Qianhan Feng
CP-Env: Evaluating Large Language Models on Clinical Pathways in a Controllable Hospital Environment
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Medical care follows complex clinical pathways that extend beyond isolated physician-patient encounters, emphasizing decision-making and transitions between different stages. Current benchmarks focusing on static exams or isolated dialogues inadequately evaluate large language models (LLMs) in dynamic clinical scenarios. We introduce CP-Env, a controllable agentic hospital environment designed to evaluate LLMs across end-to-end clinical pathways. CP-Env simulates a hospital ecosystem with patient and physician agents, constructing scenarios ranging from triage and specialist consultation to diagnostic testing and multidisciplinary team meetings for agent interaction. Following real hospital adaptive flow of healthcare, it enables branching, long-horizon task execution. We propose a three-tiered evaluation framework encompassing Clinical Efficacy, Process Competency, and Professional Ethics. Results reveal that most models struggle with pathway complexity, exhibiting hallucinations and losing critical diagnostic details. Interestingly, excessive reasoning steps can sometimes prove counterproductive, while top models tend to exhibit reduced tool dependency through internalized knowledge. CP-Env advances medical AI agents development through comprehensive end-to-end clinical evaluation. We provide the benchmark and evaluation tools for further research and development at https://github.com/SPIRAL-MED/CP_ENV.
Align-KD: Distilling Cross-Modal Alignment Knowledge for Mobile Vision-Language Model
Dec 02, 2024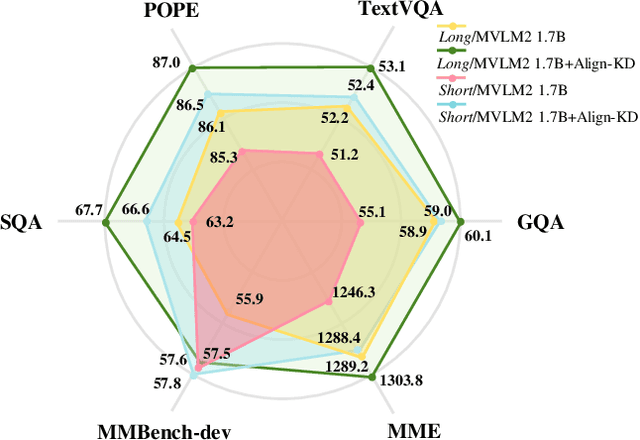
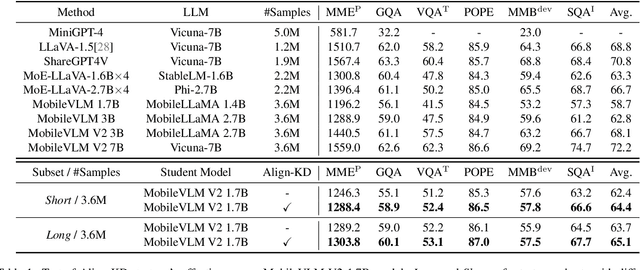
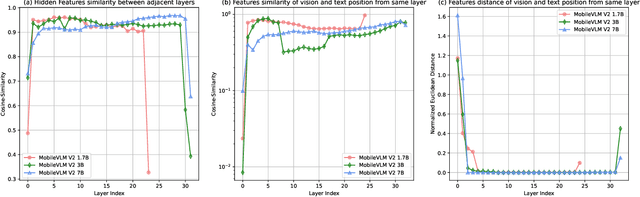
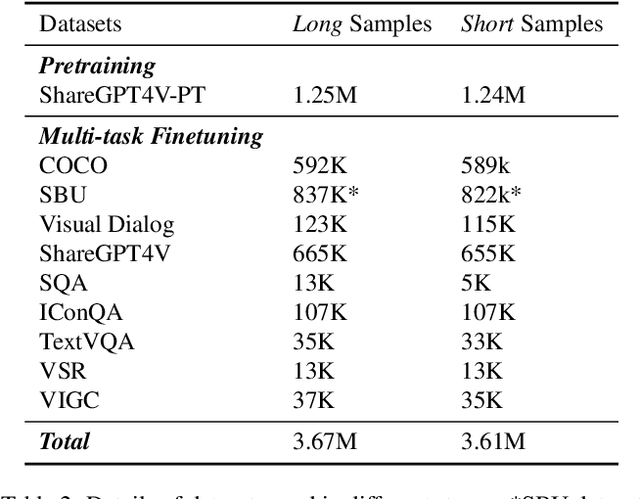
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) bring powerful understanding and reasoning capabilities to multimodal tasks. Meanwhile, the great need for capable aritificial intelligence on mobile devices also arises, such as the AI assistant software. Some efforts try to migrate VLMs to edge devices to expand their application scope. Simplifying the model structure is a common method, but as the model shrinks, the trade-off between performance and size becomes more and more difficult. Knowledge distillation (KD) can help models improve comprehensive capabilities without increasing size or data volume. However, most of the existing large model distillation techniques only consider applications on single-modal LLMs, or only use teachers to create new data environments for students. None of these methods take into account the distillation of the most important cross-modal alignment knowledge in VLMs. We propose a method called Align-KD to guide the student model to learn the cross-modal matching that occurs at the shallow layer. The teacher also helps student learn the projection of vision token into text embedding space based on the focus of text. Under the guidance of Align-KD, the 1.7B MobileVLM V2 model can learn rich knowledge from the 7B teacher model with light design of training loss, and achieve an average score improvement of 2.0 across 6 benchmarks under two training subsets respectively. Code is available at: https://github.com/fqhank/Align-KD.
Full-Stage Pseudo Label Quality Enhancement for Weakly-supervised Temporal Action Localization
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:Weakly-supervised Temporal Action Localization (WSTAL) aims to localize actions in untrimmed videos using only video-level supervision. Latest WSTAL methods introduce pseudo label learning framework to bridge the gap between classification-based training and inferencing targets at localization, and achieve cutting-edge results. In these frameworks, a classification-based model is used to generate pseudo labels for a regression-based student model to learn from. However, the quality of pseudo labels in the framework, which is a key factor to the final result, is not carefully studied. In this paper, we propose a set of simple yet efficient pseudo label quality enhancement mechanisms to build our FuSTAL framework. FuSTAL enhances pseudo label quality at three stages: cross-video contrastive learning at proposal Generation-Stage, prior-based filtering at proposal Selection-Stage and EMA-based distillation at Training-Stage. These designs enhance pseudo label quality at different stages in the framework, and help produce more informative, less false and smoother action proposals. With the help of these comprehensive designs at all stages, FuSTAL achieves an average mAP of 50.8% on THUMOS'14, outperforming the previous best method by 1.2%, and becomes the first method to reach the milestone of 50%.
VCC-INFUSE: Towards Accurate and Efficient Selection of Unlabeled Examples in Semi-supervised Learning
Apr 18, 2024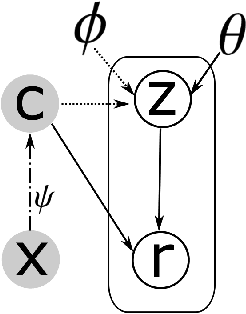

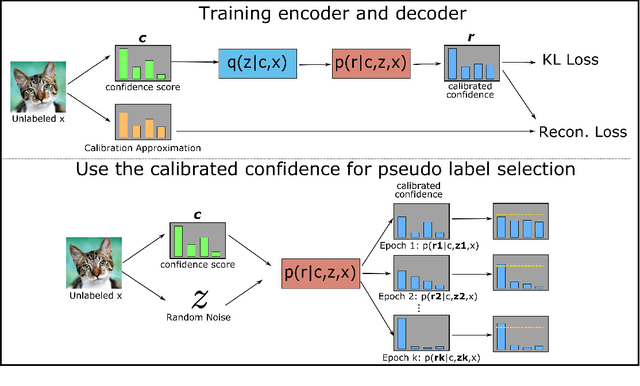

Abstract:Despite the progress of Semi-supervised Learning (SSL), existing methods fail to utilize unlabeled data effectively and efficiently. Many pseudo-label-based methods select unlabeled examples based on inaccurate confidence scores from the classifier. Most prior work also uses all available unlabeled data without pruning, making it difficult to handle large amounts of unlabeled data. To address these issues, we propose two methods: Variational Confidence Calibration (VCC) and Influence-Function-based Unlabeled Sample Elimination (INFUSE). VCC is an universal plugin for SSL confidence calibration, using a variational autoencoder to select more accurate pseudo labels based on three types of consistency scores. INFUSE is a data pruning method that constructs a core dataset of unlabeled examples under SSL. Our methods are effective in multiple datasets and settings, reducing classification errors rates and saving training time. Together, VCC-INFUSE reduces the error rate of FlexMatch on the CIFAR-100 dataset by 1.08% while saving nearly half of the training time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge