Shijie Fang
CHARM: Considering Human Attributes for Reinforcement Modeling
Jun 16, 2025
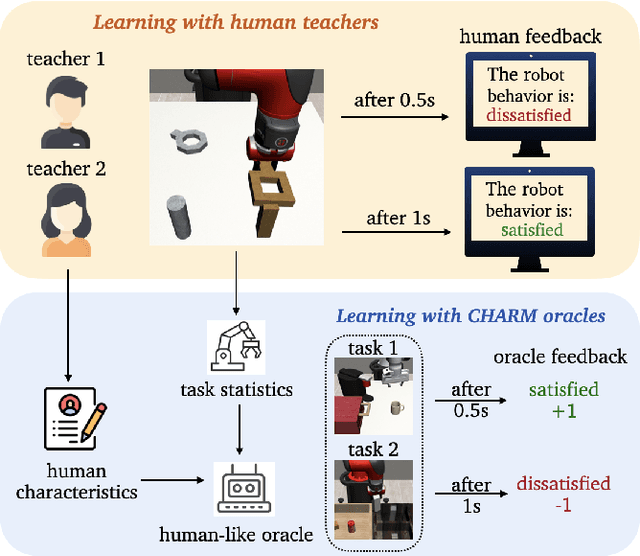

Abstract:Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback has recently achieved significant success in various fields, and its performance is highly related to feedback quality. While much prior work acknowledged that human teachers' characteristics would affect human feedback patterns, there is little work that has closely investigated the actual effects. In this work, we designed an exploratory study investigating how human feedback patterns are associated with human characteristics. We conducted a public space study with two long horizon tasks and 46 participants. We found that feedback patterns are not only correlated with task statistics, such as rewards, but also correlated with participants' characteristics, especially robot experience and educational background. Additionally, we demonstrated that human feedback value can be more accurately predicted with human characteristics compared to only using task statistics. All human feedback and characteristics we collected, and codes for our data collection and predicting more accurate human feedback are available at https://github.com/AABL-Lab/CHARM
Demonstration Sidetracks: Categorizing Systematic Non-Optimality in Human Demonstrations
Jun 12, 2025
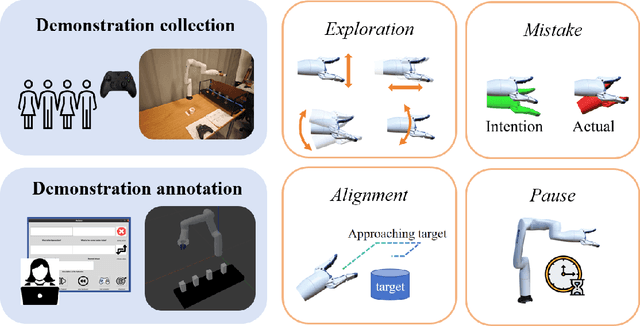
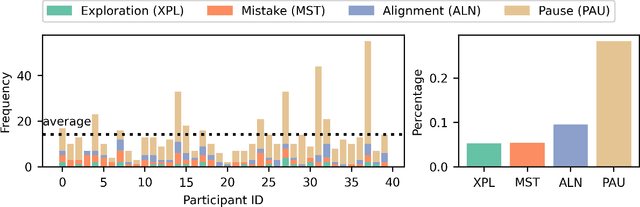
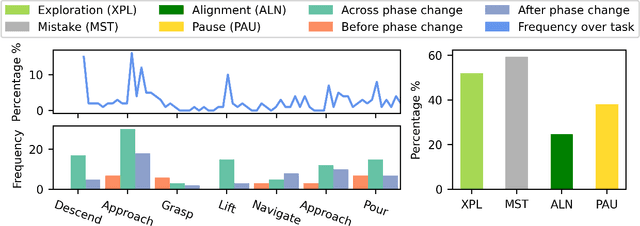
Abstract:Learning from Demonstration (LfD) is a popular approach for robots to acquire new skills, but most LfD methods suffer from imperfections in human demonstrations. Prior work typically treats these suboptimalities as random noise. In this paper we study non-optimal behaviors in non-expert demonstrations and show that they are systematic, forming what we call demonstration sidetracks. Using a public space study with 40 participants performing a long-horizon robot task, we recreated the setup in simulation and annotated all demonstrations. We identify four types of sidetracks (Exploration, Mistake, Alignment, Pause) and one control pattern (one-dimension control). Sidetracks appear frequently across participants, and their temporal and spatial distribution is tied to task context. We also find that users' control patterns depend on the control interface. These insights point to the need for better models of suboptimal demonstrations to improve LfD algorithms and bridge the gap between lab training and real-world deployment. All demonstrations, infrastructure, and annotations are available at https://github.com/AABL-Lab/Human-Demonstration-Sidetracks.
FLEX: A Framework for Learning Robot-Agnostic Force-based Skills Involving Sustained Contact Object Manipulation
Mar 17, 2025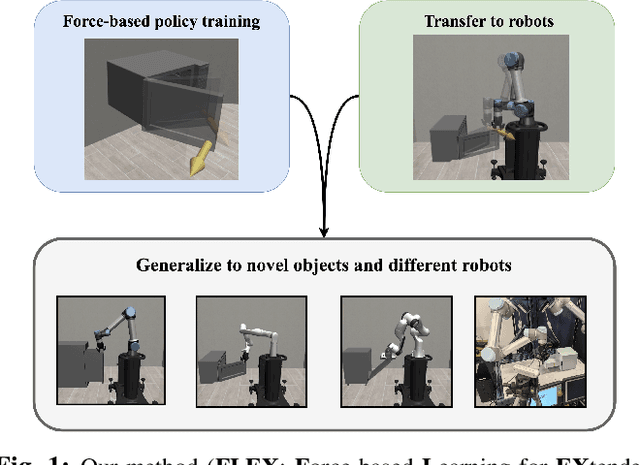
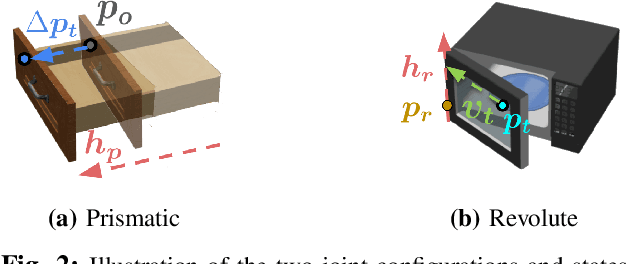
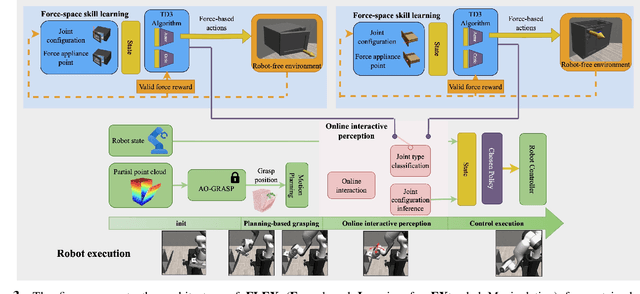
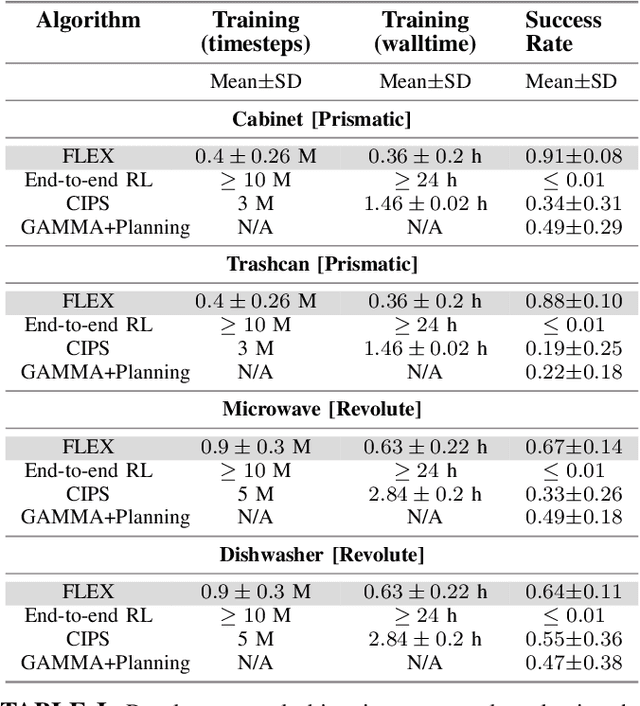
Abstract:Learning to manipulate objects efficiently, particularly those involving sustained contact (e.g., pushing, sliding) and articulated parts (e.g., drawers, doors), presents significant challenges. Traditional methods, such as robot-centric reinforcement learning (RL), imitation learning, and hybrid techniques, require massive training and often struggle to generalize across different objects and robot platforms. We propose a novel framework for learning object-centric manipulation policies in force space, decoupling the robot from the object. By directly applying forces to selected regions of the object, our method simplifies the action space, reduces unnecessary exploration, and decreases simulation overhead. This approach, trained in simulation on a small set of representative objects, captures object dynamics -- such as joint configurations -- allowing policies to generalize effectively to new, unseen objects. Decoupling these policies from robot-specific dynamics enables direct transfer to different robotic platforms (e.g., Kinova, Panda, UR5) without retraining. Our evaluations demonstrate that the method significantly outperforms baselines, achieving over an order of magnitude improvement in training efficiency compared to other state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, operating in force space enhances policy transferability across diverse robot platforms and object types. We further showcase the applicability of our method in a real-world robotic setting. For supplementary materials and videos, please visit: https://tufts-ai-robotics-group.github.io/FLEX/
How Much Progress Did I Make? An Unexplored Human Feedback Signal for Teaching Robots
Jul 08, 2024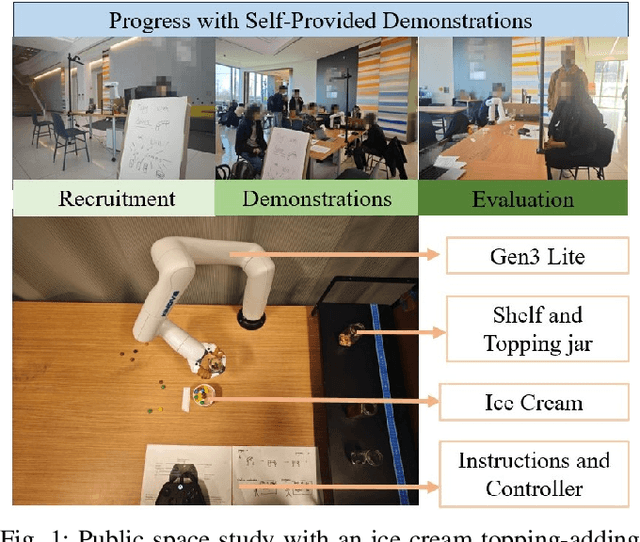
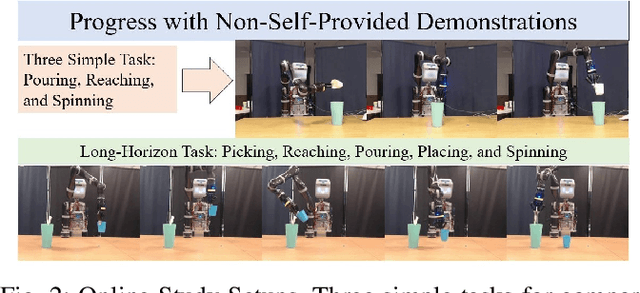
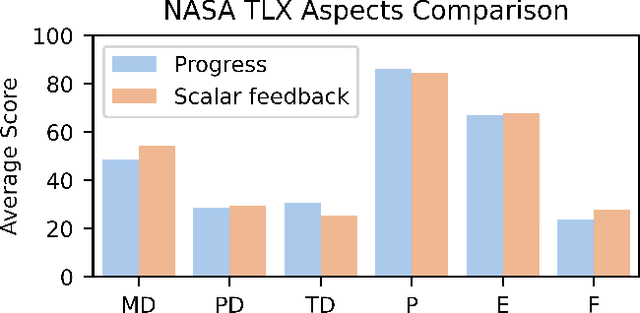
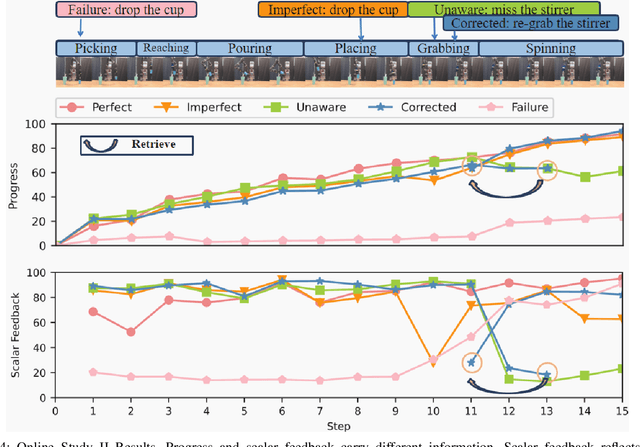
Abstract:Enhancing the expressiveness of human teaching is vital for both improving robots' learning from humans and the human-teaching-robot experience. In this work, we characterize and test a little-used teaching signal: \textit{progress}, designed to represent the completion percentage of a task. We conducted two online studies with 76 crowd-sourced participants and one public space study with 40 non-expert participants to validate the capability of this progress signal. We find that progress indicates whether the task is successfully performed, reflects the degree of task completion, identifies unproductive but harmless behaviors, and is likely to be more consistent across participants. Furthermore, our results show that giving progress does not require extra workload and time. An additional contribution of our work is a dataset of 40 non-expert demonstrations from the public space study through an ice cream topping-adding task, which we observe to be multi-policy and sub-optimal, with sub-optimality not only from teleoperation errors but also from exploratory actions and attempts. The dataset is available at \url{https://github.com/TeachingwithProgress/Non-Expert\_Demonstrations}.
VCC-INFUSE: Towards Accurate and Efficient Selection of Unlabeled Examples in Semi-supervised Learning
Apr 18, 2024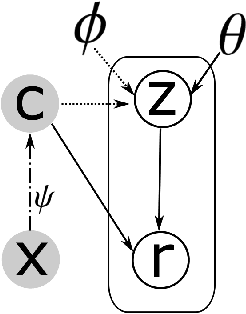

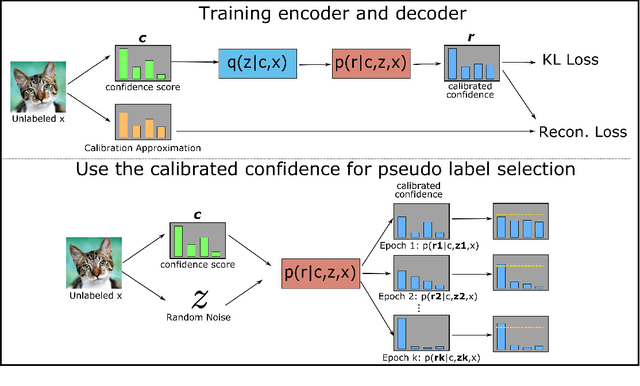

Abstract:Despite the progress of Semi-supervised Learning (SSL), existing methods fail to utilize unlabeled data effectively and efficiently. Many pseudo-label-based methods select unlabeled examples based on inaccurate confidence scores from the classifier. Most prior work also uses all available unlabeled data without pruning, making it difficult to handle large amounts of unlabeled data. To address these issues, we propose two methods: Variational Confidence Calibration (VCC) and Influence-Function-based Unlabeled Sample Elimination (INFUSE). VCC is an universal plugin for SSL confidence calibration, using a variational autoencoder to select more accurate pseudo labels based on three types of consistency scores. INFUSE is a data pruning method that constructs a core dataset of unlabeled examples under SSL. Our methods are effective in multiple datasets and settings, reducing classification errors rates and saving training time. Together, VCC-INFUSE reduces the error rate of FlexMatch on the CIFAR-100 dataset by 1.08% while saving nearly half of the training time.
Consistent Teacher Provides Better Supervision in Semi-supervised Object Detection
Sep 04, 2022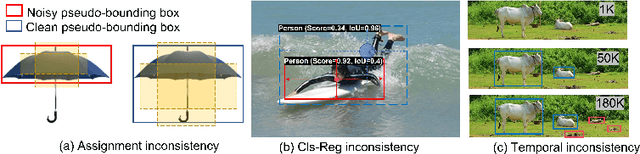

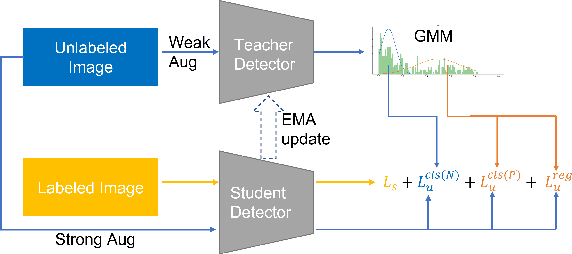
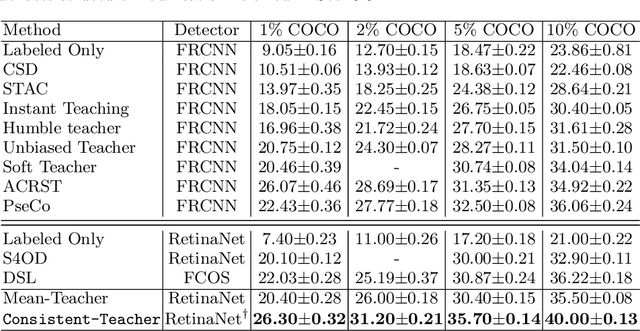
Abstract:In this study, we dive deep into the unique challenges in semi-supervised object detection~(SSOD). We observe that current detectors generally suffer from 3 inconsistency problems. 1) Assignment inconsistency, that the conventional assignment policy is sensitive to labeling noise. 2) Subtasks inconsistency, where the classification and regression predictions are misaligned at the same feature point. 3) Temporal inconsistency, that the pseudo bboxes vary dramatically at different training steps. These issues lead to inconsistent optimization objectives of the student network, thus deteriorating performance and slowing down the model convergence. We, therefore, propose a systematic solution, termed Consistent Teacher, to remedy the above-mentioned challenges. First, adaptive anchor assignment substitutes the static IoU-based strategy, which enables the student network to be resistant to noisy psudo bboxes; Then we calibrate the subtask predictions by designing a feature alignment module; Lastly, We adopt a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) to dynamically adjust the pseudo-boxes threshold. Consistent Teacher provides a new strong baseline on a large range of SSOD evaluations. It achieves 40.0 mAP with ResNet-50 backbone given only 10% of annotated MS-COCO data, which surpasses previous baselines using pseudo labels by around 4 mAP. When trained on fully annotated MS-COCO with additional unlabeled data, the performance further increases to 49.1 mAP. Our code will be open-sourced soon.
WSSOD: A New Pipeline for Weakly- and Semi-Supervised Object Detection
May 21, 2021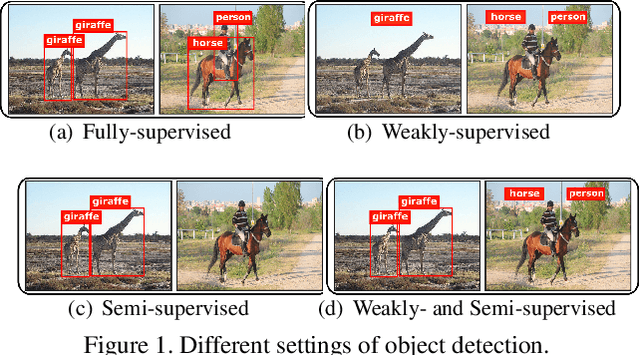
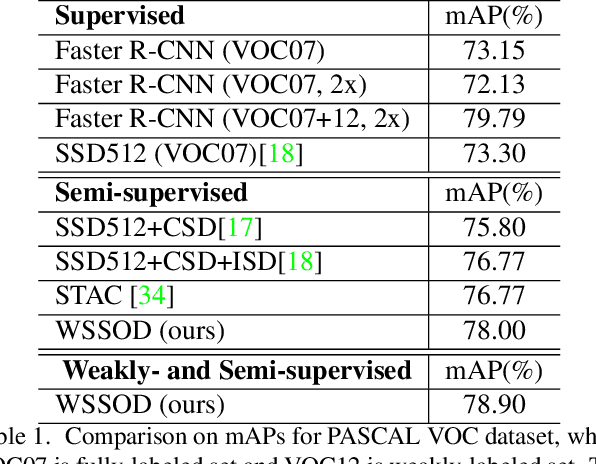
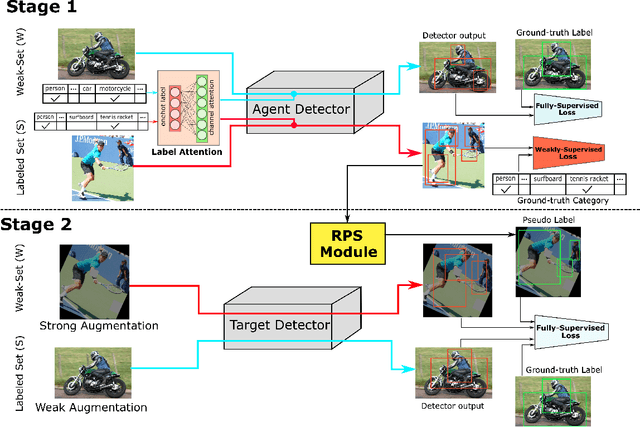
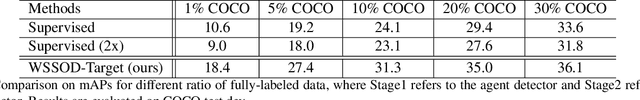
Abstract:The performance of object detection, to a great extent, depends on the availability of large annotated datasets. To alleviate the annotation cost, the research community has explored a number of ways to exploit unlabeled or weakly labeled data. However, such efforts have met with limited success so far. In this work, we revisit the problem with a pragmatic standpoint, trying to explore a new balance between detection performance and annotation cost by jointly exploiting fully and weakly annotated data. Specifically, we propose a weakly- and semi-supervised object detection framework (WSSOD), which involves a two-stage learning procedure. An agent detector is first trained on a joint dataset and then used to predict pseudo bounding boxes on weakly-annotated images. The underlying assumptions in the current as well as common semi-supervised pipelines are also carefully examined under a unified EM formulation. On top of this framework, weakly-supervised loss (WSL), label attention and random pseudo-label sampling (RPS) strategies are introduced to relax these assumptions, bringing additional improvement on the efficacy of the detection pipeline. The proposed framework demonstrates remarkable performance on PASCAL-VOC and MSCOCO benchmark, achieving a high performance comparable to those obtained in fully-supervised settings, with only one third of the annotations.
Intra-Model Collaborative Learning of Neural Networks
May 20, 2021



Abstract:Recently, collaborative learning proposed by Song and Chai has achieved remarkable improvements in image classification tasks by simultaneously training multiple classifier heads. However, huge memory footprints required by such multi-head structures may hinder the training of large-capacity baseline models. The natural question is how to achieve collaborative learning within a single network without duplicating any modules. In this paper, we propose four ways of collaborative learning among different parts of a single network with negligible engineering efforts. To improve the robustness of the network, we leverage the consistency of the output layer and intermediate layers for training under the collaborative learning framework. Besides, the similarity of intermediate representation and convolution kernel is also introduced to reduce the reduce redundant in a neural network. Compared to the method of Song and Chai, our framework further considers the collaboration inside a single model and takes smaller overhead. Extensive experiments on Cifar-10, Cifar-100, ImageNet32 and STL-10 corroborate the effectiveness of these four ways separately while combining them leads to further improvements. In particular, test errors on the STL-10 dataset are decreased by $9.28\%$ and $5.45\%$ for ResNet-18 and VGG-16 respectively. Moreover, our method is proven to be robust to label noise with experiments on Cifar-10 dataset. For example, our method has $3.53\%$ higher performance under $50\%$ noise ratio setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge