Changle Zhou
Grounding Language with Vision: A Conditional Mutual Information Calibrated Decoding Strategy for Reducing Hallucinations in LVLMs
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) are susceptible to hallucinations, where generated responses seem semantically plausible yet exhibit little or no relevance to the input image. Previous studies reveal that this issue primarily stems from LVLMs' over-reliance on language priors while disregarding the visual information during decoding. To alleviate this issue, we introduce a novel Conditional Pointwise Mutual Information (C-PMI) calibrated decoding strategy, which adaptively strengthens the mutual dependency between generated texts and input images to mitigate hallucinations. Unlike existing methods solely focusing on text token sampling, we propose to jointly model the contributions of visual and textual tokens to C-PMI, formulating hallucination mitigation as a bi-level optimization problem aimed at maximizing mutual information. To solve it, we design a token purification mechanism that dynamically regulates the decoding process by sampling text tokens remaining maximally relevant to the given image, while simultaneously refining image tokens most pertinent to the generated response. Extensive experiments across various benchmarks reveal that the proposed method significantly reduces hallucinations in LVLMs while preserving decoding efficiency.
Error Controlled Actor-Critic
Sep 07, 2021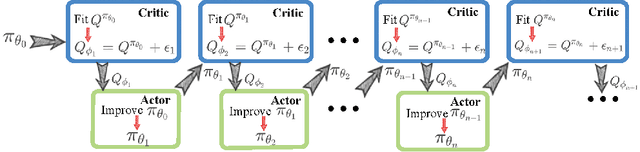
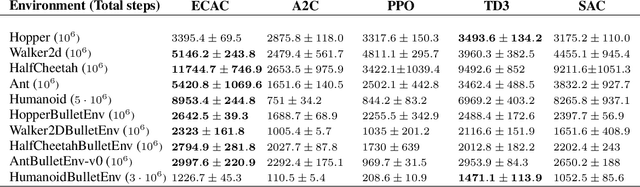
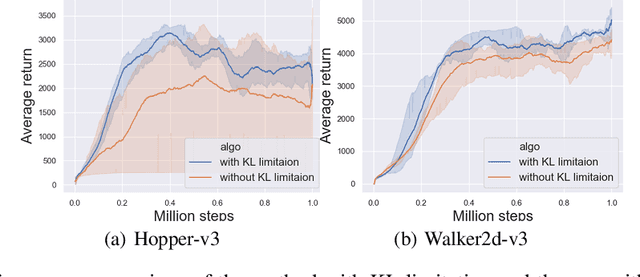
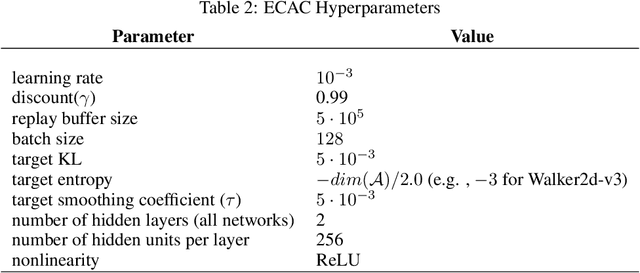
Abstract:On error of value function inevitably causes an overestimation phenomenon and has a negative impact on the convergence of the algorithms. To mitigate the negative effects of the approximation error, we propose Error Controlled Actor-critic which ensures confining the approximation error in value function. We present an analysis of how the approximation error can hinder the optimization process of actor-critic methods.Then, we derive an upper boundary of the approximation error of Q function approximator and find that the error can be lowered by restricting on the KL-divergence between every two consecutive policies when training the policy. The results of experiments on a range of continuous control tasks demonstrate that the proposed actor-critic algorithm apparently reduces the approximation error and significantly outperforms other model-free RL algorithms.
Symbol Grounding via Chaining of Morphisms
Mar 13, 2017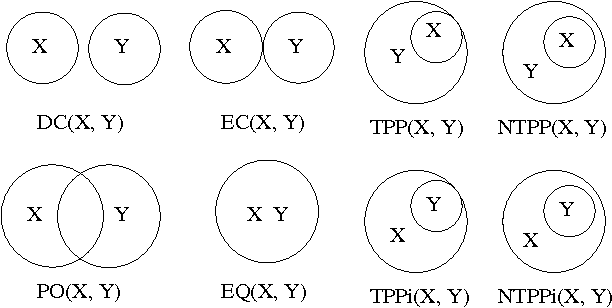
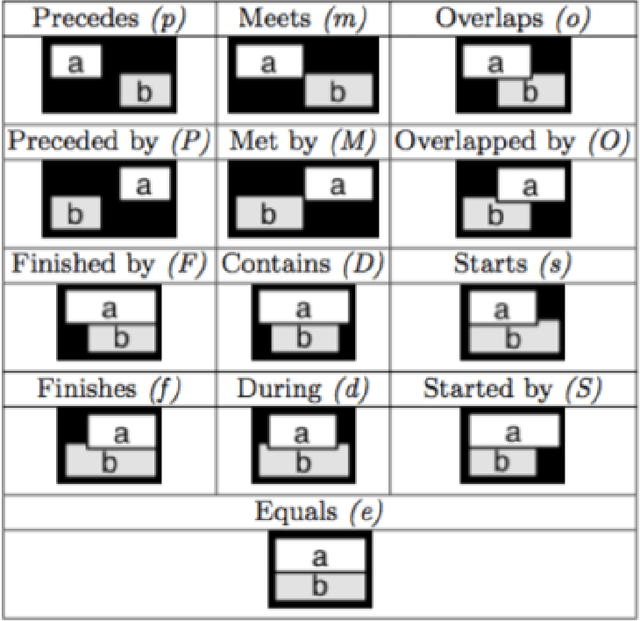
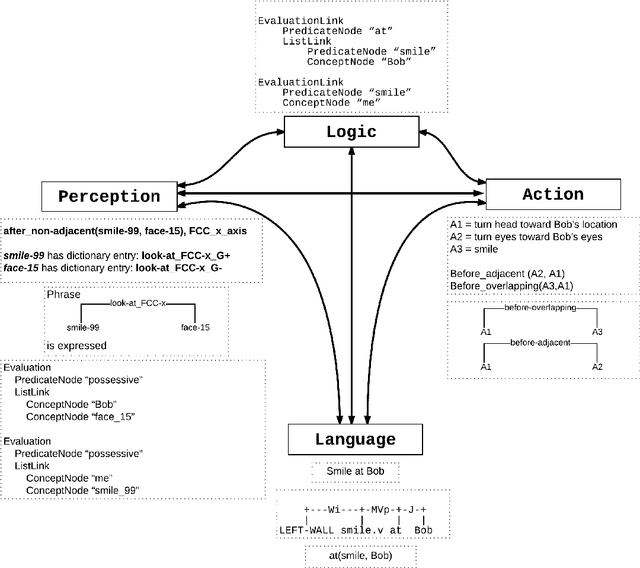
Abstract:A new model of symbol grounding is presented, in which the structures of natural language, logical semantics, perception and action are represented categorically, and symbol grounding is modeled via the composition of morphisms between the relevant categories. This model gives conceptual insight into the fundamentally systematic nature of symbol grounding, and also connects naturally to practical real-world AI systems in current research and commercial use. Specifically, it is argued that the structure of linguistic syntax can be modeled as a certain asymmetric monoidal category, as e.g. implicit in the link grammar formalism; the structure of spatiotemporal relationships and action plans can be modeled similarly using "image grammars" and "action grammars"; and common-sense logical semantic structure can be modeled using dependently-typed lambda calculus with uncertain truth values. Given these formalisms, the grounding of linguistic descriptions in spatiotemporal perceptions and coordinated actions consists of following morphisms from language to logic through to spacetime and body (for comprehension), and vice versa (for generation). The mapping is indicated between the spatial relationships in the Region Connection Calculus and Allen Interval Algebra and corresponding entries in the link grammar syntax parsing dictionary. Further, the abstractions introduced here are shown to naturally model the structures and systems currently being deployed in the context of using the OpenCog cognitive architecture to control Hanson Robotics humanoid robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge