Tyler Derr
Inverse-LLaVA: Eliminating Alignment Pre-training Through Text-to-Vision Mapping
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:Traditional multimodal learning approaches require expensive alignment pre-training to bridge vision and language modalities, typically projecting visual features into discrete text token spaces. We challenge both fundamental assumptions underlying this paradigm by proposing Inverse-LLaVA, a novel approach that eliminates alignment pre-training entirely while inverting the conventional mapping direction. Rather than projecting visual features to text space, our method maps text embeddings into continuous visual representation space and performs fusion within transformer intermediate layers. Through selective additive components in attention mechanisms, we enable dynamic integration of visual and textual representations without requiring massive image-text alignment datasets. Comprehensive experiments across nine multimodal benchmarks demonstrate nuanced performance trade-offs: Inverse-LLaVA achieves notable improvements on reasoning-intensive and cognitive tasks (MM-VET: +0.2%, VizWiz: +1.8%, ScienceQA: +0.2%, cognitive reasoning: +27.2%), while showing expected decreases in perception tasks requiring memorized visual-text associations (celebrity recognition: -49.5%, OCR: -21.3%). These results provide the first empirical evidence that alignment pre-training is not necessary for effective multimodal learning, particularly for complex reasoning tasks. Our work establishes the feasibility of a new paradigm that reduces computational requirements by 45%, challenges conventional wisdom about modality fusion, and opens new research directions for efficient multimodal architectures that preserve modality-specific characteristics. Our project website with code and additional resources is available at https://inverse-llava.github.io.
Defining and Benchmarking a Data-Centric Design Space for Brain Graph Construction
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:The construction of brain graphs from functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) data plays a crucial role in enabling graph machine learning for neuroimaging. However, current practices often rely on rigid pipelines that overlook critical data-centric choices in how brain graphs are constructed. In this work, we adopt a Data-Centric AI perspective and systematically define and benchmark a data-centric design space for brain graph construction, constrasting with primarily model-centric prior work. We organize this design space into three stages: temporal signal processing, topology extraction, and graph featurization. Our contributions lie less in novel components and more in evaluating how combinations of existing and modified techniques influence downstream performance. Specifically, we study high-amplitude BOLD signal filtering, sparsification and unification strategies for connectivity, alternative correlation metrics, and multi-view node and edge features, such as incorporating lagged dynamics. Experiments on the HCP1200 and ABIDE datasets show that thoughtful data-centric configurations consistently improve classification accuracy over standard pipelines. These findings highlight the critical role of upstream data decisions and underscore the importance of systematically exploring the data-centric design space for graph-based neuroimaging. Our code is available at https://github.com/GeQinwen/DataCentricBrainGraphs.
SimAug: Enhancing Recommendation with Pretrained Language Models for Dense and Balanced Data Augmentation
May 03, 2025Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are extensively used in collaborative filtering due to their impressive effectiveness. These systems depend on interaction data to learn user and item embeddings that are crucial for recommendations. However, the data often suffers from sparsity and imbalance issues: limited observations of user-item interactions can result in sub-optimal performance, and a predominance of interactions with popular items may introduce recommendation bias. To address these challenges, we employ Pretrained Language Models (PLMs) to enhance the interaction data with textual information, leading to a denser and more balanced dataset. Specifically, we propose a simple yet effective data augmentation method (SimAug) based on the textual similarity from PLMs, which can be seamlessly integrated to any systems as a lightweight, plug-and-play component in the pre-processing stage. Our experiments across nine datasets consistently demonstrate improvements in both utility and fairness when training with the augmented data generated by SimAug. The code is available at https://github.com/YuyingZhao/SimAug.
Towards Trustworthy Retrieval Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey
Feb 08, 2025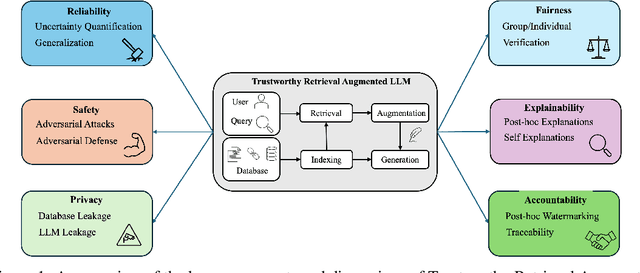
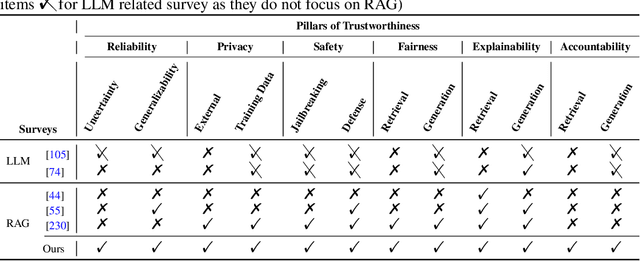
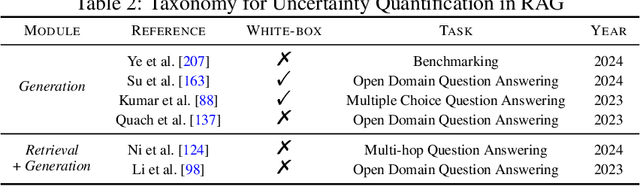
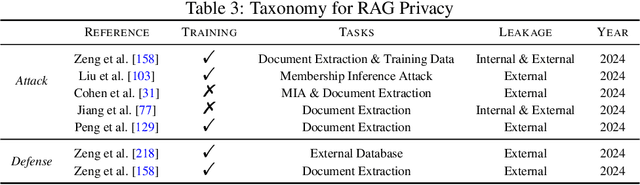
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an advanced technique designed to address the challenges of Artificial Intelligence-Generated Content (AIGC). By integrating context retrieval into content generation, RAG provides reliable and up-to-date external knowledge, reduces hallucinations, and ensures relevant context across a wide range of tasks. However, despite RAG's success and potential, recent studies have shown that the RAG paradigm also introduces new risks, including robustness issues, privacy concerns, adversarial attacks, and accountability issues. Addressing these risks is critical for future applications of RAG systems, as they directly impact their trustworthiness. Although various methods have been developed to improve the trustworthiness of RAG methods, there is a lack of a unified perspective and framework for research in this topic. Thus, in this paper, we aim to address this gap by providing a comprehensive roadmap for developing trustworthy RAG systems. We place our discussion around five key perspectives: reliability, privacy, safety, fairness, explainability, and accountability. For each perspective, we present a general framework and taxonomy, offering a structured approach to understanding the current challenges, evaluating existing solutions, and identifying promising future research directions. To encourage broader adoption and innovation, we also highlight the downstream applications where trustworthy RAG systems have a significant impact.
WelQrate: Defining the Gold Standard in Small Molecule Drug Discovery Benchmarking
Nov 14, 2024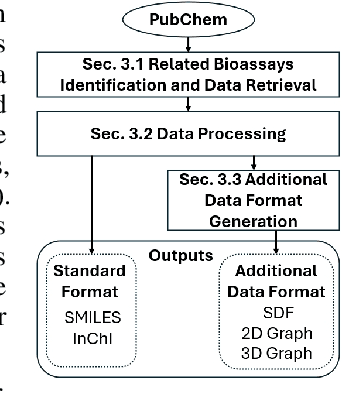
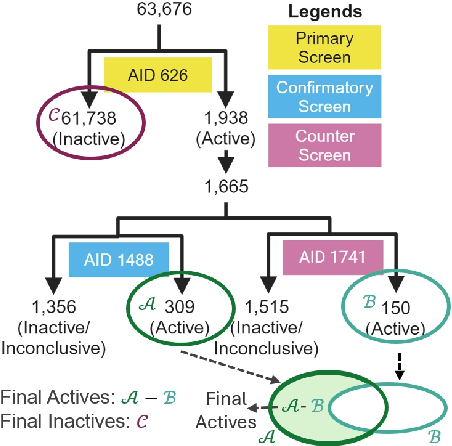
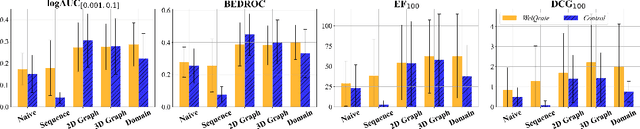
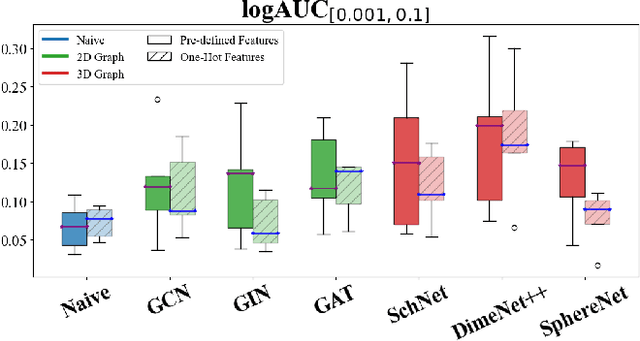
Abstract:While deep learning has revolutionized computer-aided drug discovery, the AI community has predominantly focused on model innovation and placed less emphasis on establishing best benchmarking practices. We posit that without a sound model evaluation framework, the AI community's efforts cannot reach their full potential, thereby slowing the progress and transfer of innovation into real-world drug discovery. Thus, in this paper, we seek to establish a new gold standard for small molecule drug discovery benchmarking, WelQrate. Specifically, our contributions are threefold: WelQrate Dataset Collection - we introduce a meticulously curated collection of 9 datasets spanning 5 therapeutic target classes. Our hierarchical curation pipelines, designed by drug discovery experts, go beyond the primary high-throughput screen by leveraging additional confirmatory and counter screens along with rigorous domain-driven preprocessing, such as Pan-Assay Interference Compounds (PAINS) filtering, to ensure the high-quality data in the datasets; WelQrate Evaluation Framework - we propose a standardized model evaluation framework considering high-quality datasets, featurization, 3D conformation generation, evaluation metrics, and data splits, which provides a reliable benchmarking for drug discovery experts conducting real-world virtual screening; Benchmarking - we evaluate model performance through various research questions using the WelQrate dataset collection, exploring the effects of different models, dataset quality, featurization methods, and data splitting strategies on the results. In summary, we recommend adopting our proposed WelQrate as the gold standard in small molecule drug discovery benchmarking. The WelQrate dataset collection, along with the curation codes, and experimental scripts are all publicly available at WelQrate.org.
Personalization of Large Language Models: A Survey
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:Personalization of Large Language Models (LLMs) has recently become increasingly important with a wide range of applications. Despite the importance and recent progress, most existing works on personalized LLMs have focused either entirely on (a) personalized text generation or (b) leveraging LLMs for personalization-related downstream applications, such as recommendation systems. In this work, we bridge the gap between these two separate main directions for the first time by introducing a taxonomy for personalized LLM usage and summarizing the key differences and challenges. We provide a formalization of the foundations of personalized LLMs that consolidates and expands notions of personalization of LLMs, defining and discussing novel facets of personalization, usage, and desiderata of personalized LLMs. We then unify the literature across these diverse fields and usage scenarios by proposing systematic taxonomies for the granularity of personalization, personalization techniques, datasets, evaluation methods, and applications of personalized LLMs. Finally, we highlight challenges and important open problems that remain to be addressed. By unifying and surveying recent research using the proposed taxonomies, we aim to provide a clear guide to the existing literature and different facets of personalization in LLMs, empowering both researchers and practitioners.
Large Language Model-based Augmentation for Imbalanced Node Classification on Text-Attributed Graphs
Oct 22, 2024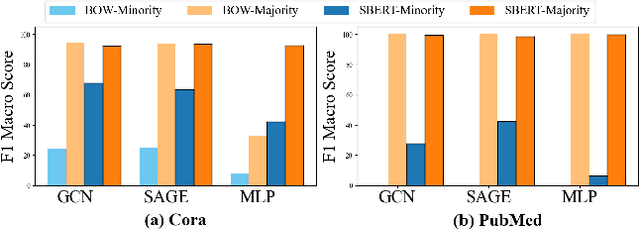
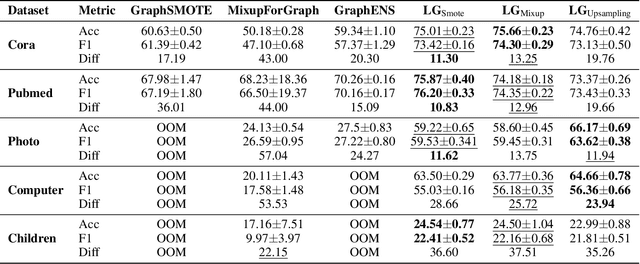
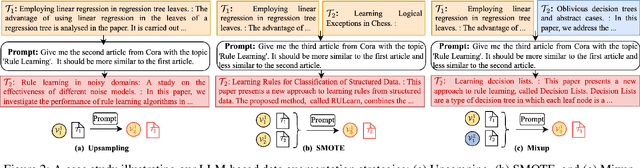
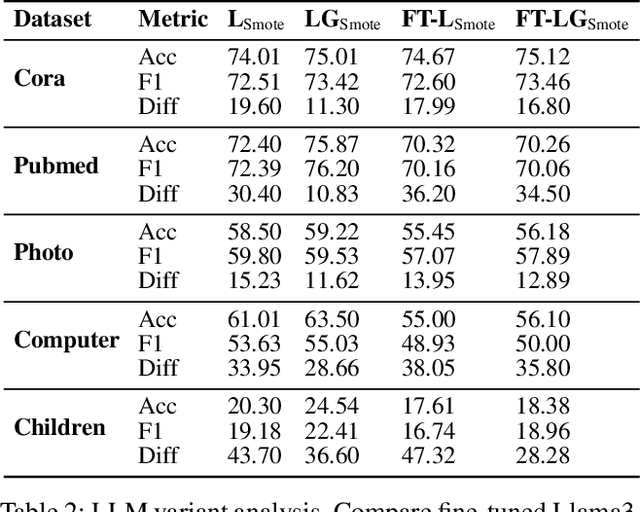
Abstract:Node classification on graphs frequently encounters the challenge of class imbalance, leading to biased performance and posing significant risks in real-world applications. Although several data-centric solutions have been proposed, none of them focus on Text-Attributed Graphs (TAGs), and therefore overlook the potential of leveraging the rich semantics encoded in textual features for boosting the classification of minority nodes. Given this crucial gap, we investigate the possibility of augmenting graph data in the text space, leveraging the textual generation power of Large Language Models (LLMs) to handle imbalanced node classification on TAGs. Specifically, we propose a novel approach called LA-TAG (LLM-based Augmentation on Text-Attributed Graphs), which prompts LLMs to generate synthetic texts based on existing node texts in the graph. Furthermore, to integrate these synthetic text-attributed nodes into the graph, we introduce a text-based link predictor to connect the synthesized nodes with the existing nodes. Our experiments across multiple datasets and evaluation metrics show that our framework significantly outperforms traditional non-textual-based data augmentation strategies and specific node imbalance solutions. This highlights the promise of using LLMs to resolve imbalance issues on TAGs.
Towards Trustworthy Knowledge Graph Reasoning: An Uncertainty Aware Perspective
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:Recently, Knowledge Graphs (KGs) have been successfully coupled with Large Language Models (LLMs) to mitigate their hallucinations and enhance their reasoning capability, such as in KG-based retrieval-augmented frameworks. However, current KG-LLM frameworks lack rigorous uncertainty estimation, limiting their reliable deployment in high-stakes applications. Directly incorporating uncertainty quantification into KG-LLM frameworks presents challenges due to their complex architectures and the intricate interactions between the knowledge graph and language model components. To address this gap, we propose a new trustworthy KG-LLM framework, Uncertainty Aware Knowledge-Graph Reasoning (UAG), which incorporates uncertainty quantification into the KG-LLM framework. We design an uncertainty-aware multi-step reasoning framework that leverages conformal prediction to provide a theoretical guarantee on the prediction set. To manage the error rate of the multi-step process, we additionally introduce an error rate control module to adjust the error rate within the individual components. Extensive experiments show that our proposed UAG can achieve any pre-defined coverage rate while reducing the prediction set/interval size by 40% on average over the baselines.
A Survey of Mamba
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:Deep learning, as a vital technique, has sparked a notable revolution in artificial intelligence. As the most representative architecture, Transformers have empowered numerous advanced models, especially the large language models that comprise billions of parameters, becoming a cornerstone in deep learning. Despite the impressive achievements, Transformers still face inherent limitations, particularly the time-consuming inference resulting from the quadratic computation complexity of attention calculation. Recently, a novel architecture named Mamba, drawing inspiration from classical state space models, has emerged as a promising alternative for building foundation models, delivering comparable modeling abilities to Transformers while preserving near-linear scalability concerning sequence length. This has sparked an increasing number of studies actively exploring Mamba's potential to achieve impressive performance across diverse domains. Given such rapid evolution, there is a critical need for a systematic review that consolidates existing Mamba-empowered models, offering a comprehensive understanding of this emerging model architecture. In this survey, we therefore conduct an in-depth investigation of recent Mamba-associated studies, covering from three main aspects: the advancements of Mamba-based models, the techniques of adapting Mamba to diverse data, and the applications where Mamba can excel. Specifically, we first recall the foundational knowledge of various representative deep learning models and the details of Mamba as preliminaries. Then, to showcase the significance of Mamba, we comprehensively review the related studies focusing on Mamba models' architecture design, data adaptability, and applications. Finally, we present an discussion of current limitations and explore various promising research directions to provide deeper insights for future investigations.
FT-AED: Benchmark Dataset for Early Freeway Traffic Anomalous Event Detection
Jun 24, 2024



Abstract:Early and accurate detection of anomalous events on the freeway, such as accidents, can improve emergency response and clearance. However, existing delays and errors in event identification and reporting make it a difficult problem to solve. Current large-scale freeway traffic datasets are not designed for anomaly detection and ignore these challenges. In this paper, we introduce the first large-scale lane-level freeway traffic dataset for anomaly detection. Our dataset consists of a month of weekday radar detection sensor data collected in 4 lanes along an 18-mile stretch of Interstate 24 heading toward Nashville, TN, comprising over 3.7 million sensor measurements. We also collect official crash reports from the Nashville Traffic Management Center and manually label all other potential anomalies in the dataset. To show the potential for our dataset to be used in future machine learning and traffic research, we benchmark numerous deep learning anomaly detection models on our dataset. We find that unsupervised graph neural network autoencoders are a promising solution for this problem and that ignoring spatial relationships leads to decreased performance. We demonstrate that our methods can reduce reporting delays by over 10 minutes on average while detecting 75% of crashes. Our dataset and all preprocessing code needed to get started are publicly released at https://vu.edu/ft-aed/ to facilitate future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge