Yuanchun Li
Institute for AI Industry Research, Shanghai AI Laboratory, Shanghai, China
AgentProg: Empowering Long-Horizon GUI Agents with Program-Guided Context Management
Dec 11, 2025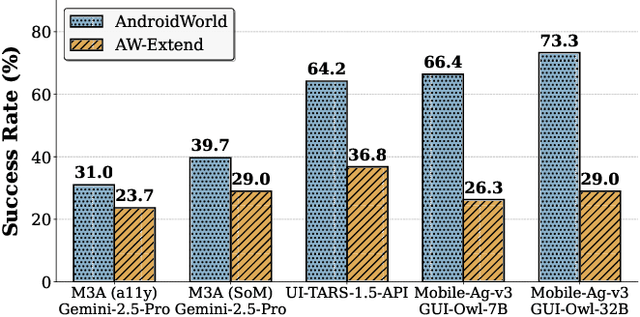

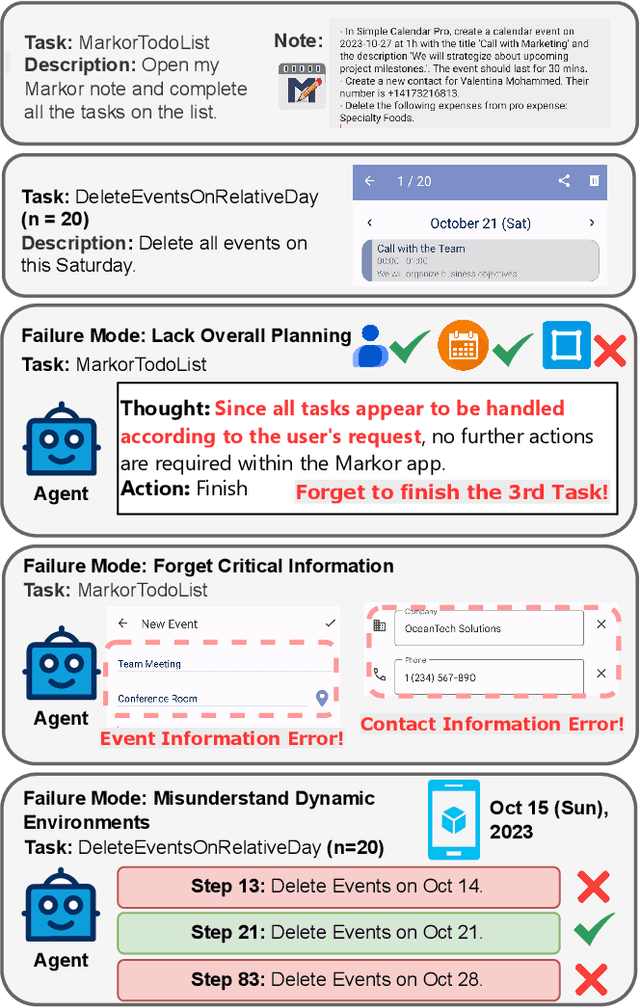

Abstract:The rapid development of mobile GUI agents has stimulated growing research interest in long-horizon task automation. However, building agents for these tasks faces a critical bottleneck: the reliance on ever-expanding interaction history incurs substantial context overhead. Existing context management and compression techniques often fail to preserve vital semantic information, leading to degraded task performance. We propose AgentProg, a program-guided approach for agent context management that reframes the interaction history as a program with variables and control flow. By organizing information according to the structure of program, this structure provides a principled mechanism to determine which information should be retained and which can be discarded. We further integrate a global belief state mechanism inspired by Belief MDP framework to handle partial observability and adapt to unexpected environmental changes. Experiments on AndroidWorld and our extended long-horizon task suite demonstrate that AgentProg has achieved the state-of-the-art success rates on these benchmarks. More importantly, it maintains robust performance on long-horizon tasks while baseline methods experience catastrophic degradation. Our system is open-sourced at https://github.com/MobileLLM/AgentProg.
BudgetThinker: Empowering Budget-aware LLM Reasoning with Control Tokens
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have leveraged increased test-time computation to enhance reasoning capabilities, a strategy that, while effective, incurs significant latency and resource costs, limiting their applicability in real-world time-constrained or cost-sensitive scenarios. This paper introduces BudgetThinker, a novel framework designed to empower LLMs with budget-aware reasoning, enabling precise control over the length of their thought processes. We propose a methodology that periodically inserts special control tokens during inference to continuously inform the model of its remaining token budget. This approach is coupled with a comprehensive two-stage training pipeline, beginning with Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) to familiarize the model with budget constraints, followed by a curriculum-based Reinforcement Learning (RL) phase that utilizes a length-aware reward function to optimize for both accuracy and budget adherence. We demonstrate that BudgetThinker significantly surpasses strong baselines in maintaining performance across a variety of reasoning budgets on challenging mathematical benchmarks. Our method provides a scalable and effective solution for developing efficient and controllable LLM reasoning, making advanced models more practical for deployment in resource-constrained and real-time environments.
GRAIL:Learning to Interact with Large Knowledge Graphs for Retrieval Augmented Reasoning
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) integrated with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques have exhibited remarkable performance across a wide range of domains. However, existing RAG approaches primarily operate on unstructured data and demonstrate limited capability in handling structured knowledge such as knowledge graphs. Meanwhile, current graph retrieval methods fundamentally struggle to capture holistic graph structures while simultaneously facing precision control challenges that manifest as either critical information gaps or excessive redundant connections, collectively undermining reasoning performance. To address this challenge, we propose GRAIL: Graph-Retrieval Augmented Interactive Learning, a framework designed to interact with large-scale graphs for retrieval-augmented reasoning. Specifically, GRAIL integrates LLM-guided random exploration with path filtering to establish a data synthesis pipeline, where a fine-grained reasoning trajectory is automatically generated for each task. Based on the synthesized data, we then employ a two-stage training process to learn a policy that dynamically decides the optimal actions at each reasoning step. The overall objective of precision-conciseness balance in graph retrieval is decoupled into fine-grained process-supervised rewards to enhance data efficiency and training stability. In practical deployment, GRAIL adopts an interactive retrieval paradigm, enabling the model to autonomously explore graph paths while dynamically balancing retrieval breadth and precision. Extensive experiments have shown that GRAIL achieves an average accuracy improvement of 21.01% and F1 improvement of 22.43% on three knowledge graph question-answering datasets. Our source code and datasets is available at https://github.com/Changgeww/GRAIL.
Mobile-Bench-v2: A More Realistic and Comprehensive Benchmark for VLM-based Mobile Agents
May 17, 2025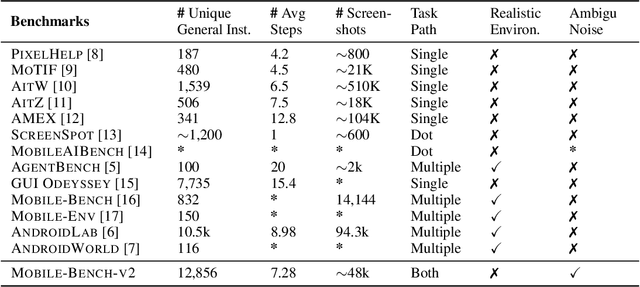
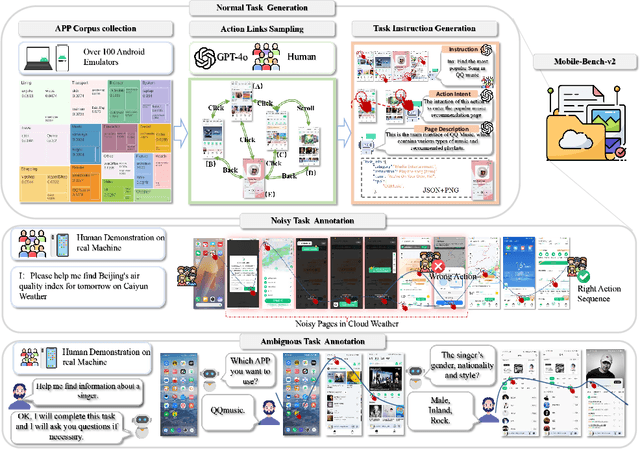
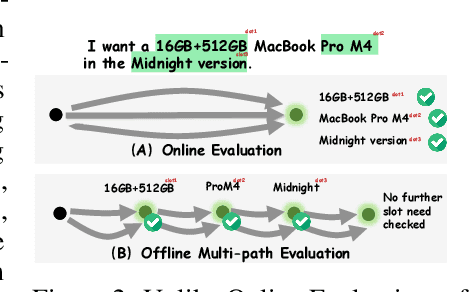
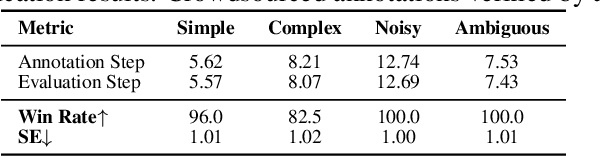
Abstract:VLM-based mobile agents are increasingly popular due to their capabilities to interact with smartphone GUIs and XML-structured texts and to complete daily tasks. However, existing online benchmarks struggle with obtaining stable reward signals due to dynamic environmental changes. Offline benchmarks evaluate the agents through single-path trajectories, which stands in contrast to the inherently multi-solution characteristics of GUI tasks. Additionally, both types of benchmarks fail to assess whether mobile agents can handle noise or engage in proactive interactions due to a lack of noisy apps or overly full instructions during the evaluation process. To address these limitations, we use a slot-based instruction generation method to construct a more realistic and comprehensive benchmark named Mobile-Bench-v2. Mobile-Bench-v2 includes a common task split, with offline multi-path evaluation to assess the agent's ability to obtain step rewards during task execution. It contains a noisy split based on pop-ups and ads apps, and a contaminated split named AITZ-Noise to formulate a real noisy environment. Furthermore, an ambiguous instruction split with preset Q\&A interactions is released to evaluate the agent's proactive interaction capabilities. We conduct evaluations on these splits using the single-agent framework AppAgent-v1, the multi-agent framework Mobile-Agent-v2, as well as other mobile agents such as UI-Tars and OS-Atlas. Code and data are available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/xwk123/MobileBench-v2.
LLM-Explorer: Towards Efficient and Affordable LLM-based Exploration for Mobile Apps
May 15, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have opened new opportunities for automated mobile app exploration, an important and challenging problem that used to suffer from the difficulty of generating meaningful UI interactions. However, existing LLM-based exploration approaches rely heavily on LLMs to generate actions in almost every step, leading to a huge cost of token fees and computational resources. We argue that such extensive usage of LLMs is neither necessary nor effective, since many actions during exploration do not require, or may even be biased by the abilities of LLMs. Further, based on the insight that a precise and compact knowledge plays the central role for effective exploration, we introduce LLM-Explorer, a new exploration agent designed for efficiency and affordability. LLM-Explorer uses LLMs primarily for maintaining the knowledge instead of generating actions, and knowledge is used to guide action generation in a LLM-less manner. Based on a comparison with 5 strong baselines on 20 typical apps, LLM-Explorer was able to achieve the fastest and highest coverage among all automated app explorers, with over 148x lower cost than the state-of-the-art LLM-based approach.
Time's Up! An Empirical Study of LLM Reasoning Ability Under Output Length Constraint
Apr 22, 2025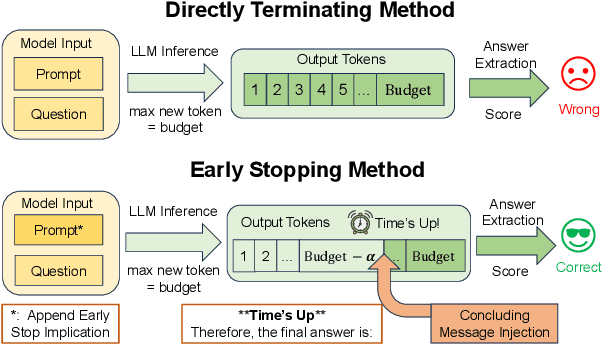
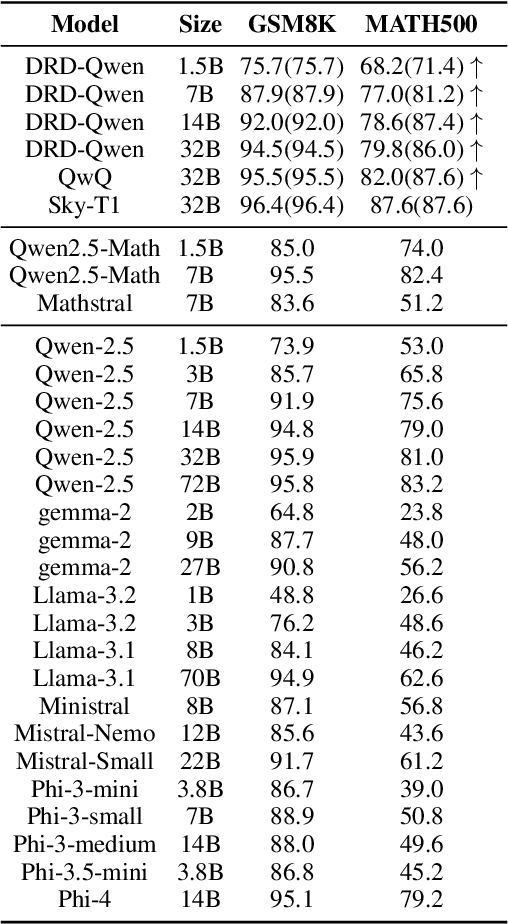
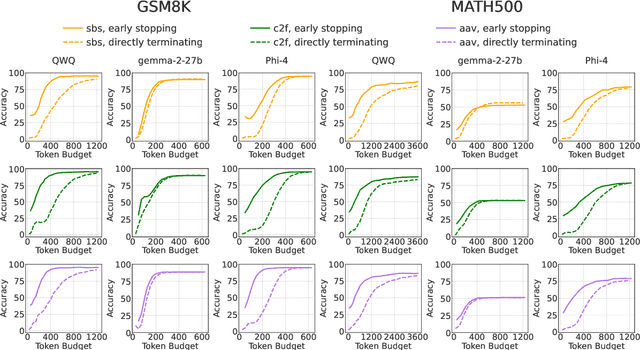
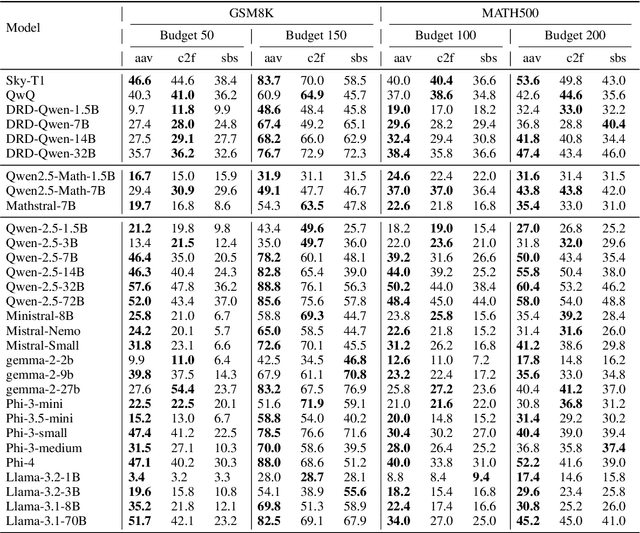
Abstract:Recent work has demonstrated the remarkable potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) in test-time scaling. By making the models think before answering, they are able to achieve much higher accuracy with extra inference computation. However, in many real-world scenarios, models are used under time constraints, where an answer should be given to the user within a certain output length. It is unclear whether and how the reasoning abilities of LLMs remain effective under such constraints. We take a first look at this problem by conducting an in-depth empirical study. Specifically, we test more than 25 LLMs on common reasoning datasets under a wide range of output length budgets, and we analyze the correlation between the inference accuracy and various properties including model type, model size, prompt style, etc. We also consider the mappings between the token budgets and the actual on-device latency budgets. The results have demonstrated several interesting findings regarding the budget-aware LLM reasoning that differ from the unconstrained situation, e.g. the optimal choices of model sizes and prompts change under different budgets. These findings offer practical guidance for users to deploy LLMs under real-world latency constraints.
Advancing Mobile GUI Agents: A Verifier-Driven Approach to Practical Deployment
Mar 21, 2025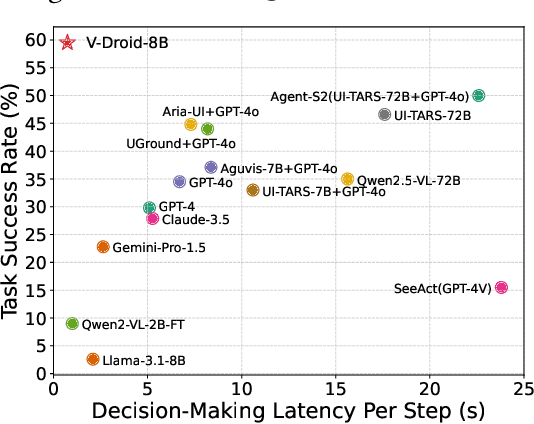
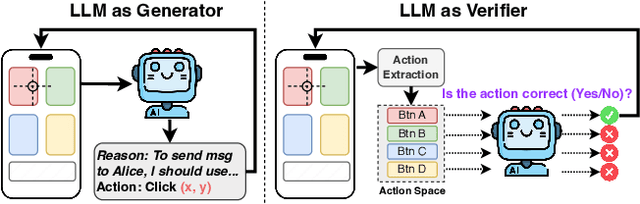
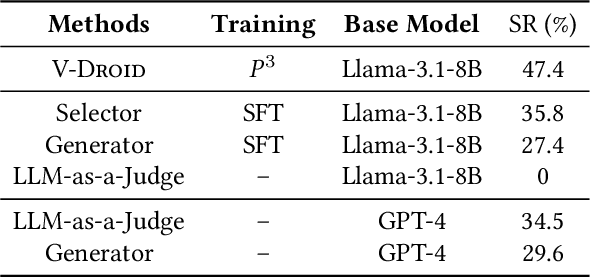
Abstract:We propose V-Droid, a mobile GUI task automation agent. Unlike previous mobile agents that utilize Large Language Models (LLMs) as generators to directly generate actions at each step, V-Droid employs LLMs as verifiers to evaluate candidate actions before making final decisions. To realize this novel paradigm, we introduce a comprehensive framework for constructing verifier-driven mobile agents: the discretized action space construction coupled with the prefilling-only workflow to accelerate the verification process, the pair-wise progress preference training to significantly enhance the verifier's decision-making capabilities, and the scalable human-agent joint annotation scheme to efficiently collect the necessary data at scale. V-Droid sets a new state-of-the-art task success rate across several public mobile task automation benchmarks: 59.5% on AndroidWorld, 38.3% on AndroidLab, and 49% on MobileAgentBench, surpassing existing agents by 9.5%, 2.1%, and 9%, respectively. Furthermore, V-Droid achieves an impressively low latency of 0.7 seconds per step, making it the first mobile agent capable of delivering near-real-time, effective decision-making capabilities.
AutoDroid-V2: Boosting SLM-based GUI Agents via Code Generation
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have brought exciting new advances to mobile UI agents, a long-standing research field that aims to complete arbitrary natural language tasks through mobile UI interactions. However, existing UI agents usually demand high reasoning capabilities of powerful large models that are difficult to be deployed locally on end-users' devices, which raises huge concerns about user privacy and centralized serving cost. One way to reduce the required model size is to customize a smaller domain-specific model with high-quality training data, e.g. large-scale human demonstrations of diverse types of apps and tasks, while such datasets are extremely difficult to obtain. Inspired by the remarkable coding abilities of recent small language models (SLMs), we propose to convert the UI task automation problem to a code generation problem, which can be effectively solved by an on-device SLM and efficiently executed with an on-device code interpreter. Unlike normal coding tasks that can be extensively pretrained with public datasets, generating UI automation code is challenging due to the diversity, complexity, and variability of target apps. Therefore, we adopt a document-centered approach that automatically builds fine-grained API documentation for each app and generates diverse task samples based on this documentation. By guiding the agent with the synthetic documents and task samples, it learns to generate precise and efficient scripts to complete unseen tasks. Based on detailed comparisons with state-of-the-art mobile UI agents, our approach effectively improves the mobile task automation with significantly higher success rates and lower latency/token consumption. Code will be open-sourced.
Threshold Neuron: A Brain-inspired Artificial Neuron for Efficient On-device Inference
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Enhancing the computational efficiency of on-device Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) remains a significant challengein mobile and edge computing. As we aim to execute increasingly complex tasks with constrained computational resources, much of the research has focused on compressing neural network structures and optimizing systems. Although many studies have focused on compressing neural network structures and parameters or optimizing underlying systems, there has been limited attention on optimizing the fundamental building blocks of neural networks: the neurons. In this study, we deliberate on a simple but important research question: Can we design artificial neurons that offer greater efficiency than the traditional neuron paradigm? Inspired by the threshold mechanisms and the excitation-inhibition balance observed in biological neurons, we propose a novel artificial neuron model, Threshold Neurons. Using Threshold Neurons, we can construct neural networks similar to those with traditional artificial neurons, while significantly reducing hardware implementation complexity. Our extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of neural networks utilizing Threshold Neurons, achieving substantial power savings of 7.51x to 8.19x and area savings of 3.89x to 4.33x at the kernel level, with minimal loss in precision. Furthermore, FPGA-based implementations of these networks demonstrate 2.52x power savings and 1.75x speed enhancements at the system level. The source code will be made available upon publication.
ChainStream: An LLM-based Framework for Unified Synthetic Sensing
Dec 13, 2024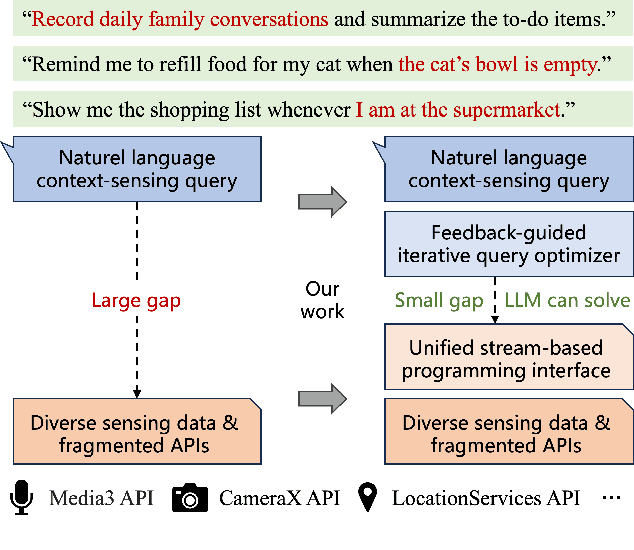
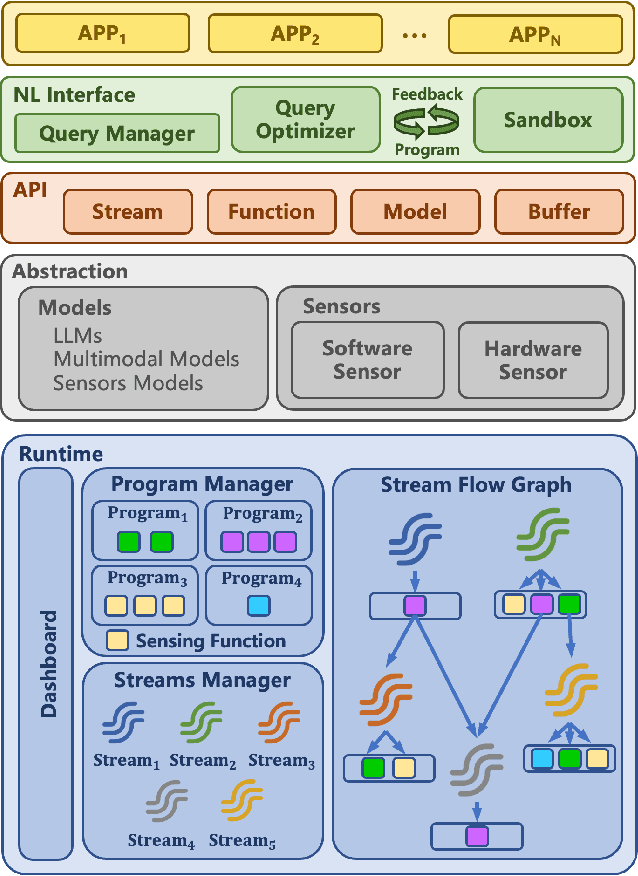
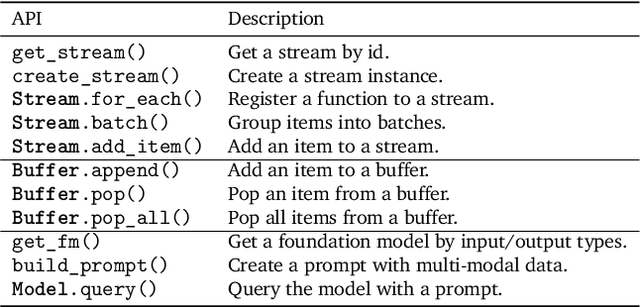
Abstract:Many applications demand context sensing to offer personalized and timely services. Yet, developing sensing programs can be challenging for developers and using them is privacy-concerning for end-users. In this paper, we propose to use natural language as the unified interface to process personal data and sense user context, which can effectively ease app development and make the data pipeline more transparent. Our work is inspired by large language models (LLMs) and other generative models, while directly applying them does not solve the problem - letting the model directly process the data cannot handle complex sensing requests and letting the model write the data processing program suffers error-prone code generation. We address the problem with 1) a unified data processing framework that makes context-sensing programs simpler and 2) a feedback-guided query optimizer that makes data query more informative. To evaluate the performance of natural language-based context sensing, we create a benchmark that contains 133 context sensing tasks. Extensive evaluation has shown that our approach is able to automatically solve the context-sensing tasks efficiently and precisely. The code is opensourced at https://github.com/MobileLLM/ChainStream.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge