Medical Segmentation Decathlon
Papers and Code
Auto-nnU-Net: Towards Automated Medical Image Segmentation
May 22, 2025Medical Image Segmentation (MIS) includes diverse tasks, from bone to organ segmentation, each with its own challenges in finding the best segmentation model. The state-of-the-art AutoML-related MIS-framework nnU-Net automates many aspects of model configuration but remains constrained by fixed hyperparameters and heuristic design choices. As a full-AutoML framework for MIS, we propose Auto-nnU-Net, a novel nnU-Net variant enabling hyperparameter optimization (HPO), neural architecture search (NAS), and hierarchical NAS (HNAS). Additionally, we propose Regularized PriorBand to balance model accuracy with the computational resources required for training, addressing the resource constraints often faced in real-world medical settings that limit the feasibility of extensive training procedures. We evaluate our approach across diverse MIS datasets from the well-established Medical Segmentation Decathlon, analyzing the impact of AutoML techniques on segmentation performance, computational efficiency, and model design choices. The results demonstrate that our AutoML approach substantially improves the segmentation performance of nnU-Net on 6 out of 10 datasets and is on par on the other datasets while maintaining practical resource requirements. Our code is available at https://github.com/LUH-AI/AutonnUNet.
TK-Mamba: Marrying KAN with Mamba for Text-Driven 3D Medical Image Segmentation
May 24, 2025



3D medical image segmentation is vital for clinical diagnosis and treatment but is challenged by high-dimensional data and complex spatial dependencies. Traditional single-modality networks, such as CNNs and Transformers, are often limited by computational inefficiency and constrained contextual modeling in 3D settings. We introduce a novel multimodal framework that leverages Mamba and Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) as an efficient backbone for long-sequence modeling. Our approach features three key innovations: First, an EGSC (Enhanced Gated Spatial Convolution) module captures spatial information when unfolding 3D images into 1D sequences. Second, we extend Group-Rational KAN (GR-KAN), a Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks variant with rational basis functions, into 3D-Group-Rational KAN (3D-GR-KAN) for 3D medical imaging - its first application in this domain - enabling superior feature representation tailored to volumetric data. Third, a dual-branch text-driven strategy leverages CLIP's text embeddings: one branch swaps one-hot labels for semantic vectors to preserve inter-organ semantic relationships, while the other aligns images with detailed organ descriptions to enhance semantic alignment. Experiments on the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) and KiTS23 datasets show our method achieving state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing approaches in accuracy and efficiency. This work highlights the power of combining advanced sequence modeling, extended network architectures, and vision-language synergy to push forward 3D medical image segmentation, delivering a scalable solution for clinical use. The source code is openly available at https://github.com/yhy-whu/TK-Mamba.
MiniGPT-Pancreas: Multimodal Large Language Model for Pancreas Cancer Classification and Detection
Dec 20, 2024

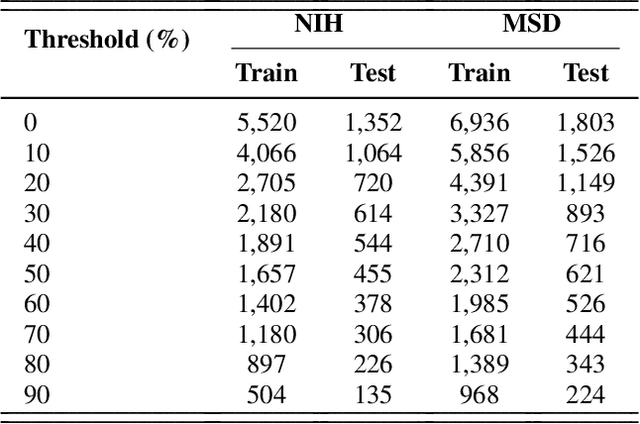
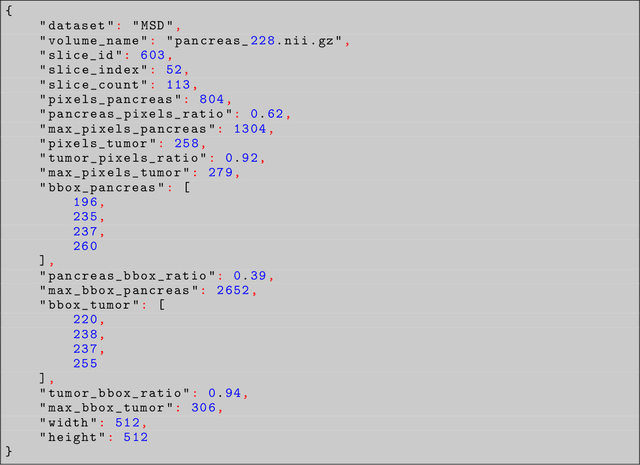
Problem: Pancreas radiological imaging is challenging due to the small size, blurred boundaries, and variability of shape and position of the organ among patients. Goal: In this work we present MiniGPT-Pancreas, a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM), as an interactive chatbot to support clinicians in pancreas cancer diagnosis by integrating visual and textual information. Methods: MiniGPT-v2, a general-purpose MLLM, was fine-tuned in a cascaded way for pancreas detection, tumor classification, and tumor detection with multimodal prompts combining questions and computed tomography scans from the National Institute of Health (NIH), and Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) datasets. The AbdomenCT-1k dataset was used to detect the liver, spleen, kidney, and pancreas. Results: MiniGPT-Pancreas achieved an Intersection over Union (IoU) of 0.595 and 0.550 for the detection of pancreas on NIH and MSD datasets, respectively. For the pancreas cancer classification task on the MSD dataset, accuracy, precision, and recall were 0.876, 0.874, and 0.878, respectively. When evaluating MiniGPT-Pancreas on the AbdomenCT-1k dataset for multi-organ detection, the IoU was 0.8399 for the liver, 0.722 for the kidney, 0.705 for the spleen, and 0.497 for the pancreas. For the pancreas tumor detection task, the IoU score was 0.168 on the MSD dataset. Conclusions: MiniGPT-Pancreas represents a promising solution to support clinicians in the classification of pancreas images with pancreas tumors. Future research is needed to improve the score on the detection task, especially for pancreas tumors.
Uncertainty-Error correlations in Evidential Deep Learning models for biomedical segmentation
Oct 24, 2024In this work, we examine the effectiveness of an uncertainty quantification framework known as Evidential Deep Learning applied in the context of biomedical image segmentation. This class of models involves assigning Dirichlet distributions as priors for segmentation labels, and enables a few distinct definitions of model uncertainties. Using the cardiac and prostate MRI images available in the Medical Segmentation Decathlon for validation, we found that Evidential Deep Learning models with U-Net backbones generally yielded superior correlations between prediction errors and uncertainties relative to the conventional baseline equipped with Shannon entropy measure, Monte-Carlo Dropout and Deep Ensemble methods. We also examined these models' effectiveness in active learning, finding that relative to the standard Shannon entropy-based sampling, they yielded higher point-biserial uncertainty-error correlations while attaining similar performances in Dice-Sorensen coefficients. These superior features of EDL models render them well-suited for segmentation tasks that warrant a critical sensitivity in detecting large model errors.
Medical Image Segmentation with SAM-generated Annotations
Sep 30, 2024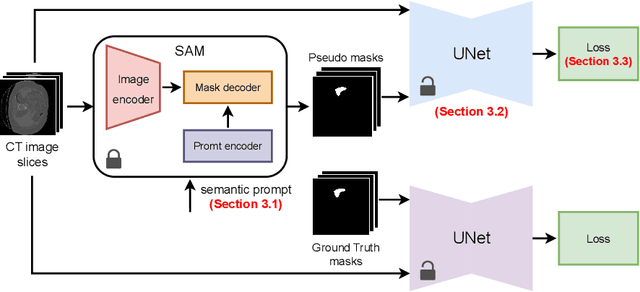
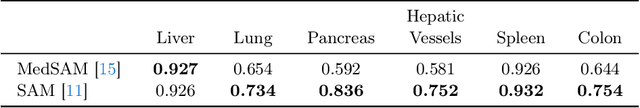
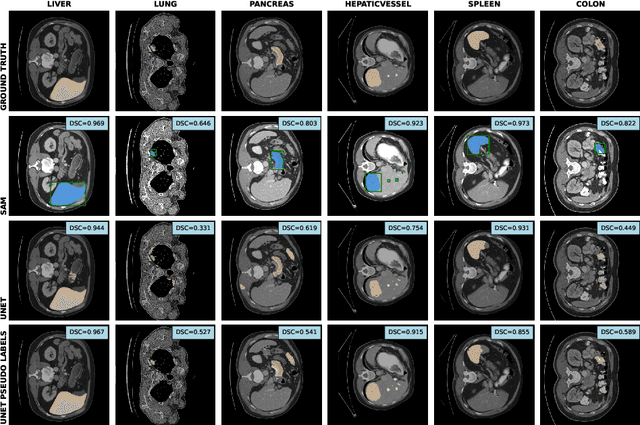
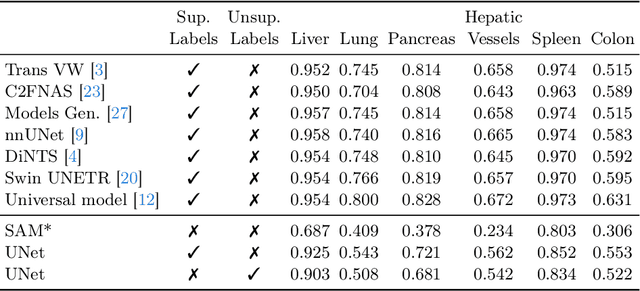
The field of medical image segmentation is hindered by the scarcity of large, publicly available annotated datasets. Not all datasets are made public for privacy reasons, and creating annotations for a large dataset is time-consuming and expensive, as it requires specialized expertise to accurately identify regions of interest (ROIs) within the images. To address these challenges, we evaluate the performance of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) as an annotation tool for medical data by using it to produce so-called "pseudo labels" on the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) computed tomography (CT) tasks. The pseudo labels are then used in place of ground truth labels to train a UNet model in a weakly-supervised manner. We experiment with different prompt types on SAM and find that the bounding box prompt is a simple yet effective method for generating pseudo labels. This method allows us to develop a weakly-supervised model that performs comparably to a fully supervised model.
Expanding the Medical Decathlon dataset: segmentation of colon and colorectal cancer from computed tomography images
Jul 31, 2024



Colorectal cancer is the third-most common cancer in the Western Hemisphere. The segmentation of colorectal and colorectal cancer by computed tomography is an urgent problem in medicine. Indeed, a system capable of solving this problem will enable the detection of colorectal cancer at early stages of the disease, facilitate the search for pathology by the radiologist, and significantly accelerate the process of diagnosing the disease. However, scientific publications on medical image processing mostly use closed, non-public data. This paper presents an extension of the Medical Decathlon dataset with colorectal markups in order to improve the quality of segmentation algorithms. An experienced radiologist validated the data, categorized it into subsets by quality, and published it in the public domain. Based on the obtained results, we trained neural network models of the UNet architecture with 5-part cross-validation and achieved a Dice metric quality of $0.6988 \pm 0.3$. The published markups will improve the quality of colorectal cancer detection and simplify the radiologist's job for study description.
Interactive 3D Medical Image Segmentation with SAM 2
Aug 05, 2024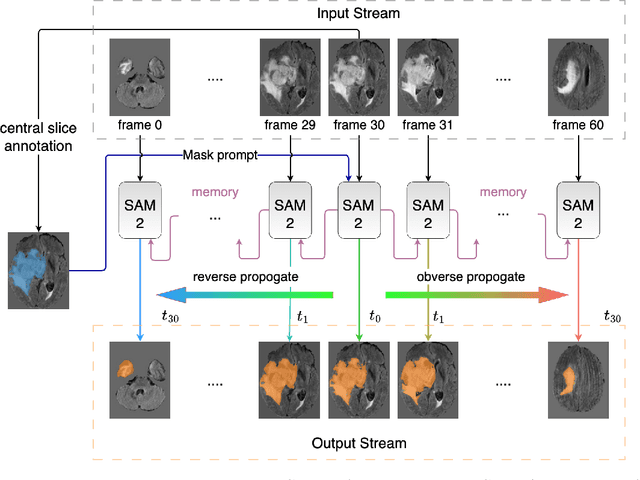
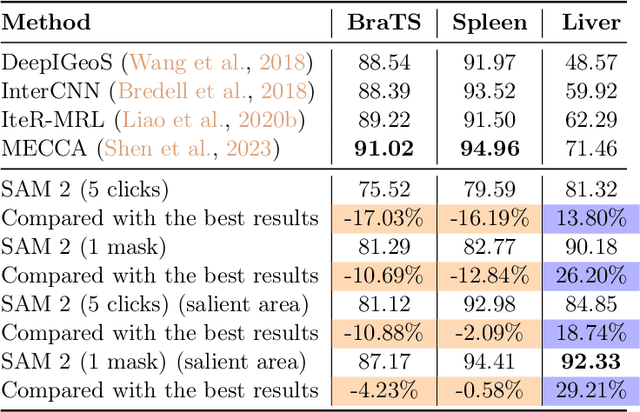
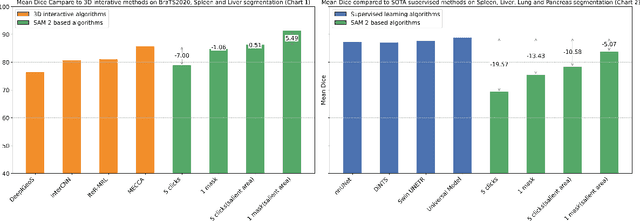
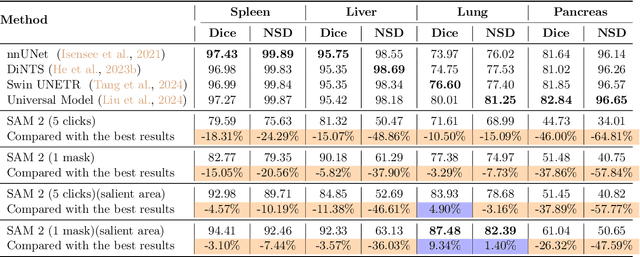
Interactive medical image segmentation (IMIS) has shown significant potential in enhancing segmentation accuracy by integrating iterative feedback from medical professionals. However, the limited availability of enough 3D medical data restricts the generalization and robustness of most IMIS methods. The Segment Anything Model (SAM), though effective for 2D images, requires expensive semi-auto slice-by-slice annotations for 3D medical images. In this paper, we explore the zero-shot capabilities of SAM 2, the next-generation Meta SAM model trained on videos, for 3D medical image segmentation. By treating sequential 2D slices of 3D images as video frames, SAM 2 can fully automatically propagate annotations from a single frame to the entire 3D volume. We propose a practical pipeline for using SAM 2 in 3D medical image segmentation and present key findings highlighting its efficiency and potential for further optimization. Concretely, numerical experiments on the BraTS2020 and the medical segmentation decathlon datasets demonstrate that SAM 2 still has a gap with supervised methods but can narrow the gap in specific settings and organ types, significantly reducing the annotation burden on medical professionals. Our code will be open-sourced and available at https://github.com/Chuyun-Shen/SAM_2_Medical_3D.
Progressive Growing of Patch Size: Resource-Efficient Curriculum Learning for Dense Prediction Tasks
Jul 11, 2024In this work, we introduce Progressive Growing of Patch Size, a resource-efficient implicit curriculum learning approach for dense prediction tasks. Our curriculum approach is defined by growing the patch size during model training, which gradually increases the task's difficulty. We integrated our curriculum into the nnU-Net framework and evaluated the methodology on all 10 tasks of the Medical Segmentation Decathlon. With our approach, we are able to substantially reduce runtime, computational costs, and CO2 emissions of network training compared to classical constant patch size training. In our experiments, the curriculum approach resulted in improved convergence. We are able to outperform standard nnU-Net training, which is trained with constant patch size, in terms of Dice Score on 7 out of 10 MSD tasks while only spending roughly 50% of the original training runtime. To the best of our knowledge, our Progressive Growing of Patch Size is the first successful employment of a sample-length curriculum in the form of patch size in the field of computer vision. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/compai-lab/2024-miccai-fischer.
Universal and Extensible Language-Vision Models for Organ Segmentation and Tumor Detection from Abdominal Computed Tomography
May 28, 2024



The advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) for organ segmentation and tumor detection is propelled by the growing availability of computed tomography (CT) datasets with detailed, per-voxel annotations. However, these AI models often struggle with flexibility for partially annotated datasets and extensibility for new classes due to limitations in the one-hot encoding, architectural design, and learning scheme. To overcome these limitations, we propose a universal, extensible framework enabling a single model, termed Universal Model, to deal with multiple public datasets and adapt to new classes (e.g., organs/tumors). Firstly, we introduce a novel language-driven parameter generator that leverages language embeddings from large language models, enriching semantic encoding compared with one-hot encoding. Secondly, the conventional output layers are replaced with lightweight, class-specific heads, allowing Universal Model to simultaneously segment 25 organs and six types of tumors and ease the addition of new classes. We train our Universal Model on 3,410 CT volumes assembled from 14 publicly available datasets and then test it on 6,173 CT volumes from four external datasets. Universal Model achieves first place on six CT tasks in the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) public leaderboard and leading performance on the Beyond The Cranial Vault (BTCV) dataset. In summary, Universal Model exhibits remarkable computational efficiency (6x faster than other dataset-specific models), demonstrates strong generalization across different hospitals, transfers well to numerous downstream tasks, and more importantly, facilitates the extensibility to new classes while alleviating the catastrophic forgetting of previously learned classes. Codes, models, and datasets are available at https://github.com/ljwztc/CLIP-Driven-Universal-Model
CycleINR: Cycle Implicit Neural Representation for Arbitrary-Scale Volumetric Super-Resolution of Medical Data
Apr 07, 2024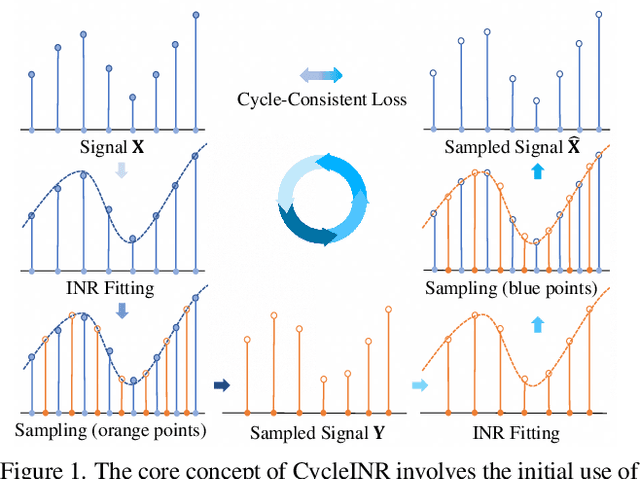
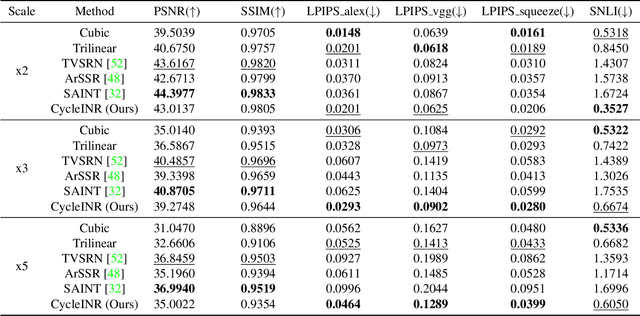
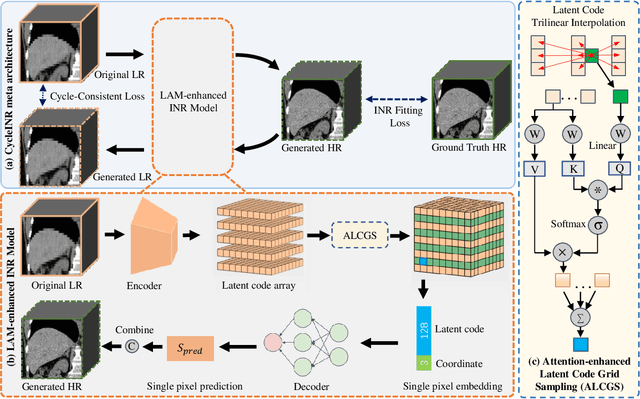
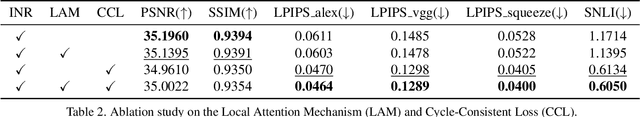
In the realm of medical 3D data, such as CT and MRI images, prevalent anisotropic resolution is characterized by high intra-slice but diminished inter-slice resolution. The lowered resolution between adjacent slices poses challenges, hindering optimal viewing experiences and impeding the development of robust downstream analysis algorithms. Various volumetric super-resolution algorithms aim to surmount these challenges, enhancing inter-slice resolution and overall 3D medical imaging quality. However, existing approaches confront inherent challenges: 1) often tailored to specific upsampling factors, lacking flexibility for diverse clinical scenarios; 2) newly generated slices frequently suffer from over-smoothing, degrading fine details, and leading to inter-slice inconsistency. In response, this study presents CycleINR, a novel enhanced Implicit Neural Representation model for 3D medical data volumetric super-resolution. Leveraging the continuity of the learned implicit function, the CycleINR model can achieve results with arbitrary up-sampling rates, eliminating the need for separate training. Additionally, we enhance the grid sampling in CycleINR with a local attention mechanism and mitigate over-smoothing by integrating cycle-consistent loss. We introduce a new metric, Slice-wise Noise Level Inconsistency (SNLI), to quantitatively assess inter-slice noise level inconsistency. The effectiveness of our approach is demonstrated through image quality evaluations on an in-house dataset and a downstream task analysis on the Medical Segmentation Decathlon liver tumor dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge