Weijun Wang
Enabling MoE on the Edge via Importance-Driven Expert Scheduling
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture has emerged as a key technique for scaling Large Language Models by activating only a subset of experts per query. Deploying MoE on consumer-grade edge hardware, however, is constrained by limited device memory, making dynamic expert offloading essential. Unlike prior work that treats offloading purely as a scheduling problem, we leverage expert importance to guide decisions, substituting low-importance activated experts with functionally similar ones already cached in GPU memory, thereby preserving accuracy. As a result, this design reduces memory usage and data transfer, while largely eliminating PCIe overhead. In addition, we introduce a scheduling policy that maximizes the reuse ratio of GPU-cached experts, further boosting efficiency. Extensive evaluations show that our approach delivers 48% lower decoding latency with over 60% expert cache hit rate, while maintaining nearly lossless accuracy.
Multi-Objective Trajectory Planning for a Robotic Arm in Curtain Wall Installation
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:In the context of labor shortages and rising costs, construction robots are regarded as the key to revolutionizing traditional construction methods and improving efficiency and quality in the construction industry. In order to ensure that construction robots can perform tasks efficiently and accurately in complex construction environments, traditional single-objective trajectory optimization methods are difficult to meet the complex requirements of the changing construction environment. Therefore, we propose a multi-objective trajectory optimization for the robotic arm used in the curtain wall installation. First, we design a robotic arm for curtain wall installation, integrating serial, parallel, and folding arm elements, while considering its physical properties and motion characteristics. In addition, this paper proposes an NSGA-III-FO algorithm (NSGA-III with Focused Operator, NSGA-III-FO) that incorporates a focus operator screening mechanism to accelerate the convergence of the algorithm towards the Pareto front, thereby effectively balancing the multi-objective constraints of construction robots. The proposed algorithm is tested against NSGA-III, MOEA/D, and MSOPS-II in ten consecutive trials on the DTLZ3 and WFG3 test functions, showing significantly better convergence efficiency than the other algorithms. Finally, we conduct two sets of experiments on the designed robotic arm platform, which confirm the efficiency and practicality of the NSGA-III-FO algorithm in solving multi-objective trajectory planning problems for curtain wall installation tasks.
Dynamic Modeling and Dimensional Optimization of Legged Mechanisms for Construction Robot
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of the construction industry, issues such as harsh working environments, high-intensity and high-risk tasks, and labor shortages have become increasingly prominent. This drives higher demands for construction robots in terms of low energy consumption, high mobility, and high load capacity. This paper focuses on the design and optimization of leg structures for construction robots, aiming to improve their dynamic performance, reduce energy consumption, and enhance load-bearing capabilities. Firstly, based on the leg configuration of ants in nature, we design a structure for the robot's leg. Secondly, we propose a novel structural optimization method. Using the Lagrangian approach, a dynamic model of the leg was established. Combining the dynamic model with the leg's motion trajectory, we formulated multiple dynamic evaluation metrics and conducted a comprehensive optimization study on the geometric parameters of each leg segment. The results show that the optimized leg structure reduces peak joint torques and energy consumption by over 20%. Finally, dynamic simulation experiments were conducted using ADAMS. The results demonstrate a significant reduction in the driving power of each joint after optimization, validating the effectiveness and rationality of the proposed strategy. This study provides a theoretical foundation and technical support for the design of heavy-load, high-performance construction robots.
Dynamic Parameter Identification of a Curtain Wall Installation Robotic Arm
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:In the construction industry, traditional methods fail to meet the modern demands for efficiency and quality. The curtain wall installation is a critical component of construction projects. We design a hydraulically driven robotic arm for curtain wall installation and a dynamic parameter identification method. We establish a Denavit-Hartenberg (D-H) model based on measured robotic arm structural parameters and integrate hydraulic cylinder dynamics to construct a composite parametric system driven by a Stribeck friction model. By designing high-signal-to-noise ratio displacement excitation signals for hydraulic cylinders and combining Fourier series to construct optimal excitation trajectories that satisfy joint constraints, this method effectively excites the characteristics of each parameter in the minimal parameter set of the dynamic model of the robotic arm. On this basis, a hierarchical progressive parameter identification strategy is proposed: least squares estimation is employed to separately identify and jointly calibrate the dynamic parameters of both the hydraulic cylinder and the robotic arm, yielding Stribeck model curves for each joint. Experimental validation on a robotic arm platform demonstrates residual standard deviations below 0.4 Nm between theoretical and measured joint torques, confirming high-precision dynamic parameter identification for the hydraulic-driven curtain wall installation robotic arm. This significantly contributes to enhancing the intelligence level of curtain wall installation operations.
GS-Matching: Reconsidering Feature Matching task in Point Cloud Registration
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Traditional point cloud registration (PCR) methods for feature matching often employ the nearest neighbor policy. This leads to many-to-one matches and numerous potential inliers without any corresponding point. Recently, some approaches have framed the feature matching task as an assignment problem to achieve optimal one-to-one matches. We argue that the transition to the Assignment problem is not reliable for general correspondence-based PCR. In this paper, we propose a heuristics stable matching policy called GS-matching, inspired by the Gale-Shapley algorithm. Compared to the other matching policies, our method can perform efficiently and find more non-repetitive inliers under low overlapping conditions. Furthermore, we employ the probability theory to analyze the feature matching task, providing new insights into this research problem. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our matching policy, achieving better registration recall on multiple datasets.
V-LoRA: An Efficient and Flexible System Boosts Vision Applications with LoRA LMM
Nov 01, 2024



Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have shown significant progress in various complex vision tasks with the solid linguistic and reasoning capacity inherited from large language models (LMMs). Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) offers a promising method to integrate external knowledge into LMMs, compensating for their limitations on domain-specific tasks. However, the existing LoRA model serving is excessively computationally expensive and causes extremely high latency. In this paper, we present an end-to-end solution that empowers diverse vision tasks and enriches vision applications with LoRA LMMs. Our system, VaLoRA, enables accurate and efficient vision tasks by 1) an accuracy-aware LoRA adapter generation approach that generates LoRA adapters rich in domain-specific knowledge to meet application-specific accuracy requirements, 2) an adaptive-tiling LoRA adapters batching operator that efficiently computes concurrent heterogeneous LoRA adapters, and 3) a flexible LoRA adapter orchestration mechanism that manages application requests and LoRA adapters to achieve the lowest average response latency. We prototype VaLoRA on five popular vision tasks on three LMMs. Experiment results reveal that VaLoRA improves 24-62% of the accuracy compared to the original LMMs and reduces 20-89% of the latency compared to the state-of-the-art LoRA model serving systems.
Sight View Constraint for Robust Point Cloud Registration
Sep 08, 2024



Abstract:Partial to Partial Point Cloud Registration (partial PCR) remains a challenging task, particularly when dealing with a low overlap rate. In comparison to the full-to-full registration task, we find that the objective of partial PCR is still not well-defined, indicating no metric can reliably identify the true transformation. We identify this as the most fundamental challenge in partial PCR tasks. In this paper, instead of directly seeking the optimal transformation, we propose a novel and general Sight View Constraint (SVC) to conclusively identify incorrect transformations, thereby enhancing the robustness of existing PCR methods. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of SVC on both indoor and outdoor scenes. On the challenging 3DLoMatch dataset, our approach increases the registration recall from 78\% to 82\%, achieving the state-of-the-art result. This research also highlights the significance of the decision version problem of partial PCR, which has the potential to provide novel insights into the partial PCR problem.
Robust Multi-Robot Global Localization with Unknown Initial Pose based on Neighbor Constraints
Jun 27, 2024
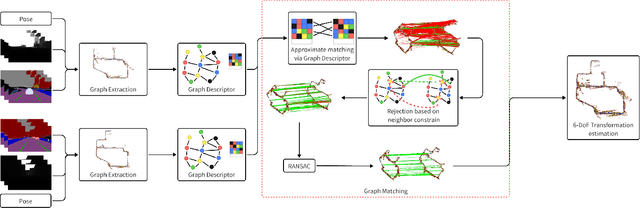

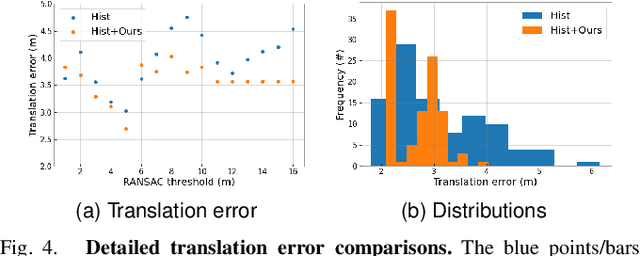
Abstract:Multi-robot global localization (MR-GL) with unknown initial positions in a large scale environment is a challenging task. The key point is the data association between different robots' viewpoints. It also makes traditional Appearance-based localization methods unusable. Recently, researchers have utilized the object's semantic invariance to generate a semantic graph to address this issue. However, previous works lack robustness and are sensitive to overlap rate of maps, resulting in unpredictable performance in real-world environments. In this paper, we propose a data association algorithm based on neighbor constraints to improve the robustness of the system. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on three different datasets, indicating a significant improvement in robustness compared to previous works.
LoRA-Switch: Boosting the Efficiency of Dynamic LLM Adapters via System-Algorithm Co-design
May 28, 2024Abstract:Recent literature has found that an effective method to customize or further improve large language models (LLMs) is to add dynamic adapters, such as low-rank adapters (LoRA) with Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) structures. Though such dynamic adapters incur modest computational complexity, they surprisingly lead to huge inference latency overhead, slowing down the decoding speed by 2.5+ times. In this paper, we analyze the fine-grained costs of the dynamic adapters and find that the fragmented CUDA kernel calls are the root cause. Therefore, we propose LoRA-Switch, a system-algorithm co-designed architecture for efficient dynamic adapters. Unlike most existing dynamic structures that adopt layer-wise or block-wise dynamic routing, LoRA-Switch introduces a token-wise routing mechanism. It switches the LoRA adapters and weights for each token and merges them into the backbone for inference. For efficiency, this switching is implemented with an optimized CUDA kernel, which fuses the merging operations for all LoRA adapters at once. Based on experiments with popular open-source LLMs on common benchmarks, our approach has demonstrated similar accuracy improvement as existing dynamic adapters, while reducing the decoding latency by more than 2.4 times.
MobileNetV4 -- Universal Models for the Mobile Ecosystem
Apr 16, 2024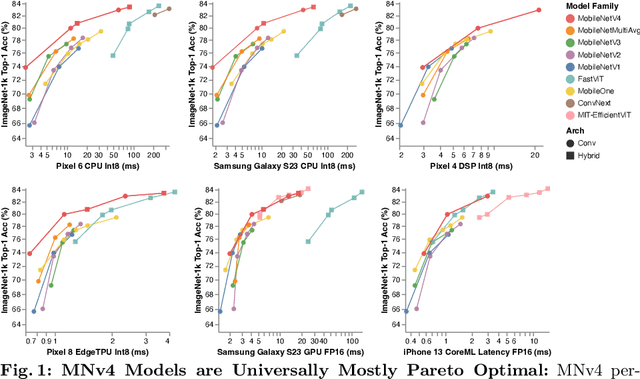
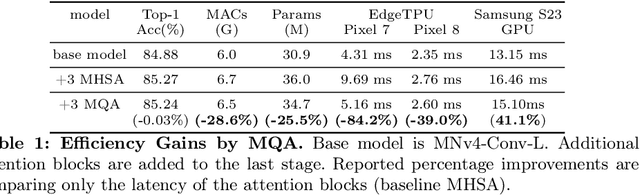
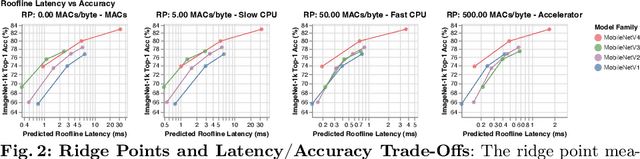
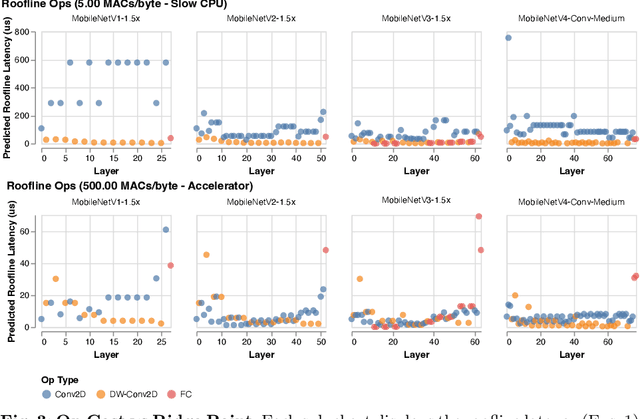
Abstract:We present the latest generation of MobileNets, known as MobileNetV4 (MNv4), featuring universally efficient architecture designs for mobile devices. At its core, we introduce the Universal Inverted Bottleneck (UIB) search block, a unified and flexible structure that merges Inverted Bottleneck (IB), ConvNext, Feed Forward Network (FFN), and a novel Extra Depthwise (ExtraDW) variant. Alongside UIB, we present Mobile MQA, an attention block tailored for mobile accelerators, delivering a significant 39% speedup. An optimized neural architecture search (NAS) recipe is also introduced which improves MNv4 search effectiveness. The integration of UIB, Mobile MQA and the refined NAS recipe results in a new suite of MNv4 models that are mostly Pareto optimal across mobile CPUs, DSPs, GPUs, as well as specialized accelerators like Apple Neural Engine and Google Pixel EdgeTPU - a characteristic not found in any other models tested. Finally, to further boost accuracy, we introduce a novel distillation technique. Enhanced by this technique, our MNv4-Hybrid-Large model delivers 87% ImageNet-1K accuracy, with a Pixel 8 EdgeTPU runtime of just 3.8ms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge