Hong Lu
Few-Shot Neuro-Symbolic Imitation Learning for Long-Horizon Planning and Acting
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:Imitation learning enables intelligent systems to acquire complex behaviors with minimal supervision. However, existing methods often focus on short-horizon skills, require large datasets, and struggle to solve long-horizon tasks or generalize across task variations and distribution shifts. We propose a novel neuro-symbolic framework that jointly learns continuous control policies and symbolic domain abstractions from a few skill demonstrations. Our method abstracts high-level task structures into a graph, discovers symbolic rules via an Answer Set Programming solver, and trains low-level controllers using diffusion policy imitation learning. A high-level oracle filters task-relevant information to focus each controller on a minimal observation and action space. Our graph-based neuro-symbolic framework enables capturing complex state transitions, including non-spatial and temporal relations, that data-driven learning or clustering techniques often fail to discover in limited demonstration datasets. We validate our approach in six domains that involve four robotic arms, Stacking, Kitchen, Assembly, and Towers of Hanoi environments, and a distinct Automated Forklift domain with two environments. The results demonstrate high data efficiency with as few as five skill demonstrations, strong zero- and few-shot generalizations, and interpretable decision making.
QuestA: Expanding Reasoning Capacity in LLMs via Question Augmentation
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has become a key component in training large language reasoning models (LLMs). However, recent studies questions its effectiveness in improving multi-step reasoning-particularly on hard problems. To address this challenge, we propose a simple yet effective strategy via Question Augmentation: introduce partial solutions during training to reduce problem difficulty and provide more informative learning signals. Our method, QuestA, when applied during RL training on math reasoning tasks, not only improves pass@1 but also pass@k-particularly on problems where standard RL struggles to make progress. This enables continual improvement over strong open-source models such as DeepScaleR and OpenMath Nemotron, further enhancing their reasoning capabilities. We achieve new state-of-the-art results on math benchmarks using 1.5B-parameter models: 67.1% (+5.3%) on AIME24, 59.5% (+10.0%) on AIME25, and 35.5% (+4.0%) on HMMT25. Further, we provide theoretical explanations that QuestA improves sample efficiency, offering a practical and generalizable pathway for expanding reasoning capability through RL.
Curiosity-Driven Imagination: Discovering Plan Operators and Learning Associated Policies for Open-World Adaptation
Mar 06, 2025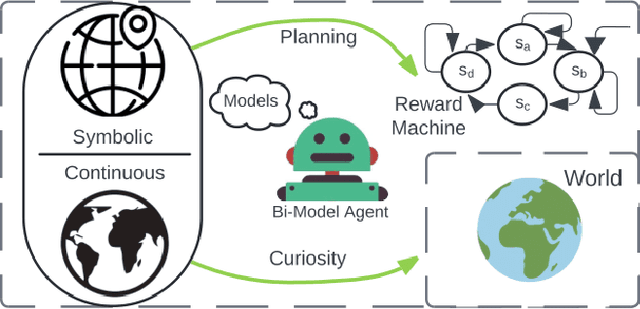
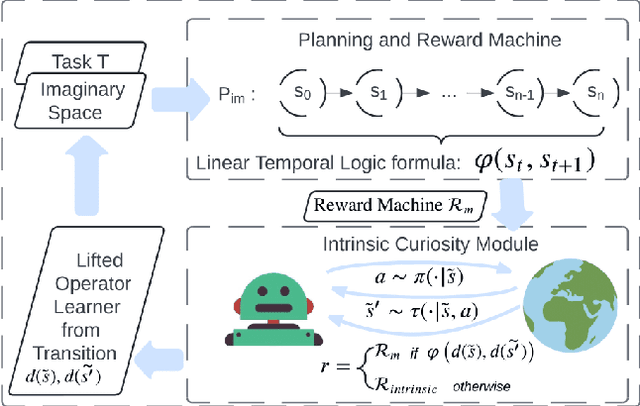
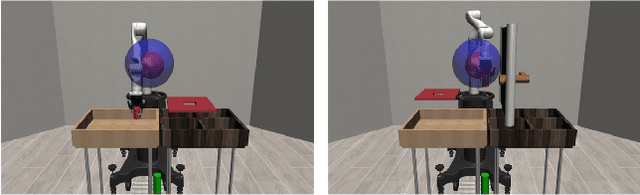
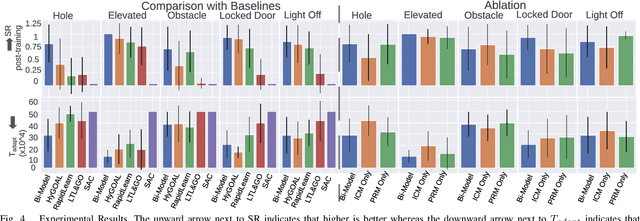
Abstract:Adapting quickly to dynamic, uncertain environments-often called "open worlds"-remains a major challenge in robotics. Traditional Task and Motion Planning (TAMP) approaches struggle to cope with unforeseen changes, are data-inefficient when adapting, and do not leverage world models during learning. We address this issue with a hybrid planning and learning system that integrates two models: a low level neural network based model that learns stochastic transitions and drives exploration via an Intrinsic Curiosity Module (ICM), and a high level symbolic planning model that captures abstract transitions using operators, enabling the agent to plan in an "imaginary" space and generate reward machines. Our evaluation in a robotic manipulation domain with sequential novelty injections demonstrates that our approach converges faster and outperforms state-of-the-art hybrid methods.
ClipGrader: Leveraging Vision-Language Models for Robust Label Quality Assessment in Object Detection
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:High-quality annotations are essential for object detection models, but ensuring label accuracy - especially for bounding boxes - remains both challenging and costly. This paper introduces ClipGrader, a novel approach that leverages vision-language models to automatically assess the accuracy of bounding box annotations. By adapting CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training) to evaluate both class label correctness and spatial precision of bounding box, ClipGrader offers an effective solution for grading object detection labels. Tested on modified object detection datasets with artificially disturbed bounding boxes, ClipGrader achieves 91% accuracy on COCO with a 1.8% false positive rate. Moreover, it maintains 87% accuracy with a 2.1% false positive rate when trained on just 10% of the COCO data. ClipGrader also scales effectively to larger datasets such as LVIS, achieving 79% accuracy across 1,203 classes. Our experiments demonstrate ClipGrader's ability to identify errors in existing COCO annotations, highlighting its potential for dataset refinement. When integrated into a semi-supervised object detection (SSOD) model, ClipGrader readily improves the pseudo label quality, helping achieve higher mAP (mean Average Precision) throughout the training process. ClipGrader thus provides a scalable AI-assisted tool for enhancing annotation quality control and verifying annotations in large-scale object detection datasets.
Probing a Vision-Language-Action Model for Symbolic States and Integration into a Cognitive Architecture
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:Vision-language-action (VLA) models hold promise as generalist robotics solutions by translating visual and linguistic inputs into robot actions, yet they lack reliability due to their black-box nature and sensitivity to environmental changes. In contrast, cognitive architectures (CA) excel in symbolic reasoning and state monitoring but are constrained by rigid predefined execution. This work bridges these approaches by probing OpenVLA's hidden layers to uncover symbolic representations of object properties, relations, and action states, enabling integration with a CA for enhanced interpretability and robustness. Through experiments on LIBERO-spatial pick-and-place tasks, we analyze the encoding of symbolic states across different layers of OpenVLA's Llama backbone. Our probing results show consistently high accuracies (> 0.90) for both object and action states across most layers, though contrary to our hypotheses, we did not observe the expected pattern of object states being encoded earlier than action states. We demonstrate an integrated DIARC-OpenVLA system that leverages these symbolic representations for real-time state monitoring, laying the foundation for more interpretable and reliable robotic manipulation.
Few-shot In-Context Preference Learning Using Large Language Models
Oct 22, 2024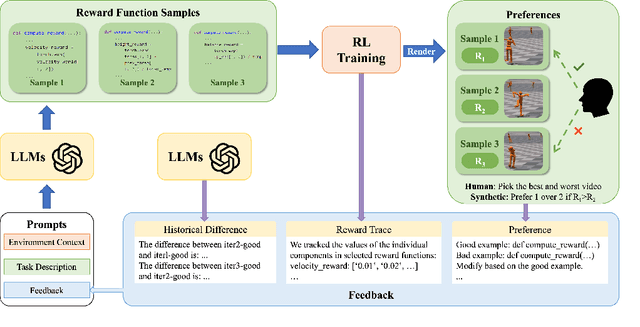

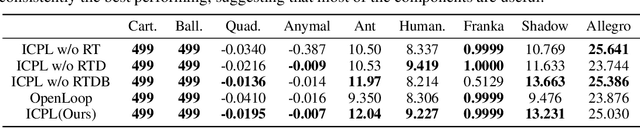
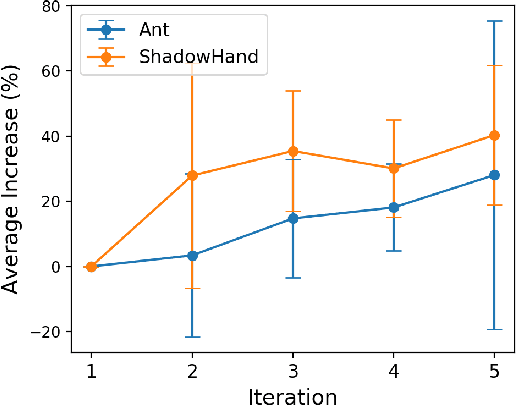
Abstract:Designing reward functions is a core component of reinforcement learning but can be challenging for truly complex behavior. Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) has been used to alleviate this challenge by replacing a hand-coded reward function with a reward function learned from preferences. However, it can be exceedingly inefficient to learn these rewards as they are often learned tabula rasa. We investigate whether Large Language Models (LLMs) can reduce this query inefficiency by converting an iterative series of human preferences into code representing the rewards. We propose In-Context Preference Learning (ICPL), a method that uses the grounding of an LLM to accelerate learning reward functions from preferences. ICPL takes the environment context and task description, synthesizes a set of reward functions, and then repeatedly updates the reward functions using human rankings of videos of the resultant policies. Using synthetic preferences, we demonstrate that ICPL is orders of magnitude more efficient than RLHF and is even competitive with methods that use ground-truth reward functions instead of preferences. Finally, we perform a series of human preference-learning trials and observe that ICPL extends beyond synthetic settings and can work effectively with humans-in-the-loop. Additional information and videos are provided at https://sites.google.com/view/few-shot-icpl/home.
General Compression Framework for Efficient Transformer Object Tracking
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Transformer-based trackers have established a dominant role in the field of visual object tracking. While these trackers exhibit promising performance, their deployment on resource-constrained devices remains challenging due to inefficiencies. To improve the inference efficiency and reduce the computation cost, prior approaches have aimed to either design lightweight trackers or distill knowledge from larger teacher models into more compact student trackers. However, these solutions often sacrifice accuracy for speed. Thus, we propose a general model compression framework for efficient transformer object tracking, named CompressTracker, to reduce the size of a pre-trained tracking model into a lightweight tracker with minimal performance degradation. Our approach features a novel stage division strategy that segments the transformer layers of the teacher model into distinct stages, enabling the student model to emulate each corresponding teacher stage more effectively. Additionally, we also design a unique replacement training technique that involves randomly substituting specific stages in the student model with those from the teacher model, as opposed to training the student model in isolation. Replacement training enhances the student model's ability to replicate the teacher model's behavior. To further forcing student model to emulate teacher model, we incorporate prediction guidance and stage-wise feature mimicking to provide additional supervision during the teacher model's compression process. Our framework CompressTracker is structurally agnostic, making it compatible with any transformer architecture. We conduct a series of experiment to verify the effectiveness and generalizability of CompressTracker. Our CompressTracker-4 with 4 transformer layers, which is compressed from OSTrack, retains about 96% performance on LaSOT (66.1% AUC) while achieves 2.17x speed up.
GlobalMapNet: An Online Framework for Vectorized Global HD Map Construction
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:High-definition (HD) maps are essential for autonomous driving systems. Traditionally, an expensive and labor-intensive pipeline is implemented to construct HD maps, which is limited in scalability. In recent years, crowdsourcing and online mapping have emerged as two alternative methods, but they have limitations respectively. In this paper, we provide a novel methodology, namely global map construction, to perform direct generation of vectorized global maps, combining the benefits of crowdsourcing and online mapping. We introduce GlobalMapNet, the first online framework for vectorized global HD map construction, which updates and utilizes a global map on the ego vehicle. To generate the global map from scratch, we propose GlobalMapBuilder to match and merge local maps continuously. We design a new algorithm, Map NMS, to remove duplicate map elements and produce a clean map. We also propose GlobalMapFusion to aggregate historical map information, improving consistency of prediction. We examine GlobalMapNet on two widely recognized datasets, Argoverse2 and nuScenes, showing that our framework is capable of generating globally consistent results.
Combining Cognitive and Generative AI for Self-explanation in Interactive AI Agents
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:The Virtual Experimental Research Assistant (VERA) is an inquiry-based learning environment that empowers a learner to build conceptual models of complex ecological systems and experiment with agent-based simulations of the models. This study investigates the convergence of cognitive AI and generative AI for self-explanation in interactive AI agents such as VERA. From a cognitive AI viewpoint, we endow VERA with a functional model of its own design, knowledge, and reasoning represented in the Task--Method--Knowledge (TMK) language. From the perspective of generative AI, we use ChatGPT, LangChain, and Chain-of-Thought to answer user questions based on the VERA TMK model. Thus, we combine cognitive and generative AI to generate explanations about how VERA works and produces its answers. The preliminary evaluation of the generation of explanations in VERA on a bank of 66 questions derived from earlier work appears promising.
Harnessing Joint Rain-/Detail-aware Representations to Eliminate Intricate Rains
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in image deraining have focused on training powerful models on mixed multiple datasets comprising diverse rain types and backgrounds. However, this approach tends to overlook the inherent differences among rainy images, leading to suboptimal results. To overcome this limitation, we focus on addressing various rainy images by delving into meaningful representations that encapsulate both the rain and background components. Leveraging these representations as instructive guidance, we put forth a Context-based Instance-level Modulation (CoI-M) mechanism adept at efficiently modulating CNN- or Transformer-based models. Furthermore, we devise a rain-/detail-aware contrastive learning strategy to help extract joint rain-/detail-aware representations. By integrating CoI-M with the rain-/detail-aware Contrastive learning, we develop CoIC, an innovative and potent algorithm tailored for training models on mixed datasets. Moreover, CoIC offers insight into modeling relationships of datasets, quantitatively assessing the impact of rain and details on restoration, and unveiling distinct behaviors of models given diverse inputs. Extensive experiments validate the efficacy of CoIC in boosting the deraining ability of CNN and Transformer models. CoIC also enhances the deraining prowess remarkably when real-world dataset is included.
* 21 pages, 14 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge