Rui An
iTFKAN: Interpretable Time Series Forecasting with Kolmogorov-Arnold Network
Apr 23, 2025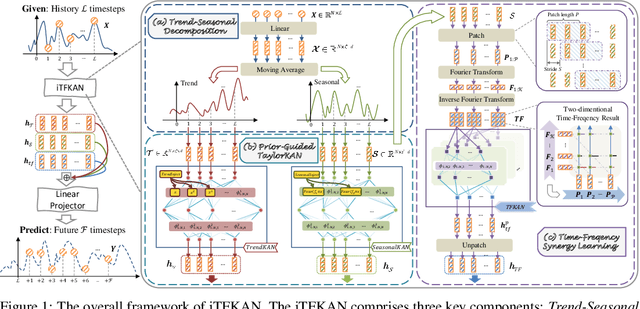



Abstract:As time evolves, data within specific domains exhibit predictability that motivates time series forecasting to predict future trends from historical data. However, current deep forecasting methods can achieve promising performance but generally lack interpretability, hindering trustworthiness and practical deployment in safety-critical applications such as auto-driving and healthcare. In this paper, we propose a novel interpretable model, iTFKAN, for credible time series forecasting. iTFKAN enables further exploration of model decision rationales and underlying data patterns due to its interpretability achieved through model symbolization. Besides, iTFKAN develops two strategies, prior knowledge injection, and time-frequency synergy learning, to effectively guide model learning under complex intertwined time series data. Extensive experimental results demonstrated that iTFKAN can achieve promising forecasting performance while simultaneously possessing high interpretive capabilities.
A Survey of Mamba
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:Deep learning, as a vital technique, has sparked a notable revolution in artificial intelligence. As the most representative architecture, Transformers have empowered numerous advanced models, especially the large language models that comprise billions of parameters, becoming a cornerstone in deep learning. Despite the impressive achievements, Transformers still face inherent limitations, particularly the time-consuming inference resulting from the quadratic computation complexity of attention calculation. Recently, a novel architecture named Mamba, drawing inspiration from classical state space models, has emerged as a promising alternative for building foundation models, delivering comparable modeling abilities to Transformers while preserving near-linear scalability concerning sequence length. This has sparked an increasing number of studies actively exploring Mamba's potential to achieve impressive performance across diverse domains. Given such rapid evolution, there is a critical need for a systematic review that consolidates existing Mamba-empowered models, offering a comprehensive understanding of this emerging model architecture. In this survey, we therefore conduct an in-depth investigation of recent Mamba-associated studies, covering from three main aspects: the advancements of Mamba-based models, the techniques of adapting Mamba to diverse data, and the applications where Mamba can excel. Specifically, we first recall the foundational knowledge of various representative deep learning models and the details of Mamba as preliminaries. Then, to showcase the significance of Mamba, we comprehensively review the related studies focusing on Mamba models' architecture design, data adaptability, and applications. Finally, we present an discussion of current limitations and explore various promising research directions to provide deeper insights for future investigations.
Fast Automatic Feature Selection for Multi-Period Sliding Window Aggregate in Time Series
Dec 02, 2020
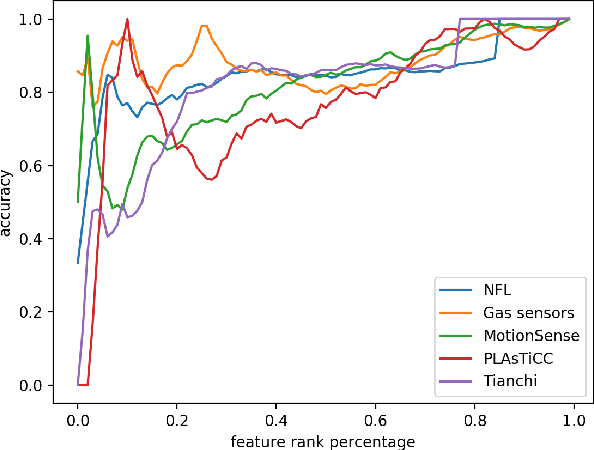
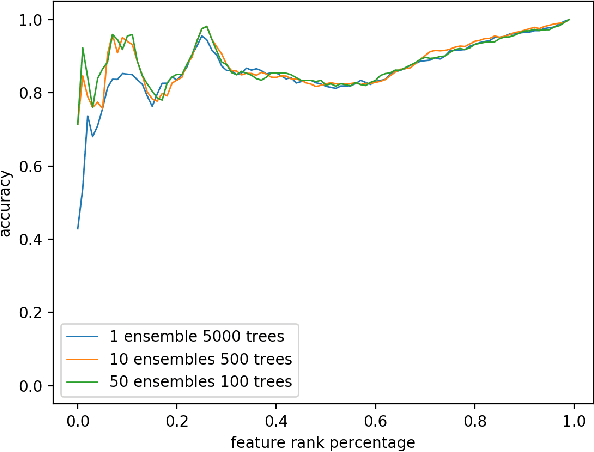
Abstract:As one of the most well-known artificial feature sampler, the sliding window is widely used in scenarios where spatial and temporal information exists, such as computer vision, natural language process, data stream, and time series. Among which time series is common in many scenarios like credit card payment, user behavior, and sensors. General feature selection for features extracted by sliding window aggregate calls for time-consuming iteration to generate features, and then traditional feature selection methods are employed to rank them. The decision of key parameter, i.e. the period of sliding windows, depends on the domain knowledge and calls for trivial. Currently, there is no automatic method to handle the sliding window aggregate features selection. As the time consumption of feature generation with different periods and sliding windows is huge, it is very hard to enumerate them all and then select them. In this paper, we propose a general framework using Markov Chain to solve this problem. This framework is very efficient and has high accuracy, such that it is able to perform feature selection on a variety of features and period options. We show the detail by 2 common sliding windows and 3 types of aggregation operators. And it is easy to extend more sliding windows and aggregation operators in this framework by employing existing theory about Markov Chain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge