Jiawen Yao
DOPPLER: Dual-Policy Learning for Device Assignment in Asynchronous Dataflow Graphs
May 29, 2025Abstract:We study the problem of assigning operations in a dataflow graph to devices to minimize execution time in a work-conserving system, with emphasis on complex machine learning workloads. Prior learning-based methods often struggle due to three key limitations: (1) reliance on bulk-synchronous systems like TensorFlow, which under-utilize devices due to barrier synchronization; (2) lack of awareness of the scheduling mechanism of underlying systems when designing learning-based methods; and (3) exclusive dependence on reinforcement learning, ignoring the structure of effective heuristics designed by experts. In this paper, we propose \textsc{Doppler}, a three-stage framework for training dual-policy networks consisting of 1) a $\mathsf{SEL}$ policy for selecting operations and 2) a $\mathsf{PLC}$ policy for placing chosen operations on devices. Our experiments show that \textsc{Doppler} outperforms all baseline methods across tasks by reducing system execution time and additionally demonstrates sampling efficiency by reducing per-episode training time.
Boosting Medical Image-based Cancer Detection via Text-guided Supervision from Reports
May 23, 2024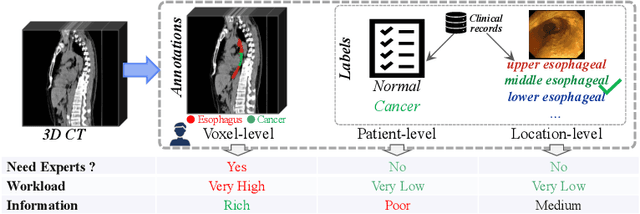
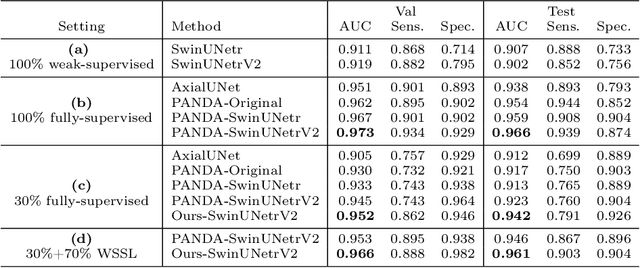
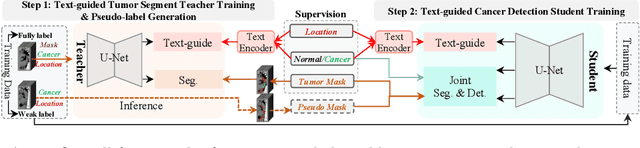
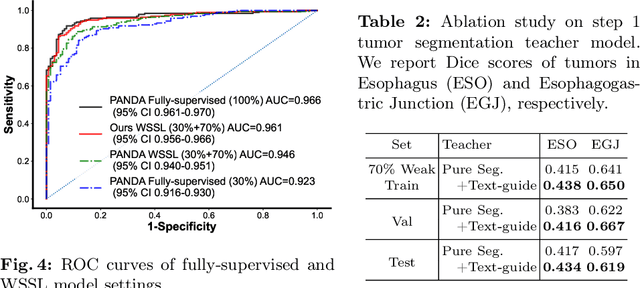
Abstract:The absence of adequately sufficient expert-level tumor annotations hinders the effectiveness of supervised learning based opportunistic cancer screening on medical imaging. Clinical reports (that are rich in descriptive textual details) can offer a "free lunch'' supervision information and provide tumor location as a type of weak label to cope with screening tasks, thus saving human labeling workloads, if properly leveraged. However, predicting cancer only using such weak labels can be very changeling since tumors are usually presented in small anatomical regions compared to the whole 3D medical scans. Weakly semi-supervised learning (WSSL) utilizes a limited set of voxel-level tumor annotations and incorporates alongside a substantial number of medical images that have only off-the-shelf clinical reports, which may strike a good balance between minimizing expert annotation workload and optimizing screening efficacy. In this paper, we propose a novel text-guided learning method to achieve highly accurate cancer detection results. Through integrating diagnostic and tumor location text prompts into the text encoder of a vision-language model (VLM), optimization of weakly supervised learning can be effectively performed in the latent space of VLM, thereby enhancing the stability of training. Our approach can leverage clinical knowledge by large-scale pre-trained VLM to enhance generalization ability, and produce reliable pseudo tumor masks to improve cancer detection. Our extensive quantitative experimental results on a large-scale cancer dataset, including 1,651 unique patients, validate that our approach can reduce human annotation efforts by at least 70% while maintaining comparable cancer detection accuracy to competing fully supervised methods (AUC value 0.961 versus 0.966).
CycleINR: Cycle Implicit Neural Representation for Arbitrary-Scale Volumetric Super-Resolution of Medical Data
Apr 07, 2024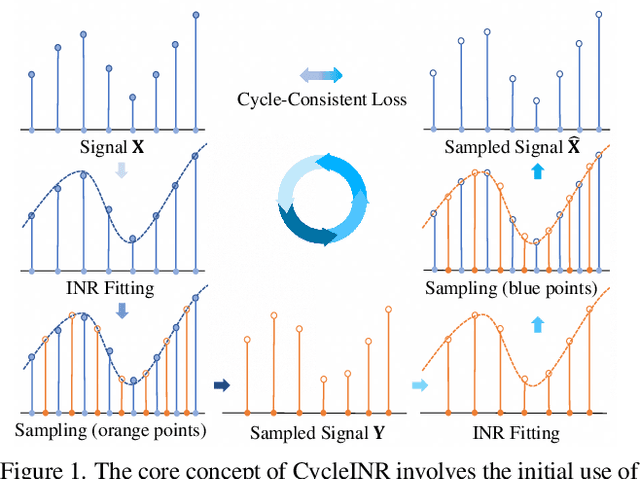
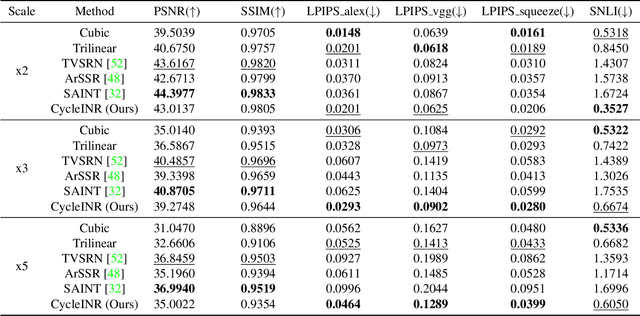
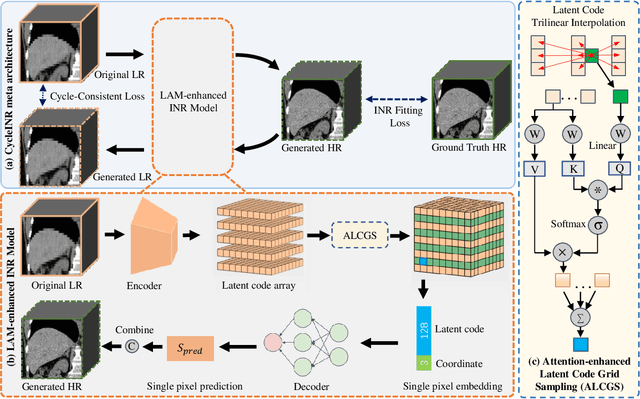
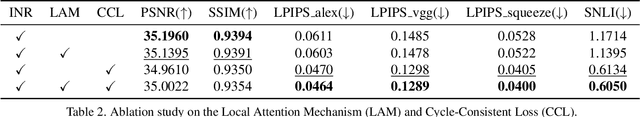
Abstract:In the realm of medical 3D data, such as CT and MRI images, prevalent anisotropic resolution is characterized by high intra-slice but diminished inter-slice resolution. The lowered resolution between adjacent slices poses challenges, hindering optimal viewing experiences and impeding the development of robust downstream analysis algorithms. Various volumetric super-resolution algorithms aim to surmount these challenges, enhancing inter-slice resolution and overall 3D medical imaging quality. However, existing approaches confront inherent challenges: 1) often tailored to specific upsampling factors, lacking flexibility for diverse clinical scenarios; 2) newly generated slices frequently suffer from over-smoothing, degrading fine details, and leading to inter-slice inconsistency. In response, this study presents CycleINR, a novel enhanced Implicit Neural Representation model for 3D medical data volumetric super-resolution. Leveraging the continuity of the learned implicit function, the CycleINR model can achieve results with arbitrary up-sampling rates, eliminating the need for separate training. Additionally, we enhance the grid sampling in CycleINR with a local attention mechanism and mitigate over-smoothing by integrating cycle-consistent loss. We introduce a new metric, Slice-wise Noise Level Inconsistency (SNLI), to quantitatively assess inter-slice noise level inconsistency. The effectiveness of our approach is demonstrated through image quality evaluations on an in-house dataset and a downstream task analysis on the Medical Segmentation Decathlon liver tumor dataset.
$M^{2}$Fusion: Bayesian-based Multimodal Multi-level Fusion on Colorectal Cancer Microsatellite Instability Prediction
Jan 15, 2024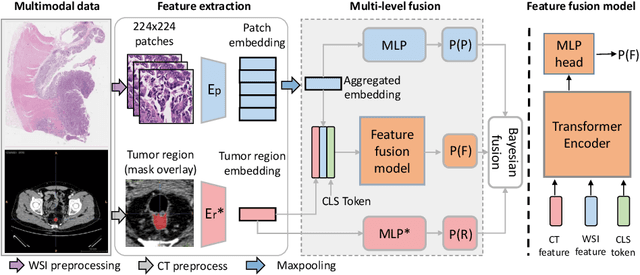
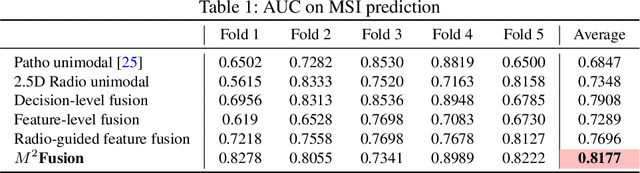
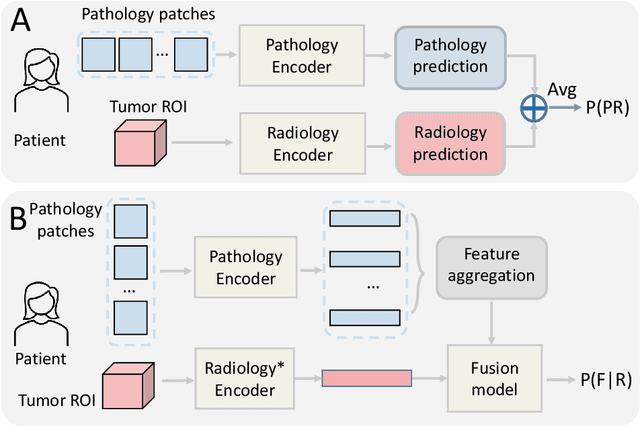
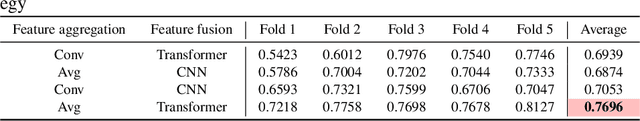
Abstract:Colorectal cancer (CRC) micro-satellite instability (MSI) prediction on histopathology images is a challenging weakly supervised learning task that involves multi-instance learning on gigapixel images. To date, radiology images have proven to have CRC MSI information and efficient patient imaging techniques. Different data modalities integration offers the opportunity to increase the accuracy and robustness of MSI prediction. Despite the progress in representation learning from the whole slide images (WSI) and exploring the potential of making use of radiology data, CRC MSI prediction remains a challenge to fuse the information from multiple data modalities (e.g., pathology WSI and radiology CT image). In this paper, we propose $M^{2}$Fusion: a Bayesian-based multimodal multi-level fusion pipeline for CRC MSI. The proposed fusion model $M^{2}$Fusion is capable of discovering more novel patterns within and across modalities that are beneficial for predicting MSI than using a single modality alone, as well as other fusion methods. The contribution of the paper is three-fold: (1) $M^{2}$Fusion is the first pipeline of multi-level fusion on pathology WSI and 3D radiology CT image for MSI prediction; (2) CT images are the first time integrated into multimodal fusion for CRC MSI prediction; (3) feature-level fusion strategy is evaluated on both Transformer-based and CNN-based method. Our approach is validated on cross-validation of 352 cases and outperforms either feature-level (0.8177 vs. 0.7908) or decision-level fusion strategy (0.8177 vs. 0.7289) on AUC score.
Improved Prognostic Prediction of Pancreatic Cancer Using Multi-Phase CT by Integrating Neural Distance and Texture-Aware Transformer
Aug 01, 2023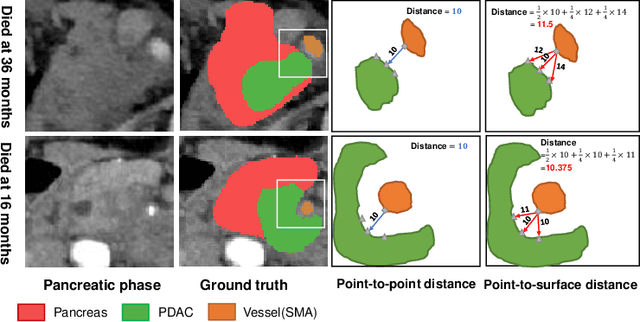
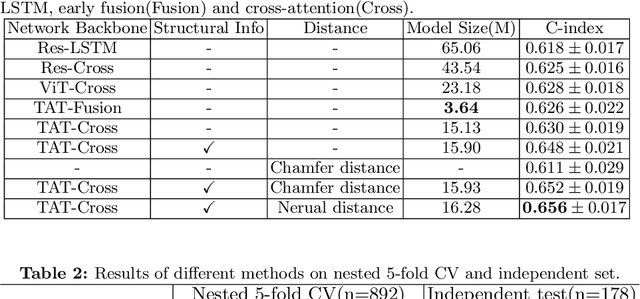
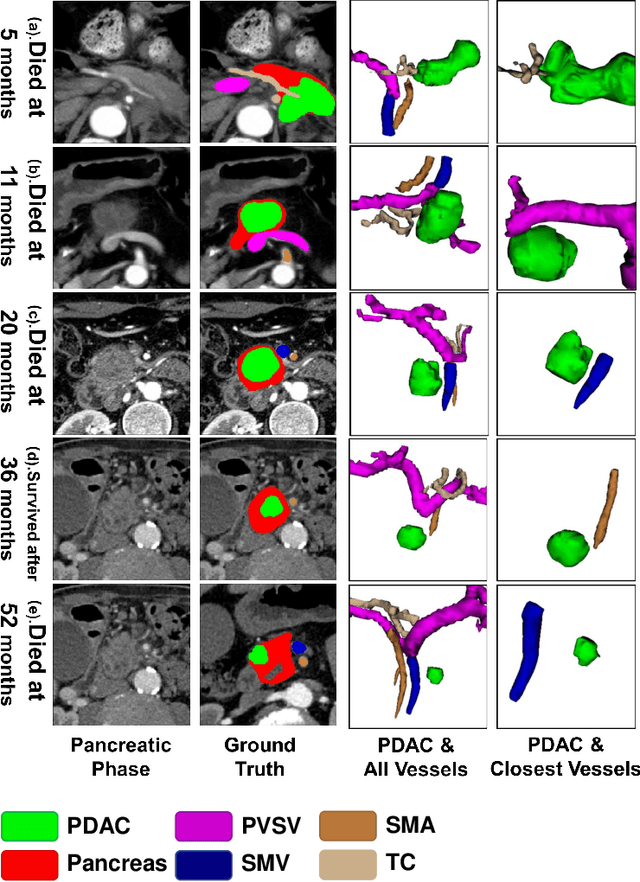
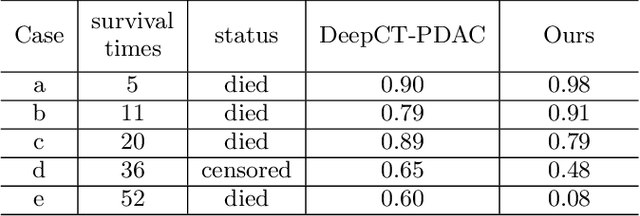
Abstract:Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly lethal cancer in which the tumor-vascular involvement greatly affects the resectability and, thus, overall survival of patients. However, current prognostic prediction methods fail to explicitly and accurately investigate relationships between the tumor and nearby important vessels. This paper proposes a novel learnable neural distance that describes the precise relationship between the tumor and vessels in CT images of different patients, adopting it as a major feature for prognosis prediction. Besides, different from existing models that used CNNs or LSTMs to exploit tumor enhancement patterns on dynamic contrast-enhanced CT imaging, we improved the extraction of dynamic tumor-related texture features in multi-phase contrast-enhanced CT by fusing local and global features using CNN and transformer modules, further enhancing the features extracted across multi-phase CT images. We extensively evaluated and compared the proposed method with existing methods in the multi-center (n=4) dataset with 1,070 patients with PDAC, and statistical analysis confirmed its clinical effectiveness in the external test set consisting of three centers. The developed risk marker was the strongest predictor of overall survival among preoperative factors and it has the potential to be combined with established clinical factors to select patients at higher risk who might benefit from neoadjuvant therapy.
Liver Tumor Screening and Diagnosis in CT with Pixel-Lesion-Patient Network
Jul 17, 2023Abstract:Liver tumor segmentation and classification are important tasks in computer aided diagnosis. We aim to address three problems: liver tumor screening and preliminary diagnosis in non-contrast computed tomography (CT), and differential diagnosis in dynamic contrast-enhanced CT. A novel framework named Pixel-Lesion-pAtient Network (PLAN) is proposed. It uses a mask transformer to jointly segment and classify each lesion with improved anchor queries and a foreground-enhanced sampling loss. It also has an image-wise classifier to effectively aggregate global information and predict patient-level diagnosis. A large-scale multi-phase dataset is collected containing 939 tumor patients and 810 normal subjects. 4010 tumor instances of eight types are extensively annotated. On the non-contrast tumor screening task, PLAN achieves 95% and 96% in patient-level sensitivity and specificity. On contrast-enhanced CT, our lesion-level detection precision, recall, and classification accuracy are 92%, 89%, and 86%, outperforming widely used CNN and transformers for lesion segmentation. We also conduct a reader study on a holdout set of 250 cases. PLAN is on par with a senior human radiologist, showing the clinical significance of our results.
Cluster-Induced Mask Transformers for Effective Opportunistic Gastric Cancer Screening on Non-contrast CT Scans
Jul 16, 2023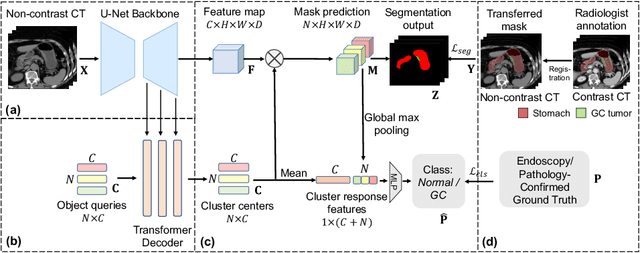
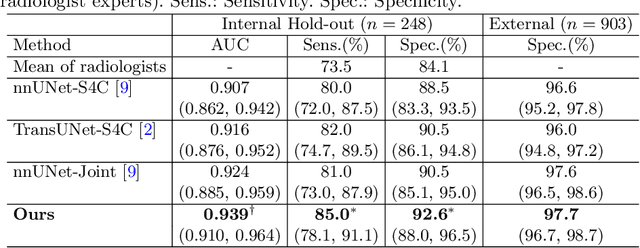
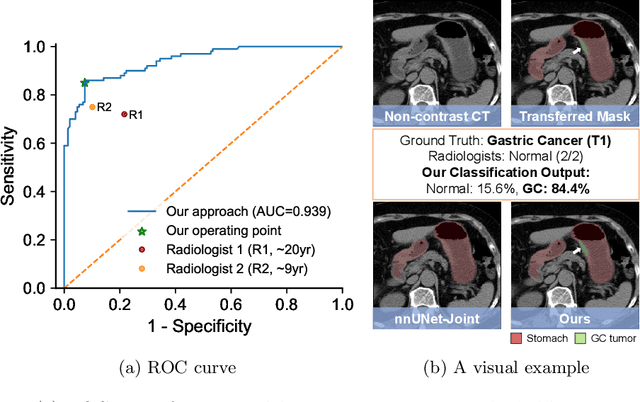
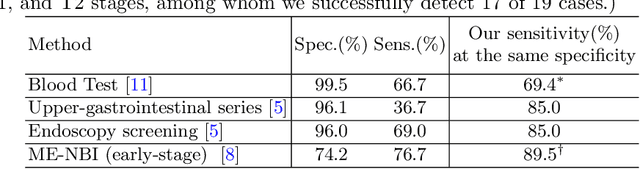
Abstract:Gastric cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, but no guideline-recommended screening test exists. Existing methods can be invasive, expensive, and lack sensitivity to identify early-stage gastric cancer. In this study, we explore the feasibility of using a deep learning approach on non-contrast CT scans for gastric cancer detection. We propose a novel cluster-induced Mask Transformer that jointly segments the tumor and classifies abnormality in a multi-task manner. Our model incorporates learnable clusters that encode the texture and shape prototypes of gastric cancer, utilizing self- and cross-attention to interact with convolutional features. In our experiments, the proposed method achieves a sensitivity of 85.0% and specificity of 92.6% for detecting gastric tumors on a hold-out test set consisting of 100 patients with cancer and 148 normal. In comparison, two radiologists have an average sensitivity of 73.5% and specificity of 84.3%. We also obtain a specificity of 97.7% on an external test set with 903 normal cases. Our approach performs comparably to established state-of-the-art gastric cancer screening tools like blood testing and endoscopy, while also being more sensitive in detecting early-stage cancer. This demonstrates the potential of our approach as a novel, non-invasive, low-cost, and accurate method for opportunistic gastric cancer screening.
Devil is in the Queries: Advancing Mask Transformers for Real-world Medical Image Segmentation and Out-of-Distribution Localization
Apr 01, 2023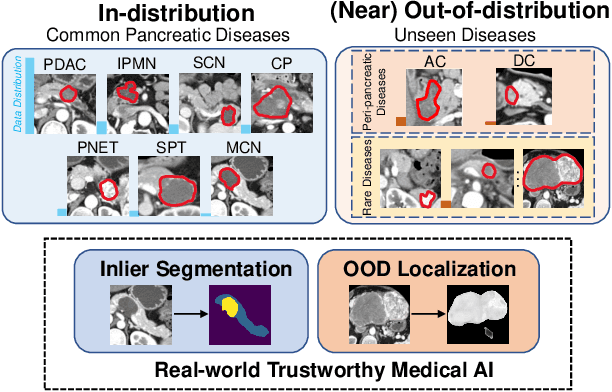
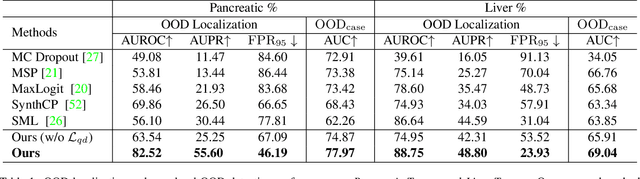
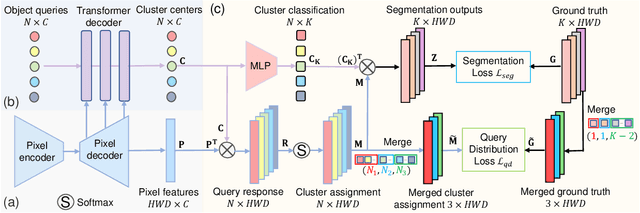
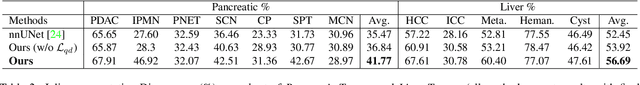
Abstract:Real-world medical image segmentation has tremendous long-tailed complexity of objects, among which tail conditions correlate with relatively rare diseases and are clinically significant. A trustworthy medical AI algorithm should demonstrate its effectiveness on tail conditions to avoid clinically dangerous damage in these out-of-distribution (OOD) cases. In this paper, we adopt the concept of object queries in Mask Transformers to formulate semantic segmentation as a soft cluster assignment. The queries fit the feature-level cluster centers of inliers during training. Therefore, when performing inference on a medical image in real-world scenarios, the similarity between pixels and the queries detects and localizes OOD regions. We term this OOD localization as MaxQuery. Furthermore, the foregrounds of real-world medical images, whether OOD objects or inliers, are lesions. The difference between them is less than that between the foreground and background, possibly misleading the object queries to focus redundantly on the background. Thus, we propose a query-distribution (QD) loss to enforce clear boundaries between segmentation targets and other regions at the query level, improving the inlier segmentation and OOD indication. Our proposed framework is tested on two real-world segmentation tasks, i.e., segmentation of pancreatic and liver tumors, outperforming previous state-of-the-art algorithms by an average of 7.39% on AUROC, 14.69% on AUPR, and 13.79% on FPR95 for OOD localization. On the other hand, our framework improves the performance of inlier segmentation by an average of 5.27% DSC when compared with the leading baseline nnUNet.
Meta-information-aware Dual-path Transformer for Differential Diagnosis of Multi-type Pancreatic Lesions in Multi-phase CT
Mar 02, 2023Abstract:Pancreatic cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death. Accurate detection, segmentation, and differential diagnosis of the full taxonomy of pancreatic lesions, i.e., normal, seven major types of lesions, and other lesions, is critical to aid the clinical decision-making of patient management and treatment. However, existing works focus on segmentation and classification for very specific lesion types (PDAC) or groups. Moreover, none of the previous work considers using lesion prevalence-related non-imaging patient information to assist the differential diagnosis. To this end, we develop a meta-information-aware dual-path transformer and exploit the feasibility of classification and segmentation of the full taxonomy of pancreatic lesions. Specifically, the proposed method consists of a CNN-based segmentation path (S-path) and a transformer-based classification path (C-path). The S-path focuses on initial feature extraction by semantic segmentation using a UNet-based network. The C-path utilizes both the extracted features and meta-information for patient-level classification based on stacks of dual-path transformer blocks that enhance the modeling of global contextual information. A large-scale multi-phase CT dataset of 3,096 patients with pathology-confirmed pancreatic lesion class labels, voxel-wise manual annotations of lesions from radiologists, and patient meta-information, was collected for training and evaluations. Our results show that our method can enable accurate classification and segmentation of the full taxonomy of pancreatic lesions, approaching the accuracy of the radiologist's report and significantly outperforming previous baselines. Results also show that adding the common meta-information, i.e., gender and age, can boost the model's performance, thus demonstrating the importance of meta-information for aiding pancreatic disease diagnosis.
Towards a Single Unified Model for Effective Detection, Segmentation, and Diagnosis of Eight Major Cancers Using a Large Collection of CT Scans
Jan 28, 2023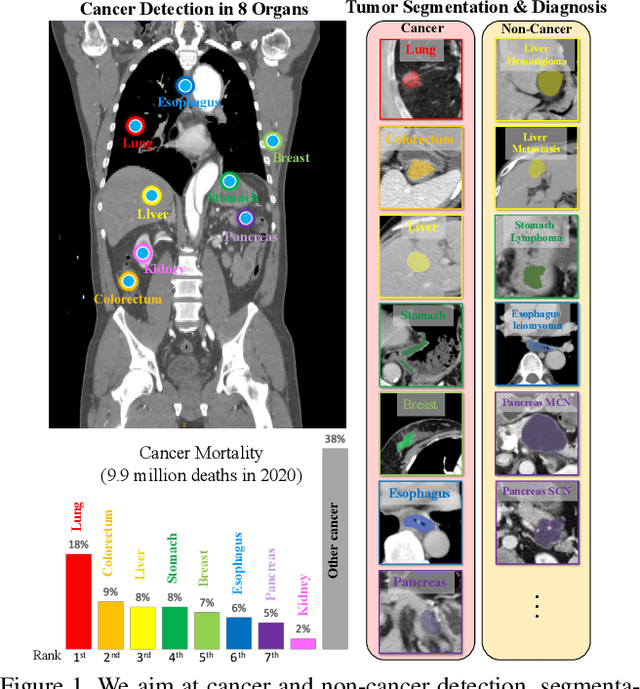
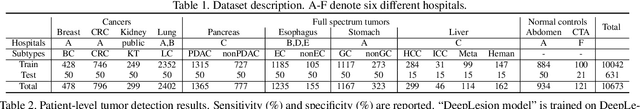
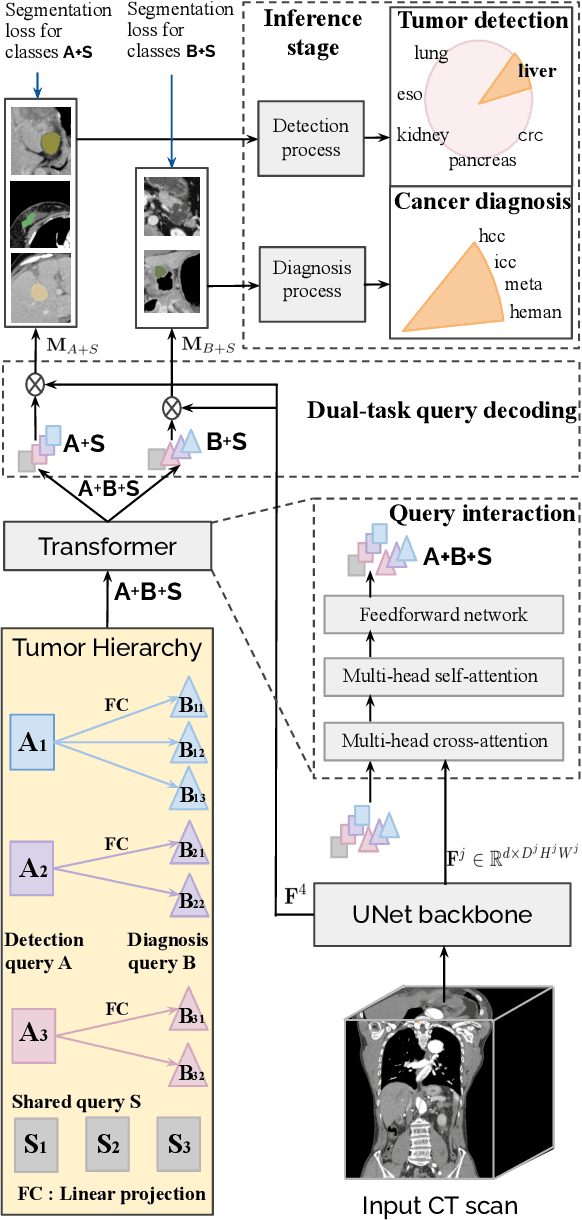
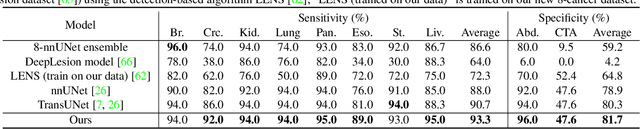
Abstract:Human readers or radiologists routinely perform full-body multi-organ multi-disease detection and diagnosis in clinical practice, while most medical AI systems are built to focus on single organs with a narrow list of a few diseases. This might severely limit AI's clinical adoption. A certain number of AI models need to be assembled non-trivially to match the diagnostic process of a human reading a CT scan. In this paper, we construct a Unified Tumor Transformer (UniT) model to detect (tumor existence and location) and diagnose (tumor characteristics) eight major cancer-prevalent organs in CT scans. UniT is a query-based Mask Transformer model with the output of multi-organ and multi-tumor semantic segmentation. We decouple the object queries into organ queries, detection queries and diagnosis queries, and further establish hierarchical relationships among the three groups. This clinically-inspired architecture effectively assists inter- and intra-organ representation learning of tumors and facilitates the resolution of these complex, anatomically related multi-organ cancer image reading tasks. UniT is trained end-to-end using a curated large-scale CT images of 10,042 patients including eight major types of cancers and occurring non-cancer tumors (all are pathology-confirmed with 3D tumor masks annotated by radiologists). On the test set of 631 patients, UniT has demonstrated strong performance under a set of clinically relevant evaluation metrics, substantially outperforming both multi-organ segmentation methods and an assembly of eight single-organ expert models in tumor detection, segmentation, and diagnosis. Such a unified multi-cancer image reading model (UniT) can significantly reduce the number of false positives produced by combined multi-system models. This moves one step closer towards a universal high-performance cancer screening tool.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge