NovelCraft: A Dataset for Novelty Detection and Discovery in Open Worlds
Paper and Code
Jun 23, 2022
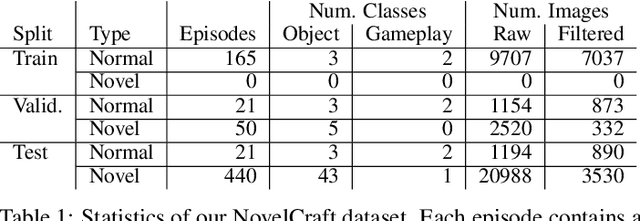
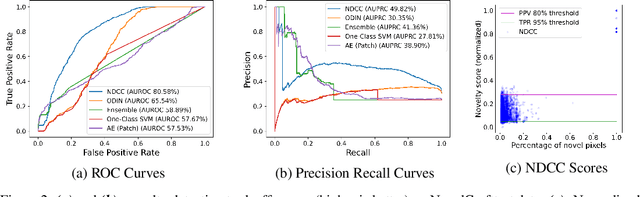
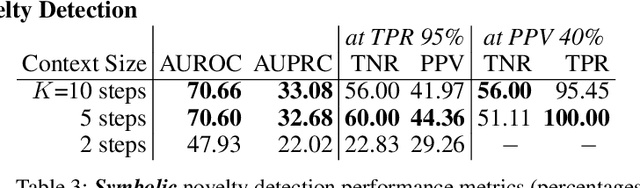
In order for artificial agents to perform useful tasks in changing environments, they must be able to both detect and adapt to novelty. However, visual novelty detection research often only evaluates on repurposed datasets such as CIFAR-10 originally intended for object classification. This practice restricts novelties to well-framed images of distinct object types. We suggest that new benchmarks are needed to represent the challenges of navigating an open world. Our new NovelCraft dataset contains multi-modal episodic data of the images and symbolic world-states seen by an agent completing a pogo-stick assembly task within a video game world. In some episodes, we insert novel objects that can impact gameplay. Novelty can vary in size, position, and occlusion within complex scenes. We benchmark state-of-the-art novelty detection and generalized category discovery models with a focus on comprehensive evaluation. Results suggest an opportunity for future research: models aware of task-specific costs of different types of mistakes could more effectively detect and adapt to novelty in open worlds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge