Xiaoyu Bai
Joint Optimization of Data- and Model-Driven Probing Beams and Beam Predictor
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:Hierarchical search in millimeter-wave (mmWave) communications incurs significant beam training overhead and delay, especially in a dynamic environment. Deep learning-enabled beam prediction is promising to significantly mitigate the overhead and delay, efficiently utilizing the site-specific channel prior. In this work, we propose to jointly optimize a data- and model-driven probe beam module and a cascaded data-driven beam predictor, with limitations in that the probe and communicate beams are restricted within the manifold space of uniform planer array and quantization of the phase modulator. First, The probe beam module senses the mmWave channel with a complex-valued neural network and outputs the counterpart RSRPs of probe beams. Second, the beam predictor estimates the RSRPs in the entire beamspace to minimize the prediction cross entropy and selects the optimal beam with the maximum RSRP value for data transmission. Additionally, we propose to add noise to the phase variables in the probe beam module, against quantization error. Simulation results show the effectiveness of our proposed scheme.
Entropy-based Probing Beam Selection and Beam Prediction via Deep Learning
Jan 03, 2024Abstract:Hierarchical beam search in mmWave communications incurs substantial training overhead, necessitating deep learning-enabled beam predictions to effectively leverage channel priors and mitigate this overhead. In this study, we introduce a comprehensive probabilistic model of power distribution in beamspace, and formulate the joint optimization problem of probing beam selection and probabilistic beam prediction as an entropy minimization problem. Then, we propose a greedy scheme to iteratively and alternately solve this problem, where a transformer-based beam predictor is trained to estimate the conditional power distribution based on the probing beams and user location within each iteration, and the trained predictor selects an unmeasured beam that minimizes the entropy of remaining beams. To further reduce the number of interactions and the computational complexity of the iterative scheme, we propose a two-stage probing beam selection scheme. Firstly, probing beams are selected from a location-specific codebook designed by an entropy-based criterion, and predictions are made with corresponding feedback. Secondly, the optimal beam is identified using additional probing beams with the highest predicted power values. Simulation results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed schemes compared to hierarchical beam search and beam prediction with uniform probing beams.
SAMv2: A Unified Framework for Learning Appearance, Semantic and Cross-Modality Anatomical Embeddings
Nov 28, 2023



Abstract:Identifying anatomical structures (e.g., lesions or landmarks) in medical images plays a fundamental role in medical image analysis. As an exemplar-based landmark detection method, Self-supervised Anatomical eMbedding (SAM) learns a discriminative embedding for each voxel in the image and has shown promising results on various tasks. However, SAM still faces challenges in: (1) differentiating voxels with similar appearance but different semantic meanings (\textit{e.g.}, two adjacent structures without clear borders); (2) matching voxels with similar semantics but markedly different appearance (e.g., the same vessel before and after contrast injection); and (3) cross-modality matching (e.g., CT-MRI registration). To overcome these challenges, we propose SAMv2, which is a unified framework designed to learn appearance, semantic, and cross-modality anatomical embeddings. Specifically, SAMv2 incorporates three key innovations: (1) semantic embedding learning with prototypical contrastive loss; (2) a fixed-point-based matching strategy; and (3) an iterative approach for cross-modality embedding learning. We thoroughly evaluated SAMv2 across three tasks, including one-shot landmark detection, lesion tracking on longitudinal CT scans, and CT-MRI affine/rigid registration with varying field of view. Our results suggest that SAMv2 outperforms SAM and other state-of-the-art methods, offering a robust and versatile approach for landmark based medical image analysis tasks. Code and trained models are available at: https://github.com/alibaba-damo-academy/self-supervised-anatomical-embedding-v2
SAME++: A Self-supervised Anatomical eMbeddings Enhanced medical image registration framework using stable sampling and regularized transformation
Nov 25, 2023Abstract:Image registration is a fundamental medical image analysis task. Ideally, registration should focus on aligning semantically corresponding voxels, i.e., the same anatomical locations. However, existing methods often optimize similarity measures computed directly on intensities or on hand-crafted features, which lack anatomical semantic information. These similarity measures may lead to sub-optimal solutions where large deformations, complex anatomical differences, or cross-modality imagery exist. In this work, we introduce a fast and accurate method for unsupervised 3D medical image registration building on top of a Self-supervised Anatomical eMbedding (SAM) algorithm, which is capable of computing dense anatomical correspondences between two images at the voxel level. We name our approach SAM-Enhanced registration (SAME++), which decomposes image registration into four steps: affine transformation, coarse deformation, deep non-parametric transformation, and instance optimization. Using SAM embeddings, we enhance these steps by finding more coherent correspondence and providing features with better semantic guidance. We extensively evaluated SAME++ using more than 50 labeled organs on three challenging inter-subject registration tasks of different body parts. As a complete registration framework, SAME++ markedly outperforms leading methods by $4.2\%$ - $8.2\%$ in terms of Dice score while being orders of magnitude faster than numerical optimization-based methods. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/alibaba-damo-academy/same}.
Tackling the Incomplete Annotation Issue in Universal Lesion Detection Task By Exploratory Training
Sep 23, 2023Abstract:Universal lesion detection has great value for clinical practice as it aims to detect various types of lesions in multiple organs on medical images. Deep learning methods have shown promising results, but demanding large volumes of annotated data for training. However, annotating medical images is costly and requires specialized knowledge. The diverse forms and contrasts of objects in medical images make fully annotation even more challenging, resulting in incomplete annotations. Directly training ULD detectors on such datasets can yield suboptimal results. Pseudo-label-based methods examine the training data and mine unlabelled objects for retraining, which have shown to be effective to tackle this issue. Presently, top-performing methods rely on a dynamic label-mining mechanism, operating at the mini-batch level. However, the model's performance varies at different iterations, leading to inconsistencies in the quality of the mined labels and limits their performance enhancement. Inspired by the observation that deep models learn concepts with increasing complexity, we introduce an innovative exploratory training to assess the reliability of mined lesions over time. Specifically, we introduce a teacher-student detection model as basis, where the teacher's predictions are combined with incomplete annotations to train the student. Additionally, we design a prediction bank to record high-confidence predictions. Each sample is trained several times, allowing us to get a sequence of records for each sample. If a prediction consistently appears in the record sequence, it is likely to be a true object, otherwise it may just a noise. This serves as a crucial criterion for selecting reliable mined lesions for retraining. Our experimental results substantiate that the proposed framework surpasses state-of-the-art methods on two medical image datasets, demonstrating its superior performance.
SLPT: Selective Labeling Meets Prompt Tuning on Label-Limited Lesion Segmentation
Aug 09, 2023


Abstract:Medical image analysis using deep learning is often challenged by limited labeled data and high annotation costs. Fine-tuning the entire network in label-limited scenarios can lead to overfitting and suboptimal performance. Recently, prompt tuning has emerged as a more promising technique that introduces a few additional tunable parameters as prompts to a task-agnostic pre-trained model, and updates only these parameters using supervision from limited labeled data while keeping the pre-trained model unchanged. However, previous work has overlooked the importance of selective labeling in downstream tasks, which aims to select the most valuable downstream samples for annotation to achieve the best performance with minimum annotation cost. To address this, we propose a framework that combines selective labeling with prompt tuning (SLPT) to boost performance in limited labels. Specifically, we introduce a feature-aware prompt updater to guide prompt tuning and a TandEm Selective LAbeling (TESLA) strategy. TESLA includes unsupervised diversity selection and supervised selection using prompt-based uncertainty. In addition, we propose a diversified visual prompt tuning strategy to provide multi-prompt-based discrepant predictions for TESLA. We evaluate our method on liver tumor segmentation and achieve state-of-the-art performance, outperforming traditional fine-tuning with only 6% of tunable parameters, also achieving 94% of full-data performance by labeling only 5% of the data.
SAMConvex: Fast Discrete Optimization for CT Registration using Self-supervised Anatomical Embedding and Correlation Pyramid
Jul 19, 2023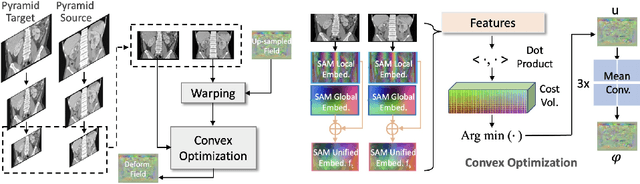
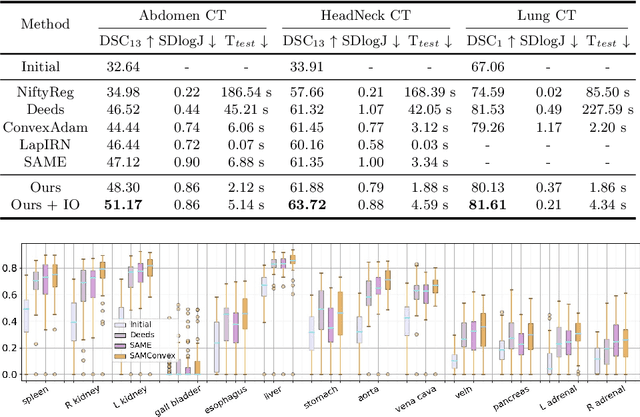
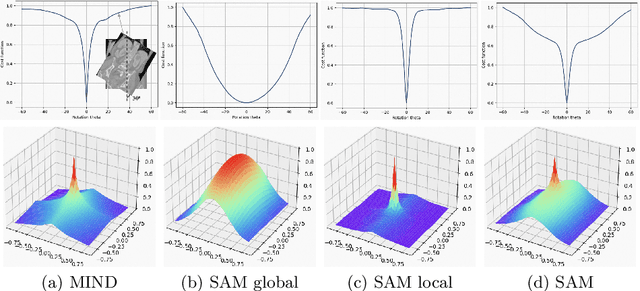
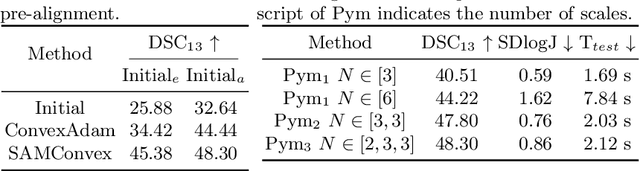
Abstract:Estimating displacement vector field via a cost volume computed in the feature space has shown great success in image registration, but it suffers excessive computation burdens. Moreover, existing feature descriptors only extract local features incapable of representing the global semantic information, which is especially important for solving large transformations. To address the discussed issues, we propose SAMConvex, a fast coarse-to-fine discrete optimization method for CT registration that includes a decoupled convex optimization procedure to obtain deformation fields based on a self-supervised anatomical embedding (SAM) feature extractor that captures both local and global information. To be specific, SAMConvex extracts per-voxel features and builds 6D correlation volumes based on SAM features, and iteratively updates a flow field by performing lookups on the correlation volumes with a coarse-to-fine scheme. SAMConvex outperforms the state-of-the-art learning-based methods and optimization-based methods over two inter-patient registration datasets (Abdomen CT and HeadNeck CT) and one intra-patient registration dataset (Lung CT). Moreover, as an optimization-based method, SAMConvex only takes $\sim2$s ($\sim5s$ with instance optimization) for one paired images.
Liver Tumor Screening and Diagnosis in CT with Pixel-Lesion-Patient Network
Jul 17, 2023Abstract:Liver tumor segmentation and classification are important tasks in computer aided diagnosis. We aim to address three problems: liver tumor screening and preliminary diagnosis in non-contrast computed tomography (CT), and differential diagnosis in dynamic contrast-enhanced CT. A novel framework named Pixel-Lesion-pAtient Network (PLAN) is proposed. It uses a mask transformer to jointly segment and classify each lesion with improved anchor queries and a foreground-enhanced sampling loss. It also has an image-wise classifier to effectively aggregate global information and predict patient-level diagnosis. A large-scale multi-phase dataset is collected containing 939 tumor patients and 810 normal subjects. 4010 tumor instances of eight types are extensively annotated. On the non-contrast tumor screening task, PLAN achieves 95% and 96% in patient-level sensitivity and specificity. On contrast-enhanced CT, our lesion-level detection precision, recall, and classification accuracy are 92%, 89%, and 86%, outperforming widely used CNN and transformers for lesion segmentation. We also conduct a reader study on a holdout set of 250 cases. PLAN is on par with a senior human radiologist, showing the clinical significance of our results.
Matching in the Wild: Learning Anatomical Embeddings for Multi-Modality Images
Jul 07, 2023



Abstract:Radiotherapists require accurate registration of MR/CT images to effectively use information from both modalities. In a typical registration pipeline, rigid or affine transformations are applied to roughly align the fixed and moving images before proceeding with the deformation step. While recent learning-based methods have shown promising results in the rigid/affine step, these methods often require images with similar field-of-view (FOV) for successful alignment. As a result, aligning images with different FOVs remains a challenging task. Self-supervised landmark detection methods like self-supervised Anatomical eMbedding (SAM) have emerged as a useful tool for mapping and cropping images to similar FOVs. However, these methods are currently limited to intra-modality use only. To address this limitation and enable cross-modality matching, we propose a new approach called Cross-SAM. Our approach utilizes a novel iterative process that alternates between embedding learning and CT-MRI registration. We start by applying aggressive contrast augmentation on both CT and MRI images to train a SAM model. We then use this SAM to identify corresponding regions on paired images using robust grid-points matching, followed by a point-set based affine/rigid registration, and a deformable fine-tuning step to produce registered paired images. We use these registered pairs to enhance the matching ability of SAM, which is then processed iteratively. We use the final model for cross-modality matching tasks. We evaluated our approach on two CT-MRI affine registration datasets and found that Cross-SAM achieved robust affine registration on both datasets, significantly outperforming other methods and achieving state-of-the-art performance.
SAM++: Enhancing Anatomic Matching using Semantic Information and Structural Inference
Jun 24, 2023



Abstract:Medical images like CT and MRI provide detailed information about the internal structure of the body, and identifying key anatomical structures from these images plays a crucial role in clinical workflows. Current methods treat it as a registration or key-point regression task, which has limitations in accurate matching and can only handle predefined landmarks. Recently, some methods have been introduced to address these limitations. One such method, called SAM, proposes using a dense self-supervised approach to learn a distinct embedding for each point on the CT image and achieving promising results. Nonetheless, SAM may still face difficulties when dealing with structures that have similar appearances but different semantic meanings or similar semantic meanings but different appearances. To overcome these limitations, we propose SAM++, a framework that simultaneously learns appearance and semantic embeddings with a novel fixed-points matching mechanism. We tested the SAM++ framework on two challenging tasks, demonstrating a significant improvement over the performance of SAM and outperforming other existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge