Tung Thai
Methods and Mechanisms for Interactive Novelty Handling in Adversarial Environments
Mar 06, 2023
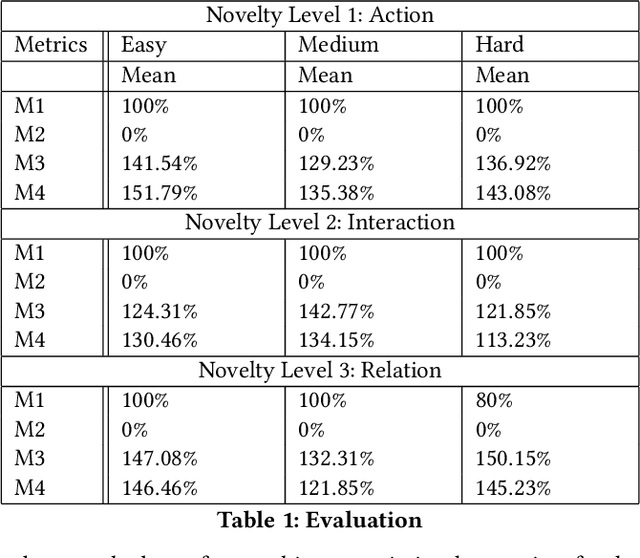
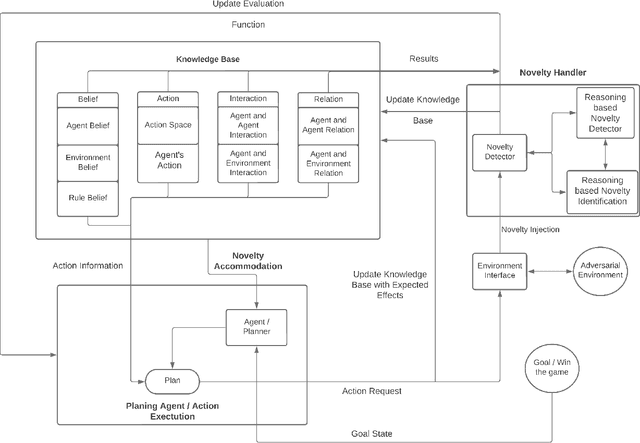
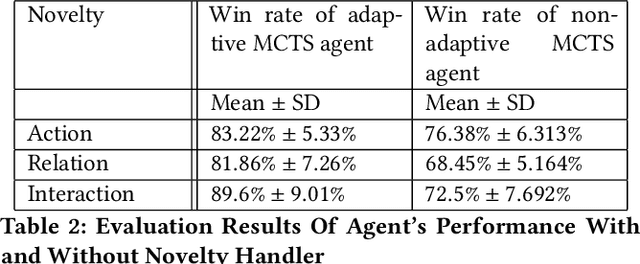
Abstract:Learning to detect, characterize and accommodate novelties is a challenge that agents operating in open-world domains need to address to be able to guarantee satisfactory task performance. Certain novelties (e.g., changes in environment dynamics) can interfere with the performance or prevent agents from accomplishing task goals altogether. In this paper, we introduce general methods and architectural mechanisms for detecting and characterizing different types of novelties, and for building an appropriate adaptive model to accommodate them utilizing logical representations and reasoning methods. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods in evaluations performed by a third party in the adversarial multi-agent board game Monopoly. The results show high novelty detection and accommodation rates across a variety of novelty types, including changes to the rules of the game, as well as changes to the agent's action capabilities.
Integrating Planning, Execution and Monitoring in the presence of Open World Novelties: Case Study of an Open World Monopoly Solver
Aug 09, 2021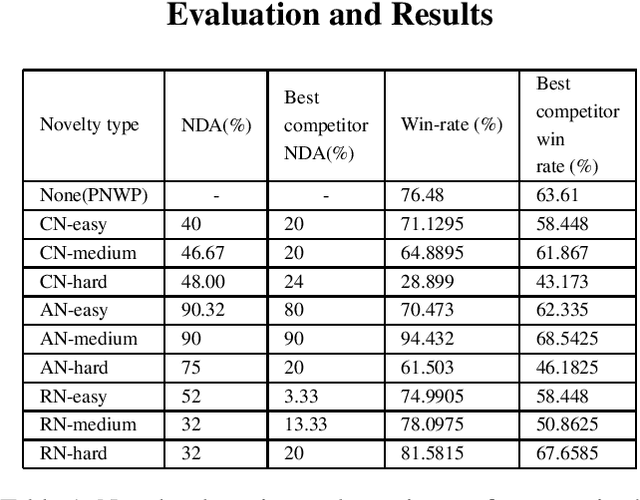
Abstract:The game of monopoly is an adversarial multi-agent domain where there is no fixed goal other than to be the last player solvent, There are useful subgoals like monopolizing sets of properties, and developing them. There is also a lot of randomness from dice rolls, card-draws, and adversaries' strategies. This unpredictability is made worse when unknown novelties are added during gameplay. Given these challenges, Monopoly was one of the test beds chosen for the DARPA-SAILON program which aims to create agents that can detect and accommodate novelties. To handle the game complexities, we developed an agent that eschews complete plans, and adapts it's policy online as the game evolves. In the most recent independent evaluation in the SAILON program, our agent was the best performing agent on most measures. We herein present our approach and results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge