Matthias Scheutz
Tufts University
Where Norms and References Collide: Evaluating LLMs on Normative Reasoning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Embodied agents, such as robots, will need to interact in situated environments where successful communication often depends on reasoning over social norms: shared expectations that constrain what actions are appropriate in context. A key capability in such settings is norm-based reference resolution (NBRR), where interpreting referential expressions requires inferring implicit normative expectations grounded in physical and social context. Yet it remains unclear whether Large Language Models (LLMs) can support this kind of reasoning. In this work, we introduce SNIC (Situated Norms in Context), a human-validated diagnostic testbed designed to probe how well state-of-the-art LLMs can extract and utilize normative principles relevant to NBRR. SNIC emphasizes physically grounded norms that arise in everyday tasks such as cleaning, tidying, and serving. Across a range of controlled evaluations, we find that even the strongest LLMs struggle to consistently identify and apply social norms, particularly when norms are implicit, underspecified, or in conflict. These findings reveal a blind spot in current LLMs and highlight a key challenge for deploying language-based systems in socially situated, embodied settings.
Achieving Safe Control Online through Integration of Harmonic Control Lyapunov-Barrier Functions with Unsafe Object-Centric Action Policies
Nov 18, 2025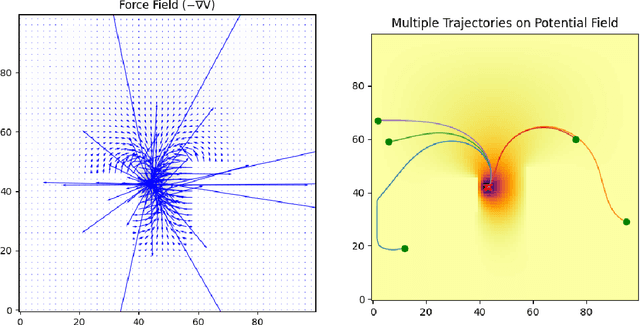
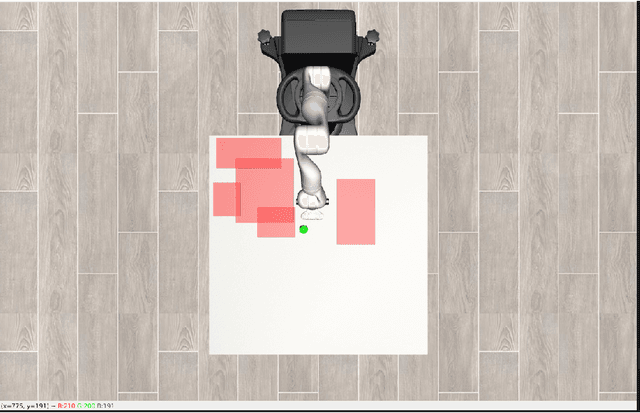
Abstract:We propose a method for combining Harmonic Control Lyapunov-Barrier Functions (HCLBFs) derived from Signal Temporal Logic (STL) specifications with any given robot policy to turn an unsafe policy into a safe one with formal guarantees. The two components are combined via HCLBF-derived safety certificates, thus producing commands that preserve both safety and task-driven behavior. We demonstrate with a simple proof-of-concept implementation for an object-centric force-based policy trained through reinforcement learning for a movement task of a stationary robot arm that is able to avoid colliding with obstacles on a table top after combining the policy with the safety constraints. The proposed method can be generalized to more complex specifications and dynamic task settings.
* In Proceedings FMAS 2025, arXiv:2511.13245
IntelliProof: An Argumentation Network-based Conversational Helper for Organized Reflection
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:We present IntelliProof, an interactive system for analyzing argumentative essays through LLMs. IntelliProof structures an essay as an argumentation graph, where claims are represented as nodes, supporting evidence is attached as node properties, and edges encode supporting or attacking relations. Unlike existing automated essay scoring systems, IntelliProof emphasizes the user experience: each relation is initially classified and scored by an LLM, then visualized for enhanced understanding. The system provides justifications for classifications and produces quantitative measures for essay coherence. It enables rapid exploration of argumentative quality while retaining human oversight. In addition, IntelliProof provides a set of tools for a better understanding of an argumentative essay and its corresponding graph in natural language, bridging the gap between the structural semantics of argumentative essays and the user's understanding of a given text. A live demo and the system are available here to try: \textbf{https://intelliproof.vercel.app}
Few-Shot Neuro-Symbolic Imitation Learning for Long-Horizon Planning and Acting
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:Imitation learning enables intelligent systems to acquire complex behaviors with minimal supervision. However, existing methods often focus on short-horizon skills, require large datasets, and struggle to solve long-horizon tasks or generalize across task variations and distribution shifts. We propose a novel neuro-symbolic framework that jointly learns continuous control policies and symbolic domain abstractions from a few skill demonstrations. Our method abstracts high-level task structures into a graph, discovers symbolic rules via an Answer Set Programming solver, and trains low-level controllers using diffusion policy imitation learning. A high-level oracle filters task-relevant information to focus each controller on a minimal observation and action space. Our graph-based neuro-symbolic framework enables capturing complex state transitions, including non-spatial and temporal relations, that data-driven learning or clustering techniques often fail to discover in limited demonstration datasets. We validate our approach in six domains that involve four robotic arms, Stacking, Kitchen, Assembly, and Towers of Hanoi environments, and a distinct Automated Forklift domain with two environments. The results demonstrate high data efficiency with as few as five skill demonstrations, strong zero- and few-shot generalizations, and interpretable decision making.
Incremental Language Understanding for Online Motion Planning of Robot Manipulators
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Human-robot interaction requires robots to process language incrementally, adapting their actions in real-time based on evolving speech input. Existing approaches to language-guided robot motion planning typically assume fully specified instructions, resulting in inefficient stop-and-replan behavior when corrections or clarifications occur. In this paper, we introduce a novel reasoning-based incremental parser which integrates an online motion planning algorithm within the cognitive architecture. Our approach enables continuous adaptation to dynamic linguistic input, allowing robots to update motion plans without restarting execution. The incremental parser maintains multiple candidate parses, leveraging reasoning mechanisms to resolve ambiguities and revise interpretations when needed. By combining symbolic reasoning with online motion planning, our system achieves greater flexibility in handling speech corrections and dynamically changing constraints. We evaluate our framework in real-world human-robot interaction scenarios, demonstrating online adaptions of goal poses, constraints, or task objectives. Our results highlight the advantages of integrating incremental language understanding with real-time motion planning for natural and fluid human-robot collaboration. The experiments are demonstrated in the accompanying video at www.acin.tuwien.ac.at/42d5.
FLEX: A Framework for Learning Robot-Agnostic Force-based Skills Involving Sustained Contact Object Manipulation
Mar 17, 2025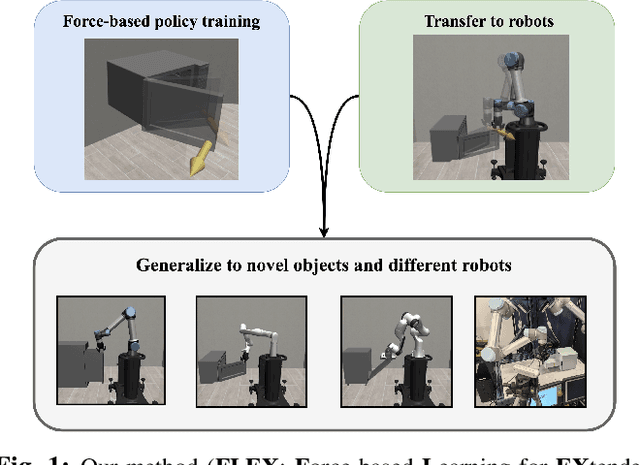
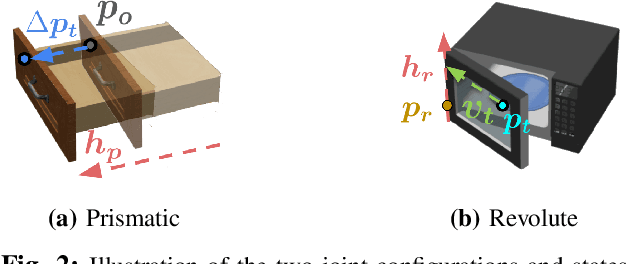
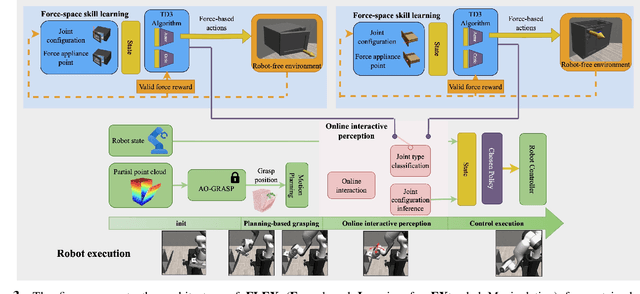
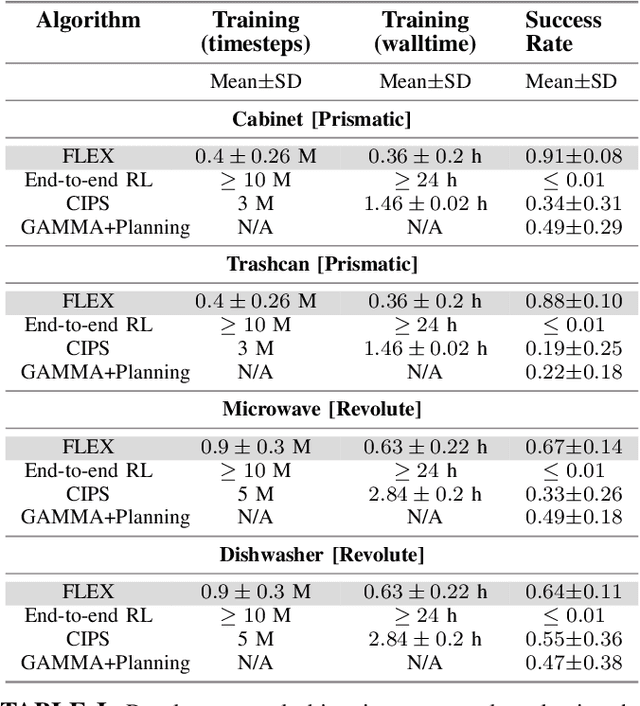
Abstract:Learning to manipulate objects efficiently, particularly those involving sustained contact (e.g., pushing, sliding) and articulated parts (e.g., drawers, doors), presents significant challenges. Traditional methods, such as robot-centric reinforcement learning (RL), imitation learning, and hybrid techniques, require massive training and often struggle to generalize across different objects and robot platforms. We propose a novel framework for learning object-centric manipulation policies in force space, decoupling the robot from the object. By directly applying forces to selected regions of the object, our method simplifies the action space, reduces unnecessary exploration, and decreases simulation overhead. This approach, trained in simulation on a small set of representative objects, captures object dynamics -- such as joint configurations -- allowing policies to generalize effectively to new, unseen objects. Decoupling these policies from robot-specific dynamics enables direct transfer to different robotic platforms (e.g., Kinova, Panda, UR5) without retraining. Our evaluations demonstrate that the method significantly outperforms baselines, achieving over an order of magnitude improvement in training efficiency compared to other state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, operating in force space enhances policy transferability across diverse robot platforms and object types. We further showcase the applicability of our method in a real-world robotic setting. For supplementary materials and videos, please visit: https://tufts-ai-robotics-group.github.io/FLEX/
Curiosity-Driven Imagination: Discovering Plan Operators and Learning Associated Policies for Open-World Adaptation
Mar 06, 2025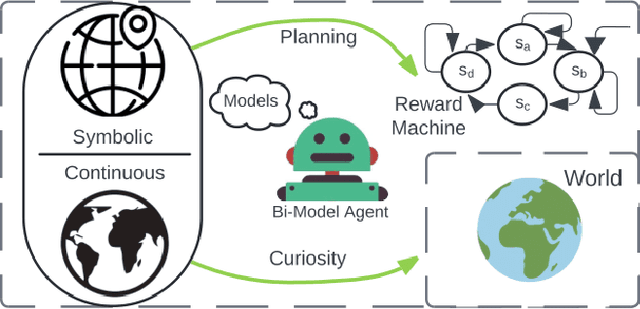
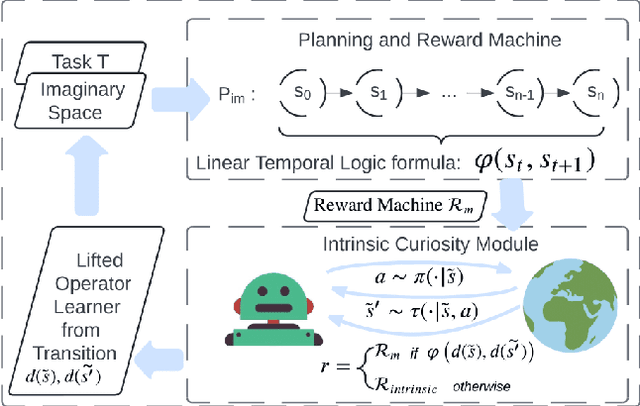
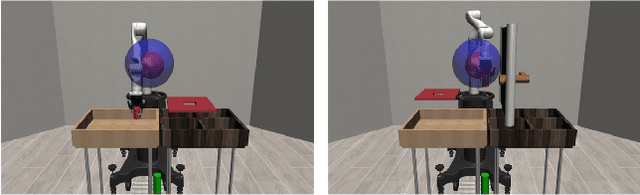
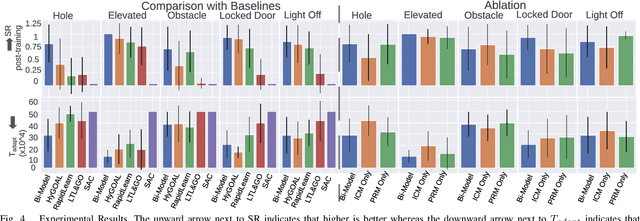
Abstract:Adapting quickly to dynamic, uncertain environments-often called "open worlds"-remains a major challenge in robotics. Traditional Task and Motion Planning (TAMP) approaches struggle to cope with unforeseen changes, are data-inefficient when adapting, and do not leverage world models during learning. We address this issue with a hybrid planning and learning system that integrates two models: a low level neural network based model that learns stochastic transitions and drives exploration via an Intrinsic Curiosity Module (ICM), and a high level symbolic planning model that captures abstract transitions using operators, enabling the agent to plan in an "imaginary" space and generate reward machines. Our evaluation in a robotic manipulation domain with sequential novelty injections demonstrates that our approach converges faster and outperforms state-of-the-art hybrid methods.
Probing a Vision-Language-Action Model for Symbolic States and Integration into a Cognitive Architecture
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:Vision-language-action (VLA) models hold promise as generalist robotics solutions by translating visual and linguistic inputs into robot actions, yet they lack reliability due to their black-box nature and sensitivity to environmental changes. In contrast, cognitive architectures (CA) excel in symbolic reasoning and state monitoring but are constrained by rigid predefined execution. This work bridges these approaches by probing OpenVLA's hidden layers to uncover symbolic representations of object properties, relations, and action states, enabling integration with a CA for enhanced interpretability and robustness. Through experiments on LIBERO-spatial pick-and-place tasks, we analyze the encoding of symbolic states across different layers of OpenVLA's Llama backbone. Our probing results show consistently high accuracies (> 0.90) for both object and action states across most layers, though contrary to our hypotheses, we did not observe the expected pattern of object states being encoded earlier than action states. We demonstrate an integrated DIARC-OpenVLA system that leverages these symbolic representations for real-time state monitoring, laying the foundation for more interpretable and reliable robotic manipulation.
NovelGym: A Flexible Ecosystem for Hybrid Planning and Learning Agents Designed for Open Worlds
Jan 07, 2024



Abstract:As AI agents leave the lab and venture into the real world as autonomous vehicles, delivery robots, and cooking robots, it is increasingly necessary to design and comprehensively evaluate algorithms that tackle the ``open-world''. To this end, we introduce NovelGym, a flexible and adaptable ecosystem designed to simulate gridworld environments, serving as a robust platform for benchmarking reinforcement learning (RL) and hybrid planning and learning agents in open-world contexts. The modular architecture of NovelGym facilitates rapid creation and modification of task environments, including multi-agent scenarios, with multiple environment transformations, thus providing a dynamic testbed for researchers to develop open-world AI agents.
A principled approach to model validation in domain generalization
Apr 02, 2023Abstract:Domain generalization aims to learn a model with good generalization ability, that is, the learned model should not only perform well on several seen domains but also on unseen domains with different data distributions. State-of-the-art domain generalization methods typically train a representation function followed by a classifier jointly to minimize both the classification risk and the domain discrepancy. However, when it comes to model selection, most of these methods rely on traditional validation routines that select models solely based on the lowest classification risk on the validation set. In this paper, we theoretically demonstrate a trade-off between minimizing classification risk and mitigating domain discrepancy, i.e., it is impossible to achieve the minimum of these two objectives simultaneously. Motivated by this theoretical result, we propose a novel model selection method suggesting that the validation process should account for both the classification risk and the domain discrepancy. We validate the effectiveness of the proposed method by numerical results on several domain generalization datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge