal models. We open-source our dataset, codebase, and model checkpoints to foster further research and application in this domain.
Visual Representation Learning from Unlabeled Video using Contrastive Masked Autoencoders
Mar 21, 2023



Abstract:Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) learn self-supervised representations by randomly masking input image patches and a reconstruction loss. Alternatively, contrastive learning self-supervised methods encourage two versions of the same input to have a similar representation, while pulling apart the representations for different inputs. We propose ViC-MAE, a general method that combines both MAE and contrastive learning by pooling the local feature representations learned under the MAE reconstruction objective and leveraging this global representation under a contrastive objective across video frames. We show that visual representations learned under ViC-MAE generalize well to both video classification and image classification tasks. Using a backbone ViT-B/16 network pre-trained on the Moments in Time (MiT) dataset, we obtain state-of-the-art transfer learning from video to images on Imagenet-1k by improving 1.58% in absolute top-1 accuracy from a recent previous work. Moreover, our method maintains a competitive transfer-learning performance of 81.50% top-1 accuracy on the Kinetics-400 video classification benchmark. In addition, we show that despite its simplicity, ViC-MAE yields improved results compared to combining MAE pre-training with previously proposed contrastive objectives such as VicReg and SiamSiam.
A fast multi-object tracking system using an object detector ensemble
Aug 06, 2019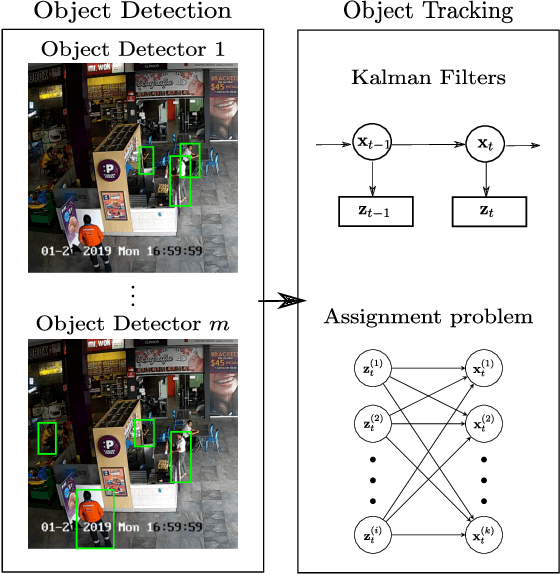
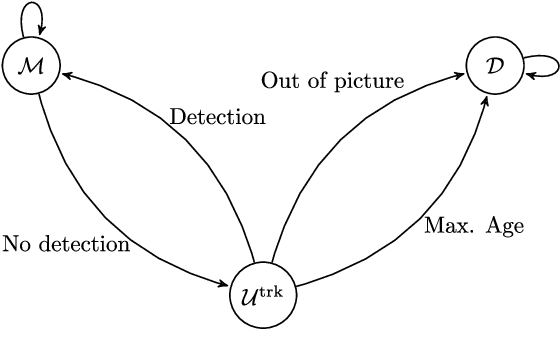
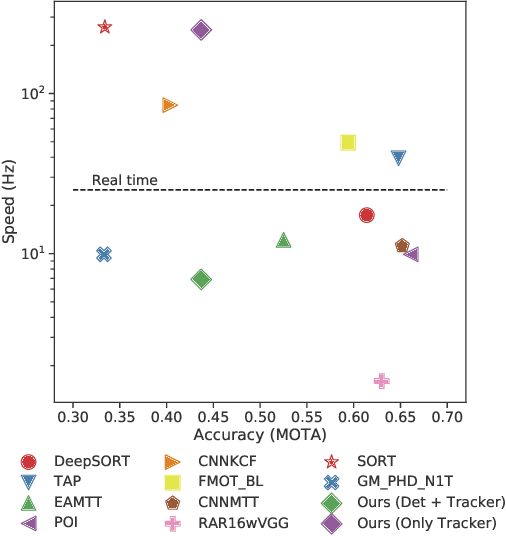
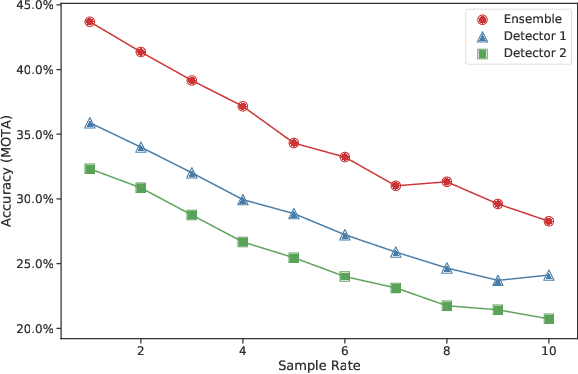
Abstract:Multiple-Object Tracking (MOT) is of crucial importance for applications such as retail video analytics and video surveillance. Object detectors are often the computational bottleneck of modern MOT systems, limiting their use for real-time applications. In this paper, we address this issue by leveraging on an ensemble of detectors, each running every f frames. We measured the performance of our system in the MOT16 benchmark. The proposed model surpassed other online entries of the MOT16 challenge in speed, while maintaining an acceptable accuracy.
Learning from multivariate discrete sequential data using a restricted Boltzmann machine model
Apr 28, 2018



Abstract:A restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) is a generative neural-network model with many novel applications such as collaborative filtering and acoustic modeling. An RBM lacks the capacity to retain memory, making it inappropriate for dynamic data modeling as in time-series analysis. In this paper we address this issue by proposing the p-RBM model, a generalization of the regular RBM model, capable of retaining memory of p past states. We further show how to train the p-RBM model using contrastive divergence and test our model on the problem of predicting the stock market direction considering 100 stocks of the NASDAQ-100 index. Obtained results show that the p-RBM offer promising prediction potential.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge