Curiosity-Driven Imagination: Discovering Plan Operators and Learning Associated Policies for Open-World Adaptation
Paper and Code
Mar 06, 2025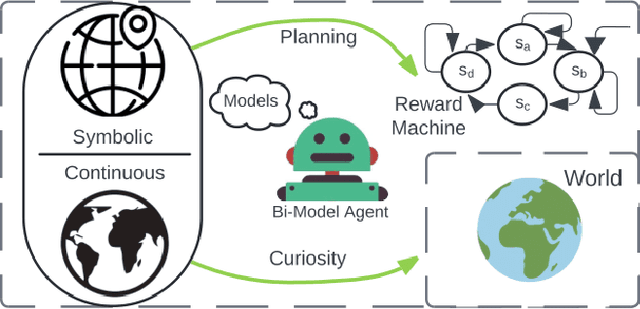
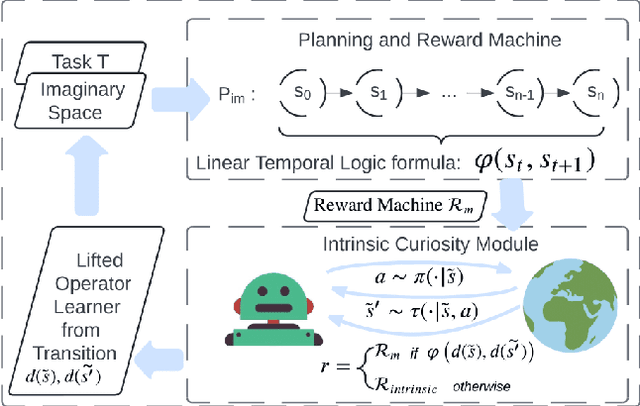
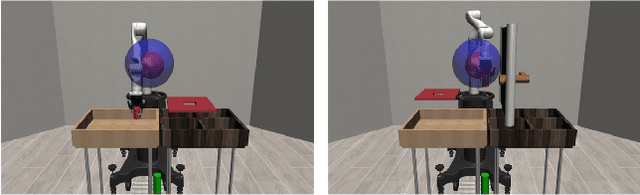
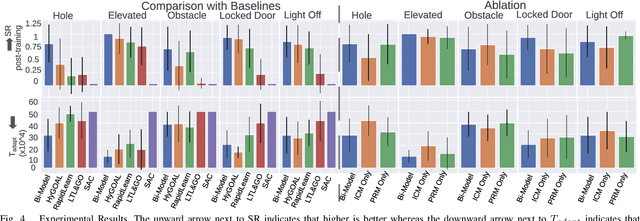
Adapting quickly to dynamic, uncertain environments-often called "open worlds"-remains a major challenge in robotics. Traditional Task and Motion Planning (TAMP) approaches struggle to cope with unforeseen changes, are data-inefficient when adapting, and do not leverage world models during learning. We address this issue with a hybrid planning and learning system that integrates two models: a low level neural network based model that learns stochastic transitions and drives exploration via an Intrinsic Curiosity Module (ICM), and a high level symbolic planning model that captures abstract transitions using operators, enabling the agent to plan in an "imaginary" space and generate reward machines. Our evaluation in a robotic manipulation domain with sequential novelty injections demonstrates that our approach converges faster and outperforms state-of-the-art hybrid methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge