Zhaoxing Li
HMCF: A Human-in-the-loop Multi-Robot Collaboration Framework Based on Large Language Models
May 01, 2025Abstract:Rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have enabled robots to performcomplex tasks autonomously with increasing precision. However, multi-robot systems (MRSs) face challenges in generalization, heterogeneity, and safety, especially when scaling to large-scale deployments like disaster response. Traditional approaches often lack generalization, requiring extensive engineering for new tasks and scenarios, and struggle with managing diverse robots. To overcome these limitations, we propose a Human-in-the-loop Multi-Robot Collaboration Framework (HMCF) powered by large language models (LLMs). LLMs enhance adaptability by reasoning over diverse tasks and robot capabilities, while human oversight ensures safety and reliability, intervening only when necessary. Our framework seamlessly integrates human oversight, LLM agents, and heterogeneous robots to optimize task allocation and execution. Each robot is equipped with an LLM agent capable of understanding its capabilities, converting tasks into executable instructions, and reducing hallucinations through task verification and human supervision. Simulation results show that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art task planning methods, achieving higher task success rates with an improvement of 4.76%. Real-world tests demonstrate its robust zero-shot generalization feature and ability to handle diverse tasks and environments with minimal human intervention.
Quattro: Transformer-Accelerated Iterative Linear Quadratic Regulator Framework for Fast Trajectory Optimization
Apr 02, 2025
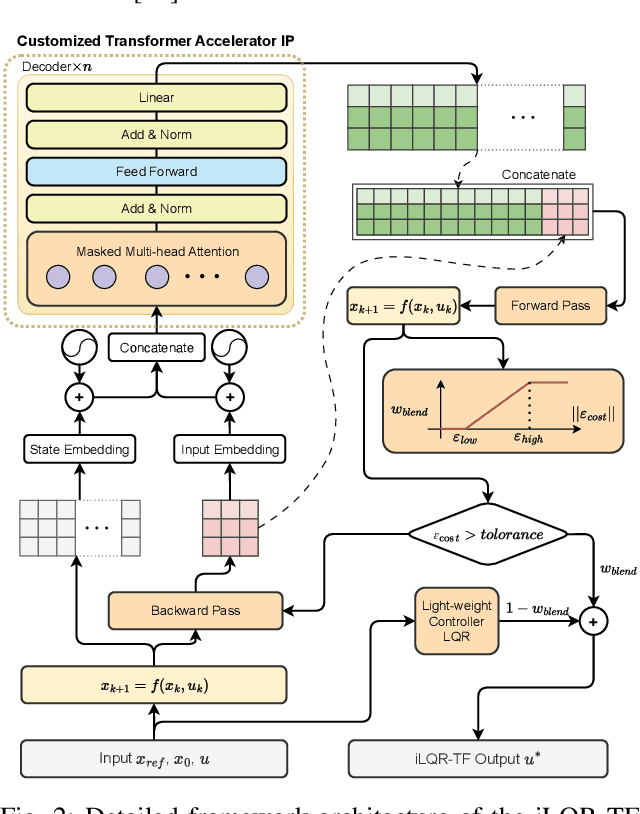


Abstract:Real-time optimal control remains a fundamental challenge in robotics, especially for nonlinear systems with stringent performance requirements. As one of the representative trajectory optimization algorithms, the iterative Linear Quadratic Regulator (iLQR) faces limitations due to their inherently sequential computational nature, which restricts the efficiency and applicability of real-time control for robotic systems. While existing parallel implementations aim to overcome the above limitations, they typically demand additional computational iterations and high-performance hardware, leading to only modest practical improvements. In this paper, we introduce Quattro, a transformer-accelerated iLQR framework employing an algorithm-hardware co-design strategy to predict intermediate feedback and feedforward matrices. It facilitates effective parallel computations on resource-constrained devices without sacrificing accuracy. Experiments on cart-pole and quadrotor systems show an algorithm-level acceleration of up to 5.3$\times$ and 27$\times$ per iteration, respectively. When integrated into a Model Predictive Control (MPC) framework, Quattro achieves overall speedups of 2.8$\times$ for the cart-pole and 17.8$\times$ for the quadrotor compared to the one that applies traditional iLQR. Transformer inference is deployed on FPGA to maximize performance, achieving up to 27.3$\times$ speedup over commonly used computing devices, with around 2 to 4$\times$ power reduction and acceptable hardware overhead.
Refining Interactions: Enhancing Anisotropy in Graph Neural Networks with Language Semantics
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) with Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) has recently been explored to enhance the capabilities of Text Attribute Graphs (TAGs). Most existing methods feed textual descriptions of the graph structure or neighbouring nodes' text directly into LLMs. However, these approaches often cause LLMs to treat structural information simply as general contextual text, thus limiting their effectiveness in graph-related tasks. In this paper, we introduce LanSAGNN (Language Semantic Anisotropic Graph Neural Network), a framework that extends the concept of anisotropic GNNs to the natural language level. This model leverages LLMs to extract tailor-made semantic information for node pairs, effectively capturing the unique interactions within node relationships. In addition, we propose an efficient dual-layer LLMs finetuning architecture to better align LLMs' outputs with graph tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that LanSAGNN significantly enhances existing LLM-based methods without increasing complexity while also exhibiting strong robustness against interference.
Facilitating Automated Online Consensus Building through Parallel Thinking
Mar 16, 2025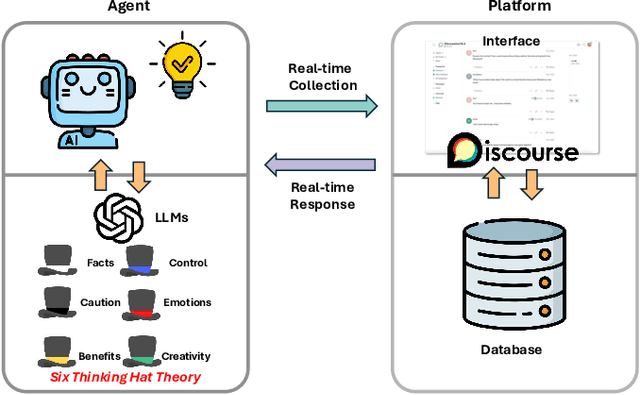

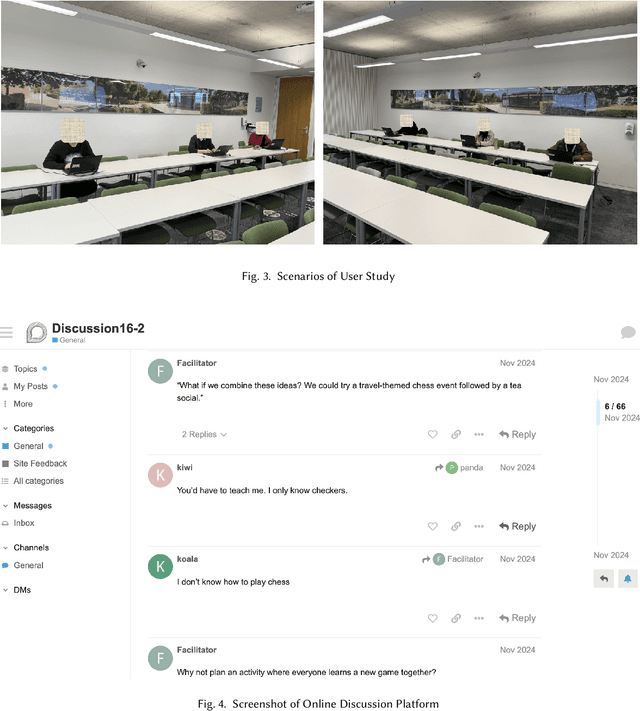
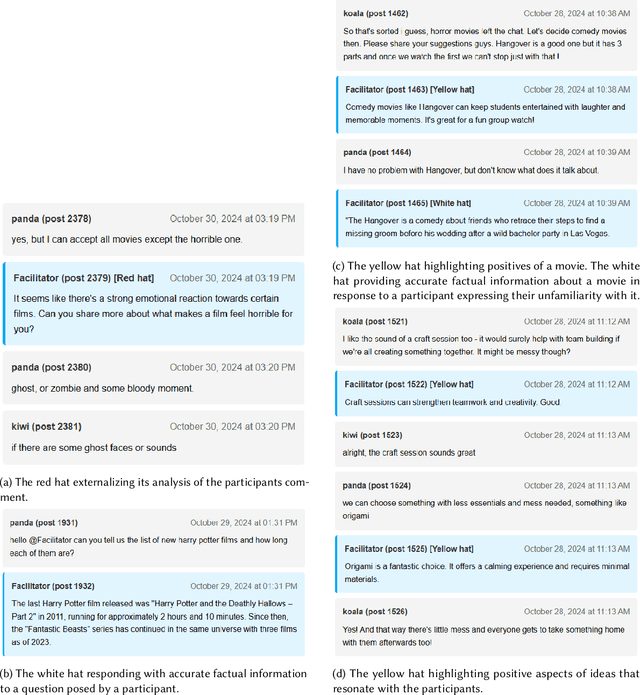
Abstract:Consensus building is inherently challenging due to the diverse opinions held by stakeholders. Effective facilitation is crucial to support the consensus building process and enable efficient group decision making. However, the effectiveness of facilitation is often constrained by human factors such as limited experience and scalability. In this research, we propose a Parallel Thinking-based Facilitation Agent (PTFA) that facilitates online, text-based consensus building processes. The PTFA automatically collects textual posts and leverages large language models (LLMs) to perform all of the six distinct roles of the well-established Six Thinking Hats technique in parallel thinking. To illustrate the potential of PTFA, a pilot study was carried out and PTFA's ability in idea generation, emotional probing, and deeper analysis of ideas was demonstrated. Furthermore, a comprehensive dataset that contains not only the conversational content among the participants but also between the participants and the agent is constructed for future study.
Integrating LSTM and BERT for Long-Sequence Data Analysis in Intelligent Tutoring Systems
Apr 24, 2024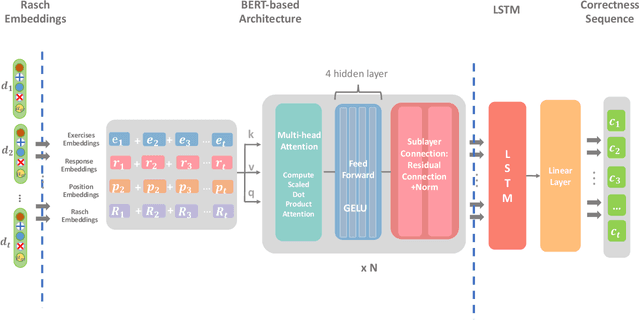
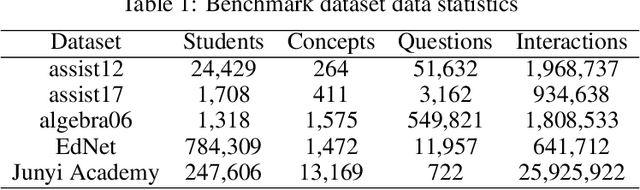
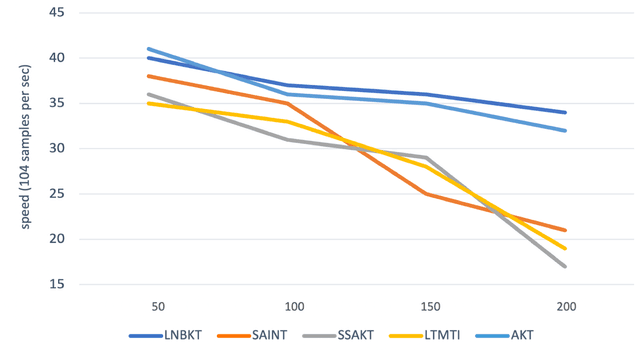
Abstract:The field of Knowledge Tracing aims to understand how students learn and master knowledge over time by analyzing their historical behaviour data. To achieve this goal, many researchers have proposed Knowledge Tracing models that use data from Intelligent Tutoring Systems to predict students' subsequent actions. However, with the development of Intelligent Tutoring Systems, large-scale datasets containing long-sequence data began to emerge. Recent deep learning based Knowledge Tracing models face obstacles such as low efficiency, low accuracy, and low interpretability when dealing with large-scale datasets containing long-sequence data. To address these issues and promote the sustainable development of Intelligent Tutoring Systems, we propose a LSTM BERT-based Knowledge Tracing model for long sequence data processing, namely LBKT, which uses a BERT-based architecture with a Rasch model-based embeddings block to deal with different difficulty levels information and an LSTM block to process the sequential characteristic in students' actions. LBKT achieves the best performance on most benchmark datasets on the metrics of ACC and AUC. Additionally, an ablation study is conducted to analyse the impact of each component of LBKT's overall performance. Moreover, we used t-SNE as the visualisation tool to demonstrate the model's embedding strategy. The results indicate that LBKT is faster, more interpretable, and has a lower memory cost than the traditional deep learning based Knowledge Tracing methods.
LI-Net: Large-Pose Identity-Preserving Face Reenactment Network
Apr 07, 2021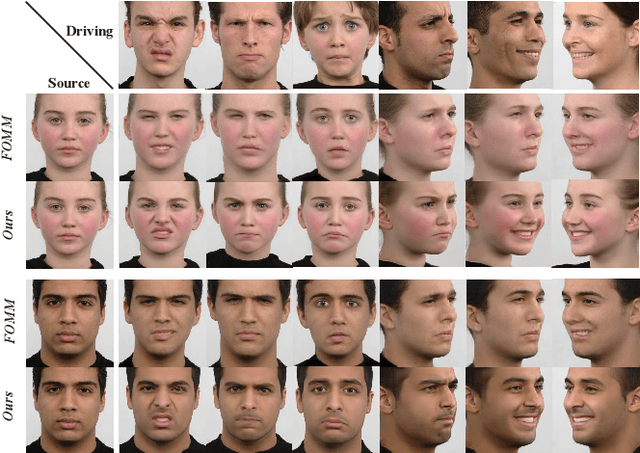



Abstract:Face reenactment is a challenging task, as it is difficult to maintain accurate expression, pose and identity simultaneously. Most existing methods directly apply driving facial landmarks to reenact source faces and ignore the intrinsic gap between two identities, resulting in the identity mismatch issue. Besides, they neglect the entanglement of expression and pose features when encoding driving faces, leading to inaccurate expressions and visual artifacts on large-pose reenacted faces. To address these problems, we propose a Large-pose Identity-preserving face reenactment network, LI-Net. Specifically, the Landmark Transformer is adopted to adjust driving landmark images, which aims to narrow the identity gap between driving and source landmark images. Then the Face Rotation Module and the Expression Enhancing Generator decouple the transformed landmark image into pose and expression features, and reenact those attributes separately to generate identity-preserving faces with accurate expressions and poses. Both qualitative and quantitative experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge