Yaojie Zhang
TimeChat-Captioner: Scripting Multi-Scene Videos with Time-Aware and Structural Audio-Visual Captions
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:This paper proposes Omni Dense Captioning, a novel task designed to generate continuous, fine-grained, and structured audio-visual narratives with explicit timestamps. To ensure dense semantic coverage, we introduce a six-dimensional structural schema to create "script-like" captions, enabling readers to vividly imagine the video content scene by scene, akin to a cinematographic screenplay. To facilitate research, we construct OmniDCBench, a high-quality, human-annotated benchmark, and propose SodaM, a unified metric that evaluates time-aware detailed descriptions while mitigating scene boundary ambiguity. Furthermore, we construct a training dataset, TimeChatCap-42K, and present TimeChat-Captioner-7B, a strong baseline trained via SFT and GRPO with task-specific rewards. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TimeChat-Captioner-7B achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing Gemini-2.5-Pro, while its generated dense descriptions significantly boost downstream capabilities in audio-visual reasoning (DailyOmni and WorldSense) and temporal grounding (Charades-STA). All datasets, models, and code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/yaolinli/TimeChat-Captioner.
Innovator-VL: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Scientific Discovery
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:We present Innovator-VL, a scientific multimodal large language model designed to advance understanding and reasoning across diverse scientific domains while maintaining excellent performance on general vision tasks. Contrary to the trend of relying on massive domain-specific pretraining and opaque pipelines, our work demonstrates that principled training design and transparent methodology can yield strong scientific intelligence with substantially reduced data requirements. (i) First, we provide a fully transparent, end-to-end reproducible training pipeline, covering data collection, cleaning, preprocessing, supervised fine-tuning, reinforcement learning, and evaluation, along with detailed optimization recipes. This facilitates systematic extension by the community. (ii) Second, Innovator-VL exhibits remarkable data efficiency, achieving competitive performance on various scientific tasks using fewer than five million curated samples without large-scale pretraining. These results highlight that effective reasoning can be achieved through principled data selection rather than indiscriminate scaling. (iii) Third, Innovator-VL demonstrates strong generalization, achieving competitive performance on general vision, multimodal reasoning, and scientific benchmarks. This indicates that scientific alignment can be integrated into a unified model without compromising general-purpose capabilities. Our practices suggest that efficient, reproducible, and high-performing scientific multimodal models can be built even without large-scale data, providing a practical foundation for future research.
Accelerating Diffusion Large Language Models with SlowFast: The Three Golden Principles
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Diffusion-based language models (dLLMs) have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional autoregressive LLMs by enabling parallel token generation and significantly reducing inference latency. However, existing sampling strategies for dLLMs, such as confidence-based or semi-autoregressive decoding, often suffer from static behavior, leading to suboptimal efficiency and limited flexibility. In this paper, we propose SlowFast Sampling, a novel dynamic sampling strategy that adaptively alternates between exploratory and accelerated decoding stages. Our method is guided by three golden principles: certainty principle, convergence principle, and positional principle, which govern when and where tokens can be confidently and efficiently decoded. We further integrate our strategy with dLLM-Cache to reduce redundant computation. Extensive experiments across benchmarks and models show that SlowFast Sampling achieves up to 15.63$\times$ speedup on LLaDA with minimal accuracy drop, and up to 34.22$\times$ when combined with caching. Notably, our approach outperforms strong autoregressive baselines like LLaMA3 8B in throughput, demonstrating that well-designed sampling can unlock the full potential of dLLMs for fast and high-quality generation.
GS-Matching: Reconsidering Feature Matching task in Point Cloud Registration
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Traditional point cloud registration (PCR) methods for feature matching often employ the nearest neighbor policy. This leads to many-to-one matches and numerous potential inliers without any corresponding point. Recently, some approaches have framed the feature matching task as an assignment problem to achieve optimal one-to-one matches. We argue that the transition to the Assignment problem is not reliable for general correspondence-based PCR. In this paper, we propose a heuristics stable matching policy called GS-matching, inspired by the Gale-Shapley algorithm. Compared to the other matching policies, our method can perform efficiently and find more non-repetitive inliers under low overlapping conditions. Furthermore, we employ the probability theory to analyze the feature matching task, providing new insights into this research problem. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our matching policy, achieving better registration recall on multiple datasets.
Sight View Constraint for Robust Point Cloud Registration
Sep 08, 2024



Abstract:Partial to Partial Point Cloud Registration (partial PCR) remains a challenging task, particularly when dealing with a low overlap rate. In comparison to the full-to-full registration task, we find that the objective of partial PCR is still not well-defined, indicating no metric can reliably identify the true transformation. We identify this as the most fundamental challenge in partial PCR tasks. In this paper, instead of directly seeking the optimal transformation, we propose a novel and general Sight View Constraint (SVC) to conclusively identify incorrect transformations, thereby enhancing the robustness of existing PCR methods. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of SVC on both indoor and outdoor scenes. On the challenging 3DLoMatch dataset, our approach increases the registration recall from 78\% to 82\%, achieving the state-of-the-art result. This research also highlights the significance of the decision version problem of partial PCR, which has the potential to provide novel insights into the partial PCR problem.
Robust Multi-Robot Global Localization with Unknown Initial Pose based on Neighbor Constraints
Jun 27, 2024
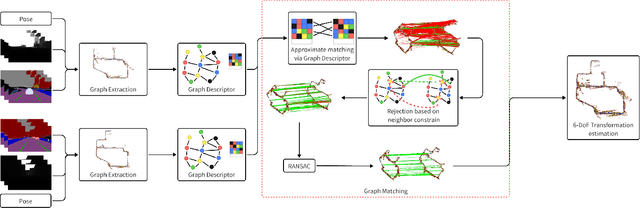

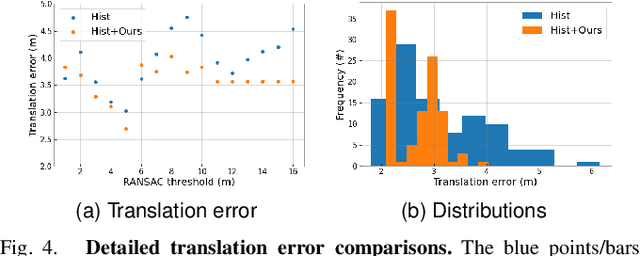
Abstract:Multi-robot global localization (MR-GL) with unknown initial positions in a large scale environment is a challenging task. The key point is the data association between different robots' viewpoints. It also makes traditional Appearance-based localization methods unusable. Recently, researchers have utilized the object's semantic invariance to generate a semantic graph to address this issue. However, previous works lack robustness and are sensitive to overlap rate of maps, resulting in unpredictable performance in real-world environments. In this paper, we propose a data association algorithm based on neighbor constraints to improve the robustness of the system. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on three different datasets, indicating a significant improvement in robustness compared to previous works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge