Tao Liang
LongCat-Flash-Thinking-2601 Technical Report
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:We introduce LongCat-Flash-Thinking-2601, a 560-billion-parameter open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) reasoning model with superior agentic reasoning capability. LongCat-Flash-Thinking-2601 achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models on a wide range of agentic benchmarks, including agentic search, agentic tool use, and tool-integrated reasoning. Beyond benchmark performance, the model demonstrates strong generalization to complex tool interactions and robust behavior under noisy real-world environments. Its advanced capability stems from a unified training framework that combines domain-parallel expert training with subsequent fusion, together with an end-to-end co-design of data construction, environments, algorithms, and infrastructure spanning from pre-training to post-training. In particular, the model's strong generalization capability in complex tool-use are driven by our in-depth exploration of environment scaling and principled task construction. To optimize long-tailed, skewed generation and multi-turn agentic interactions, and to enable stable training across over 10,000 environments spanning more than 20 domains, we systematically extend our asynchronous reinforcement learning framework, DORA, for stable and efficient large-scale multi-environment training. Furthermore, recognizing that real-world tasks are inherently noisy, we conduct a systematic analysis and decomposition of real-world noise patterns, and design targeted training procedures to explicitly incorporate such imperfections into the training process, resulting in improved robustness for real-world applications. To further enhance performance on complex reasoning tasks, we introduce a Heavy Thinking mode that enables effective test-time scaling by jointly expanding reasoning depth and width through intensive parallel thinking.
DiffHash: Text-Guided Targeted Attack via Diffusion Models against Deep Hashing Image Retrieval
Sep 16, 2025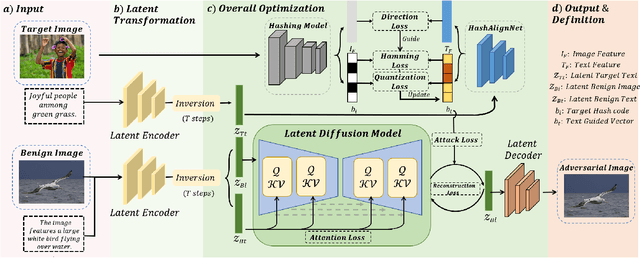
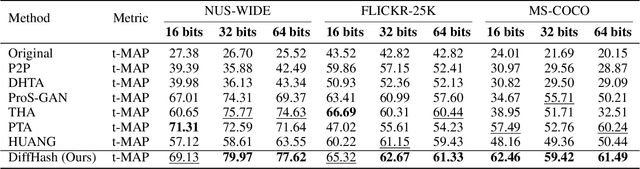
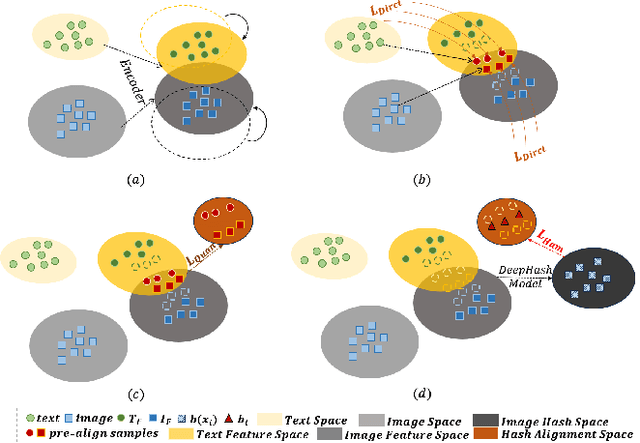
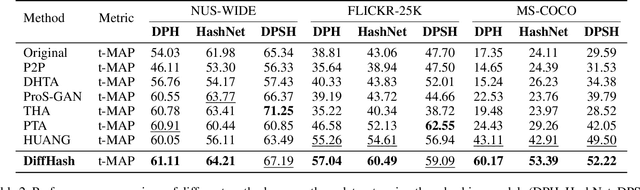
Abstract:Deep hashing models have been widely adopted to tackle the challenges of large-scale image retrieval. However, these approaches face serious security risks due to their vulnerability to adversarial examples. Despite the increasing exploration of targeted attacks on deep hashing models, existing approaches still suffer from a lack of multimodal guidance, reliance on labeling information and dependence on pixel-level operations for attacks. To address these limitations, we proposed DiffHash, a novel diffusion-based targeted attack for deep hashing. Unlike traditional pixel-based attacks that directly modify specific pixels and lack multimodal guidance, our approach focuses on optimizing the latent representations of images, guided by text information generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) for the target image. Furthermore, we designed a multi-space hash alignment network to align the high-dimension image space and text space to the low-dimension binary hash space. During reconstruction, we also incorporated text-guided attention mechanisms to refine adversarial examples, ensuring them aligned with the target semantics while maintaining visual plausibility. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that our method outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) targeted attack methods, achieving better black-box transferability and offering more excellent stability across datasets.
Interpretable Reward Model via Sparse Autoencoder
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been widely deployed across numerous fields. Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) leverages reward models (RMs) as proxies for human preferences to align LLM behaviors with human values, making the accuracy, reliability, and interpretability of RMs critical for effective alignment. However, traditional RMs lack interpretability, offer limited insight into the reasoning behind reward assignments, and are inflexible toward user preference shifts. While recent multidimensional RMs aim for improved interpretability, they often fail to provide feature-level attribution and require costly annotations. To overcome these limitations, we introduce the Sparse Autoencoder-enhanced Reward Model (\textbf{SARM}), a novel architecture that integrates a pretrained Sparse Autoencoder (SAE) into a reward model. SARM maps the hidden activations of LLM-based RM into an interpretable, sparse, and monosemantic feature space, from which a scalar head aggregates feature activations to produce transparent and conceptually meaningful reward scores. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that SARM facilitates direct feature-level attribution of reward assignments, allows dynamic adjustment to preference shifts, and achieves superior alignment performance compared to conventional reward models. Our code is available at https://github.com/schrieffer-z/sarm.
LLMEval-3: A Large-Scale Longitudinal Study on Robust and Fair Evaluation of Large Language Models
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Existing evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) on static benchmarks is vulnerable to data contamination and leaderboard overfitting, critical issues that obscure true model capabilities. To address this, we introduce LLMEval-3, a framework for dynamic evaluation of LLMs. LLMEval-3 is built on a proprietary bank of 220k graduate-level questions, from which it dynamically samples unseen test sets for each evaluation run. Its automated pipeline ensures integrity via contamination-resistant data curation, a novel anti-cheating architecture, and a calibrated LLM-as-a-judge process achieving 90% agreement with human experts, complemented by a relative ranking system for fair comparison. An 20-month longitudinal study of nearly 50 leading models reveals a performance ceiling on knowledge memorization and exposes data contamination vulnerabilities undetectable by static benchmarks. The framework demonstrates exceptional robustness in ranking stability and consistency, providing strong empirical validation for the dynamic evaluation paradigm. LLMEval-3 offers a robust and credible methodology for assessing the true capabilities of LLMs beyond leaderboard scores, promoting the development of more trustworthy evaluation standards.
Grounding Language with Vision: A Conditional Mutual Information Calibrated Decoding Strategy for Reducing Hallucinations in LVLMs
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) are susceptible to hallucinations, where generated responses seem semantically plausible yet exhibit little or no relevance to the input image. Previous studies reveal that this issue primarily stems from LVLMs' over-reliance on language priors while disregarding the visual information during decoding. To alleviate this issue, we introduce a novel Conditional Pointwise Mutual Information (C-PMI) calibrated decoding strategy, which adaptively strengthens the mutual dependency between generated texts and input images to mitigate hallucinations. Unlike existing methods solely focusing on text token sampling, we propose to jointly model the contributions of visual and textual tokens to C-PMI, formulating hallucination mitigation as a bi-level optimization problem aimed at maximizing mutual information. To solve it, we design a token purification mechanism that dynamically regulates the decoding process by sampling text tokens remaining maximally relevant to the given image, while simultaneously refining image tokens most pertinent to the generated response. Extensive experiments across various benchmarks reveal that the proposed method significantly reduces hallucinations in LVLMs while preserving decoding efficiency.
Code2Logic: Game-Code-Driven Data Synthesis for Enhancing VLMs General Reasoning
May 20, 2025Abstract:Visual-language Chain-of-Thought (CoT) data resources are relatively scarce compared to text-only counterparts, limiting the improvement of reasoning capabilities in Vision Language Models (VLMs). However, high-quality vision-language reasoning data is expensive and labor-intensive to annotate. To address this issue, we leverage a promising resource: game code, which naturally contains logical structures and state transition processes. Therefore, we propose Code2Logic, a novel game-code-driven approach for multimodal reasoning data synthesis. Our approach leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to adapt game code, enabling automatic acquisition of reasoning processes and results through code execution. Using the Code2Logic approach, we developed the GameQA dataset to train and evaluate VLMs. GameQA is cost-effective and scalable to produce, challenging for state-of-the-art models, and diverse with 30 games and 158 tasks. Surprisingly, despite training solely on game data, VLMs demonstrated out of domain generalization, specifically Qwen2.5-VL-7B improving performance by 2.33\% across 7 diverse vision-language benchmarks. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/tongjingqi/Code2Logic.
Route Sparse Autoencoder to Interpret Large Language Models
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Mechanistic interpretability of large language models (LLMs) aims to uncover the internal processes of information propagation and reasoning. Sparse autoencoders (SAEs) have demonstrated promise in this domain by extracting interpretable and monosemantic features. However, prior works primarily focus on feature extraction from a single layer, failing to effectively capture activations that span multiple layers. In this paper, we introduce Route Sparse Autoencoder (RouteSAE), a new framework that integrates a routing mechanism with a shared SAE to efficiently extract features from multiple layers. It dynamically assigns weights to activations from different layers, incurring minimal parameter overhead while achieving high interpretability and flexibility for targeted feature manipulation. We evaluate RouteSAE through extensive experiments on Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct. Specifically, under the same sparsity constraint of 64, RouteSAE extracts 22.5% more features than baseline SAEs while achieving a 22.3% higher interpretability score. These results underscore the potential of RouteSAE as a scalable and effective method for LLM interpretability, with applications in feature discovery and model intervention. Our codes are available at https://github.com/swei2001/RouteSAEs.
SPEED: Scalable, Precise, and Efficient Concept Erasure for Diffusion Models
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Erasing concepts from large-scale text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models has become increasingly crucial due to the growing concerns over copyright infringement, offensive content, and privacy violations. However, existing methods either require costly fine-tuning or degrade image quality for non-target concepts (i.e., prior) due to inherent optimization limitations. In this paper, we introduce SPEED, a model editing-based concept erasure approach that leverages null-space constraints for scalable, precise, and efficient erasure. Specifically, SPEED incorporates Influence-based Prior Filtering (IPF) to retain the most affected non-target concepts during erasing, Directed Prior Augmentation (DPA) to expand prior coverage while maintaining semantic consistency, and Invariant Equality Constraints (IEC) to regularize model editing by explicitly preserving key invariants during the T2I generation process. Extensive evaluations across multiple concept erasure tasks demonstrate that SPEED consistently outperforms existing methods in prior preservation while achieving efficient and high-fidelity concept erasure, successfully removing 100 concepts within just 5 seconds. Our code and models are available at: https://github.com/Ouxiang-Li/SPEED.
PFDial: A Structured Dialogue Instruction Fine-tuning Method Based on UML Flowcharts
Mar 09, 2025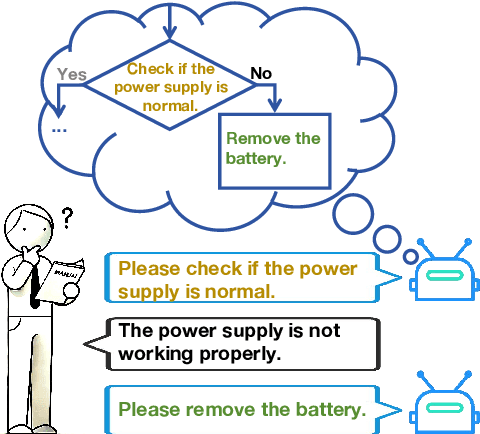
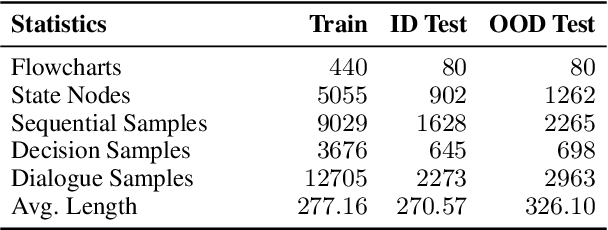
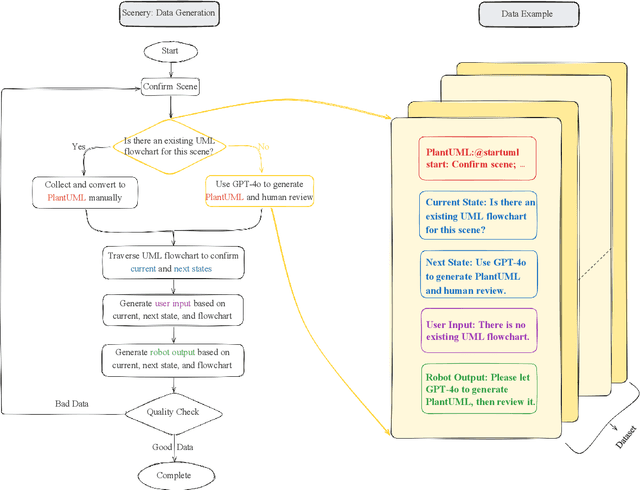
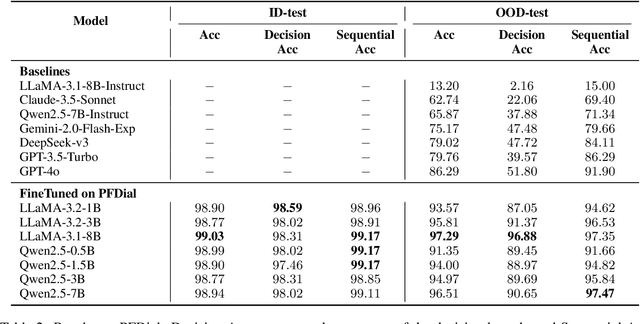
Abstract:Process-driven dialogue systems, which operate under strict predefined process constraints, are essential in customer service and equipment maintenance scenarios. Although Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable progress in dialogue and reasoning, they still struggle to solve these strictly constrained dialogue tasks. To address this challenge, we construct Process Flow Dialogue (PFDial) dataset, which contains 12,705 high-quality Chinese dialogue instructions derived from 440 flowcharts containing 5,055 process nodes. Based on PlantUML specification, each UML flowchart is converted into atomic dialogue units i.e., structured five-tuples. Experimental results demonstrate that a 7B model trained with merely 800 samples, and a 0.5B model trained on total data both can surpass 90% accuracy. Additionally, the 8B model can surpass GPT-4o up to 43.88% with an average of 11.00%. We further evaluate models' performance on challenging backward transitions in process flows and conduct an in-depth analysis of various dataset formats to reveal their impact on model performance in handling decision and sequential branches. The data is released in https://github.com/KongLongGeFDU/PFDial.
Predicting Large Language Model Capabilities on Closed-Book QA Tasks Using Only Information Available Prior to Training
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:The GPT-4 technical report from OpenAI suggests that model performance on specific tasks can be predicted prior to training, though methodologies remain unspecified. This approach is crucial for optimizing resource allocation and ensuring data alignment with target tasks. To achieve this vision, we focus on predicting performance on Closed-book Question Answering (CBQA) tasks, which are closely tied to pre-training data and knowledge retention. We address three major challenges: 1) mastering the entire pre-training process, especially data construction; 2) evaluating a model's knowledge retention; and 3) predicting task-specific knowledge retention using only information available prior to training. To tackle these challenges, we pre-train three large language models (i.e., 1.6B, 7B, and 13B) using 560k dollars and 520k GPU hours. We analyze the pre-training data with knowledge triples and assess knowledge retention using established methods. Additionally, we introduce the SMI metric, an information-theoretic measure that quantifies the relationship between pre-training data, model size, and task-specific knowledge retention. Our experiments reveal a strong linear correlation ($\text{R}^2 > 0.84$) between the SMI metric and the model's accuracy on CBQA tasks across models of varying sizes (i.e., 1.1B, 1.6B, 7B, and 13B). The dataset, model, and code are available at https://github.com/yuhui1038/SMI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge