Changjing Shang
3C: Confidence-Guided Clustering and Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification
Aug 18, 2024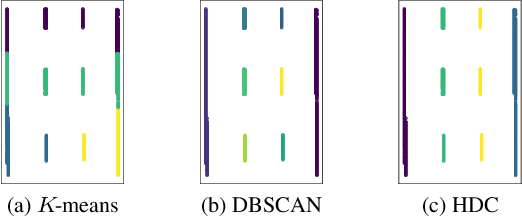

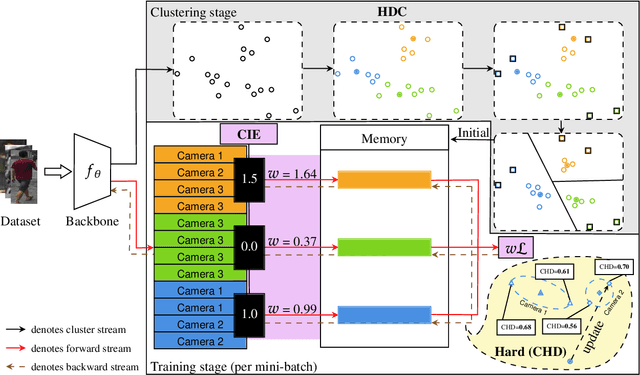

Abstract:Unsupervised person re-identification (Re-ID) aims to learn a feature network with cross-camera retrieval capability in unlabelled datasets. Although the pseudo-label based methods have achieved great progress in Re-ID, their performance in the complex scenario still needs to sharpen up. In order to reduce potential misguidance, including feature bias, noise pseudo-labels and invalid hard samples, accumulated during the learning process, in this pa per, a confidence-guided clustering and contrastive learning (3C) framework is proposed for unsupervised person Re-ID. This 3C framework presents three confidence degrees. i) In the clustering stage, the confidence of the discrepancy between samples and clusters is proposed to implement a harmonic discrepancy clustering algorithm (HDC). ii) In the forward-propagation training stage, the confidence of the camera diversity of a cluster is evaluated via a novel camera information entropy (CIE). Then, the clusters with high CIE values will play leading roles in training the model. iii) In the back-propagation training stage, the confidence of the hard sample in each cluster is designed and further used in a confidence integrated harmonic discrepancy (CHD), to select the informative sample for updating the memory in contrastive learning. Extensive experiments on three popular Re-ID benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of the proposed framework. Particularly, the 3C framework achieves state-of-the-art results: 86.7%/94.7%, 45.3%/73.1% and 47.1%/90.6% in terms of mAP/Rank-1 accuracy on Market-1501, the com plex datasets MSMT17 and VeRi-776, respectively. Code is available at https://github.com/stone5265/3C-reid.
Error Controlled Actor-Critic
Sep 07, 2021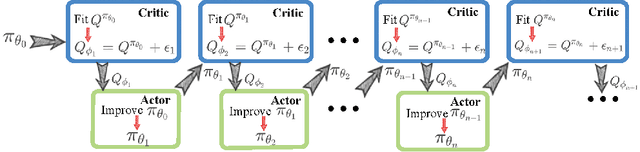
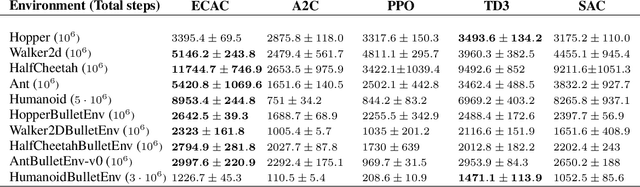
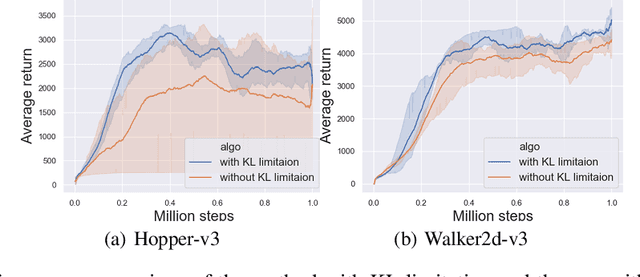
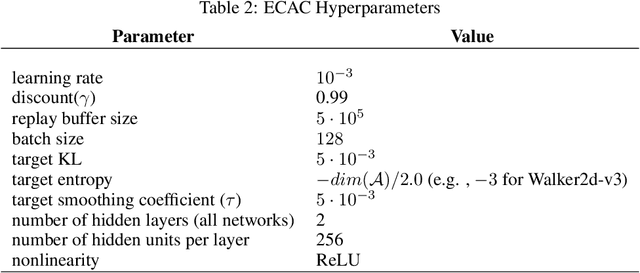
Abstract:On error of value function inevitably causes an overestimation phenomenon and has a negative impact on the convergence of the algorithms. To mitigate the negative effects of the approximation error, we propose Error Controlled Actor-critic which ensures confining the approximation error in value function. We present an analysis of how the approximation error can hinder the optimization process of actor-critic methods.Then, we derive an upper boundary of the approximation error of Q function approximator and find that the error can be lowered by restricting on the KL-divergence between every two consecutive policies when training the policy. The results of experiments on a range of continuous control tasks demonstrate that the proposed actor-critic algorithm apparently reduces the approximation error and significantly outperforms other model-free RL algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge