Pingyi Zhou
XL3M: A Training-free Framework for LLM Length Extension Based on Segment-wise Inference
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Length generalization failure problem, namely the large language model (LLM) fails to generalize to texts longer than its maximum training length, greatly restricts the application of LLM in the scenarios with streaming long inputs. To address this problem, the existing methods either require substantial costs or introduce precision loss. In this paper, we empirically find that the accuracy of the LLM's prediction is highly correlated to its certainty. Based on this, we propose an efficient training free framework, named XL3M (it means extra-long large language model), which enables the LLMs trained on short sequences to reason extremely long sequence without any further training or fine-tuning. Under the XL3M framework, the input context will be firstly decomposed into multiple short sub-contexts, where each sub-context contains an independent segment and a common ``question'' which is a few tokens from the end of the original context. Then XL3M gives a method to measure the relevance between each segment and the ``question'', and constructs a concise key context by splicing all the relevant segments in chronological order. The key context is further used instead of the original context to complete the inference task. Evaluations on comprehensive benchmarks show the superiority of XL3M. Using our framework, a Llama2-7B model is able to reason 20M long sequences on an 8-card Huawei Ascend 910B NPU machine with 64GB memory per card.
Extending Context Window of Large Language Models via Semantic Compression
Dec 15, 2023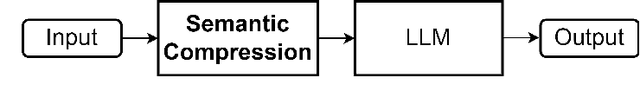
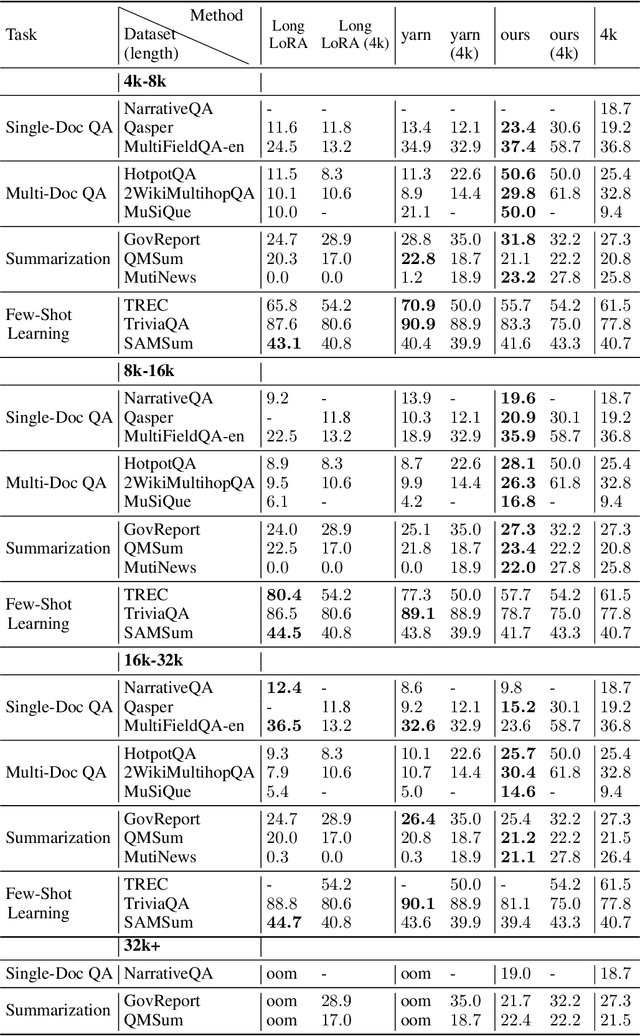
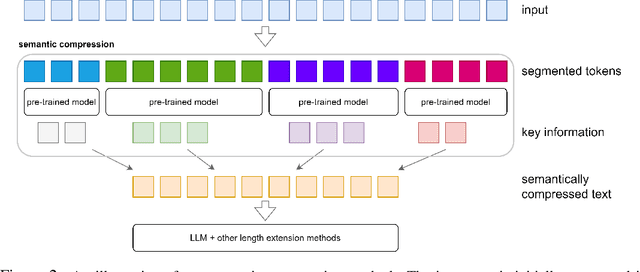
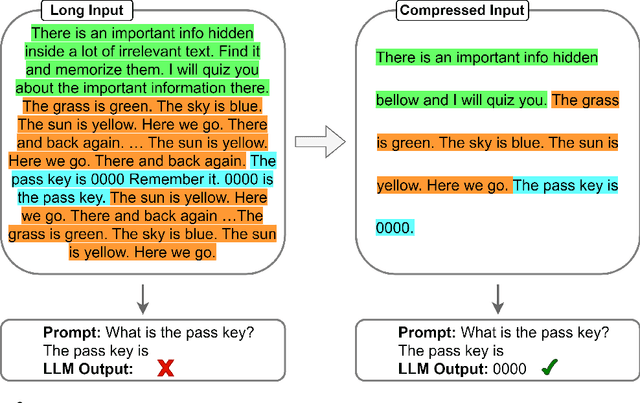
Abstract:Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) often impose limitations on the length of the text input to ensure the generation of fluent and relevant responses. This constraint restricts their applicability in scenarios involving long texts. We propose a novel semantic compression method that enables generalization to texts that are 6-8 times longer, without incurring significant computational costs or requiring fine-tuning. Our proposed framework draws inspiration from source coding in information theory and employs a pre-trained model to reduce the semantic redundancy of long inputs before passing them to the LLMs for downstream tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively extends the context window of LLMs across a range of tasks including question answering, summarization, few-shot learning, and information retrieval. Furthermore, the proposed semantic compression method exhibits consistent fluency in text generation while reducing the associated computational overhead.
PanGu-Σ: Towards Trillion Parameter Language Model with Sparse Heterogeneous Computing
Mar 20, 2023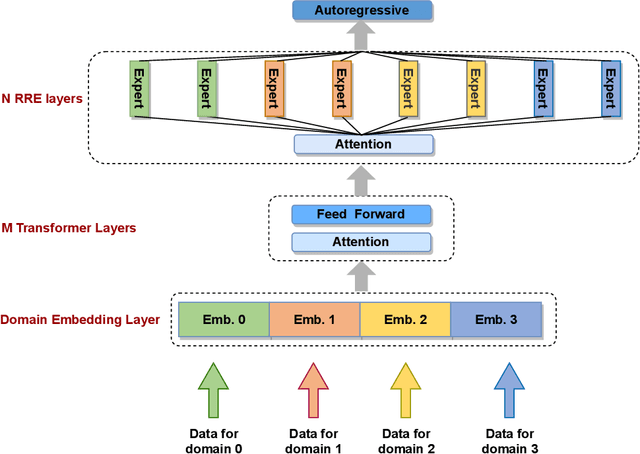
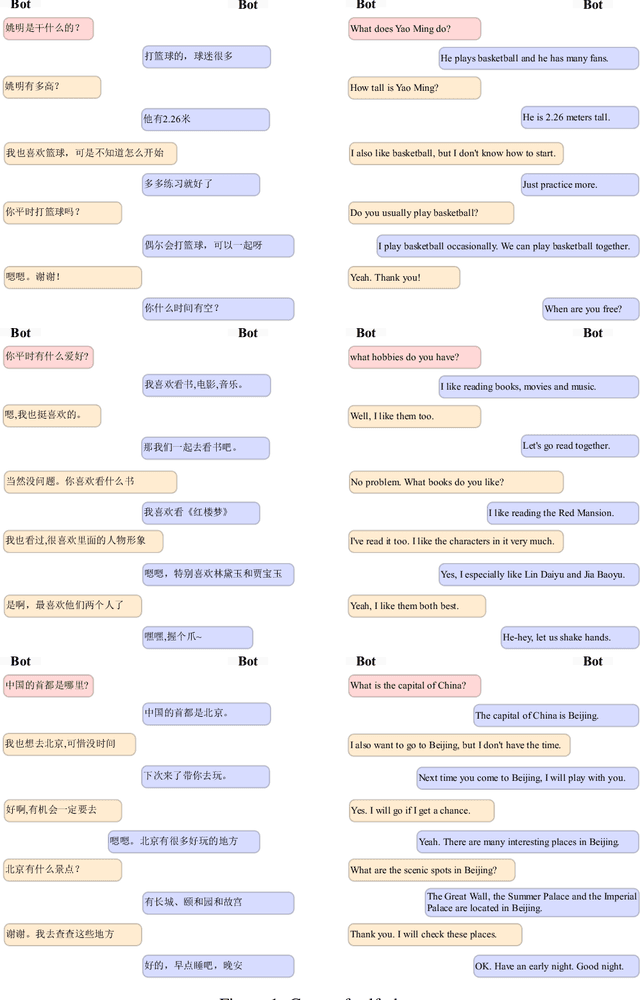
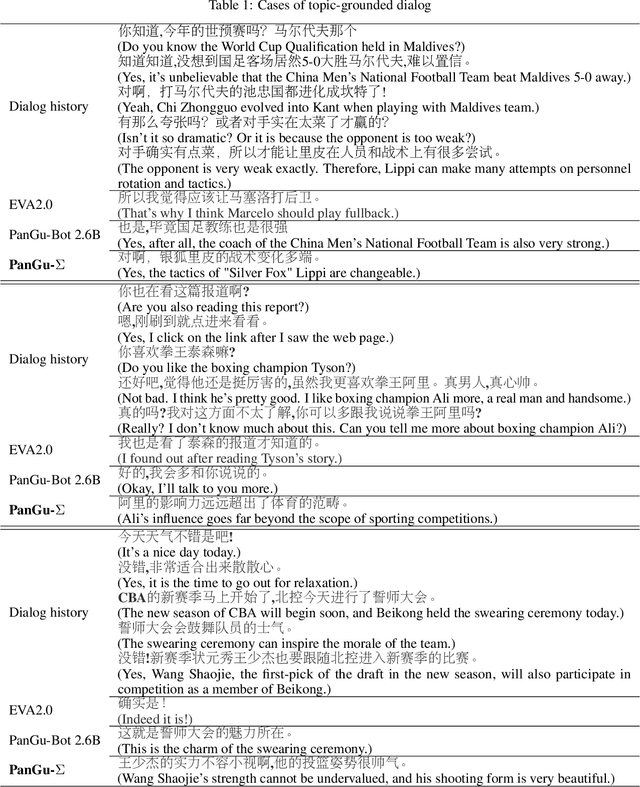
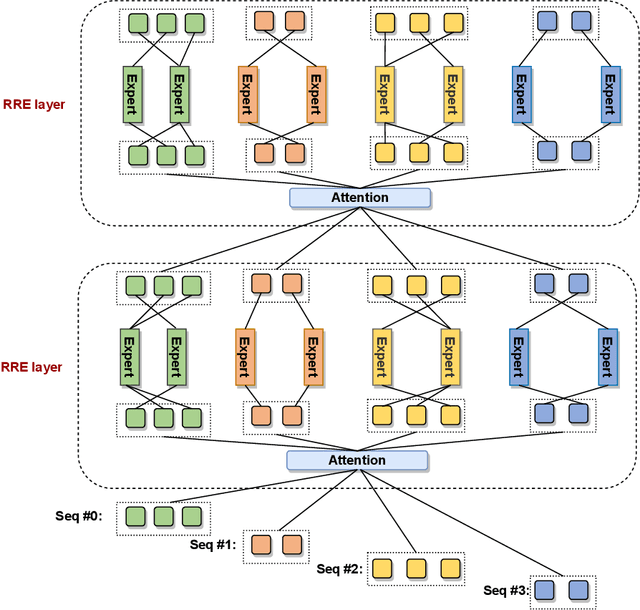
Abstract:The scaling of large language models has greatly improved natural language understanding, generation, and reasoning. In this work, we develop a system that trained a trillion-parameter language model on a cluster of Ascend 910 AI processors and MindSpore framework, and present the language model with 1.085T parameters named PanGu-{\Sigma}. With parameter inherent from PanGu-{\alpha}, we extend the dense Transformer model to sparse one with Random Routed Experts (RRE), and efficiently train the model over 329B tokens by using Expert Computation and Storage Separation(ECSS). This resulted in a 6.3x increase in training throughput through heterogeneous computing. Our experimental findings show that PanGu-{\Sigma} provides state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot learning of various Chinese NLP downstream tasks. Moreover, it demonstrates strong abilities when fine-tuned in application data of open-domain dialogue, question answering, machine translation and code generation.
MultiCoder: Multi-Programming-Lingual Pre-Training for Low-Resource Code Completion
Dec 19, 2022Abstract:Code completion is a valuable topic in both academia and industry. Recently, large-scale mono-programming-lingual (MonoPL) pre-training models have been proposed to boost the performance of code completion. However, the code completion on low-resource programming languages (PL) is difficult for the data-driven paradigm, while there are plenty of developers using low-resource PLs. On the other hand, there are few studies exploring the effects of multi-programming-lingual (MultiPL) pre-training for the code completion, especially the impact on low-resource programming languages. To this end, we propose the MultiCoder to enhance the low-resource code completion via MultiPL pre-training and MultiPL Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) layers. We further propose a novel PL-level MoE routing strategy (PL-MoE) for improving the code completion on all PLs. Experimental results on CodeXGLUE and MultiCC demonstrate that 1) the proposed MultiCoder significantly outperforms the MonoPL baselines on low-resource programming languages, and 2) the PL-MoE module further boosts the performance on six programming languages. In addition, we analyze the effects of the proposed method in details and explore the effectiveness of our method in a variety of scenarios.
PanGu-Coder: Program Synthesis with Function-Level Language Modeling
Jul 22, 2022
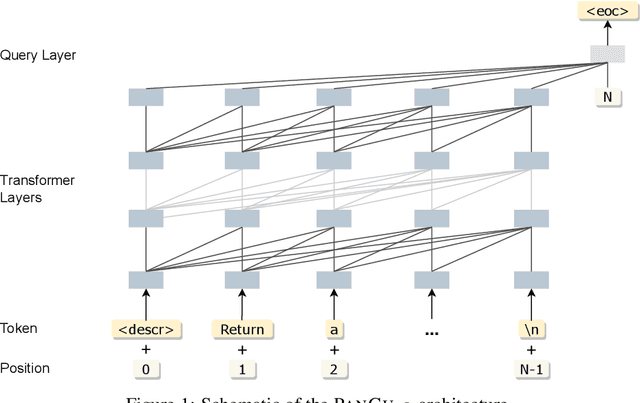
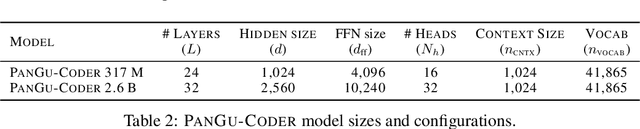
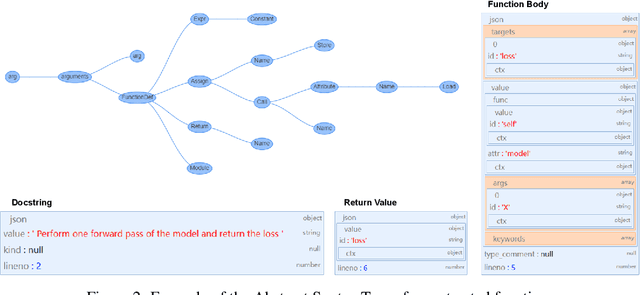
Abstract:We present PanGu-Coder, a pretrained decoder-only language model adopting the PanGu-Alpha architecture for text-to-code generation, i.e. the synthesis of programming language solutions given a natural language problem description. We train PanGu-Coder using a two-stage strategy: the first stage employs Causal Language Modelling (CLM) to pre-train on raw programming language data, while the second stage uses a combination of Causal Language Modelling and Masked Language Modelling (MLM) training objectives that focus on the downstream task of text-to-code generation and train on loosely curated pairs of natural language program definitions and code functions. Finally, we discuss PanGu-Coder-FT, which is fine-tuned on a combination of competitive programming problems and code with continuous integration tests. We evaluate PanGu-Coder with a focus on whether it generates functionally correct programs and demonstrate that it achieves equivalent or better performance than similarly sized models, such as CodeX, while attending a smaller context window and training on less data.
CODE-MVP: Learning to Represent Source Code from Multiple Views with Contrastive Pre-Training
May 04, 2022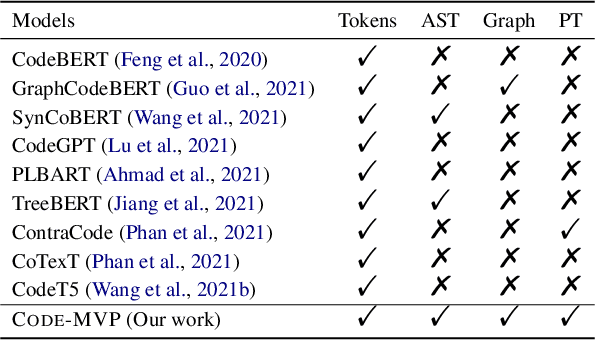
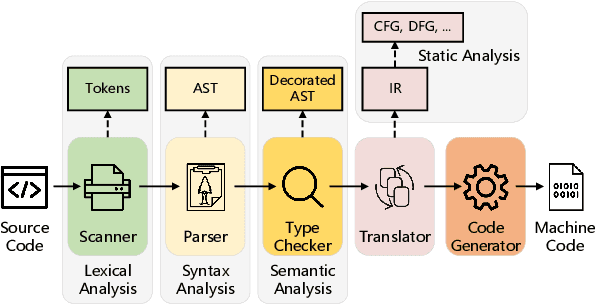
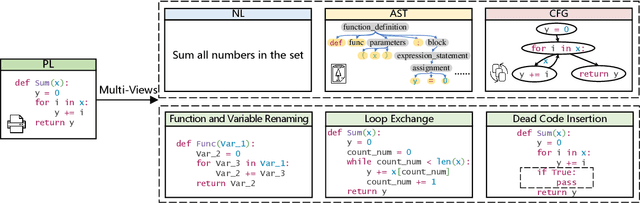
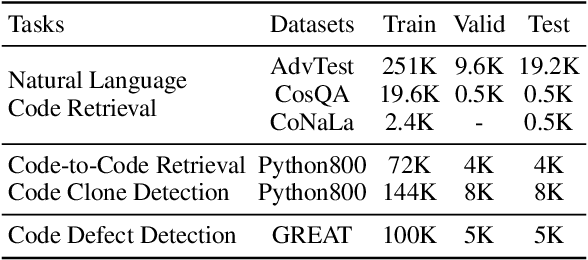
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed increasing interest in code representation learning, which aims to represent the semantics of source code into distributed vectors. Currently, various works have been proposed to represent the complex semantics of source code from different views, including plain text, Abstract Syntax Tree (AST), and several kinds of code graphs (e.g., Control/Data Flow Graph). However, most of them only consider a single view of source code independently, ignoring the correspondences among different views. In this paper, we propose to integrate different views with the natural-language description of source code into a unified framework with Multi-View contrastive Pre-training, and name our model as CODE-MVP. Specifically, we first extract multiple code views using compiler tools, and learn the complementary information among them under a contrastive learning framework. Inspired by the type checking in compilation, we also design a fine-grained type inference objective in the pre-training. Experiments on three downstream tasks over five datasets demonstrate the superiority of CODE-MVP when compared with several state-of-the-art baselines. For example, we achieve 2.4/2.3/1.1 gain in terms of MRR/MAP/Accuracy metrics on natural language code retrieval, code similarity, and code defect detection tasks, respectively.
Compilable Neural Code Generation with Compiler Feedback
Mar 10, 2022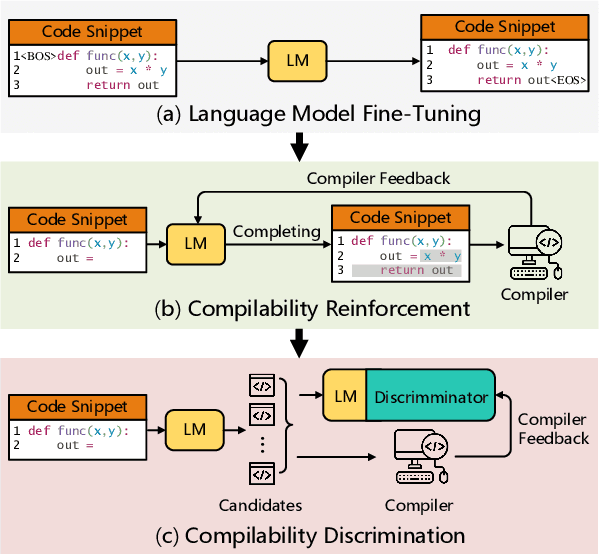
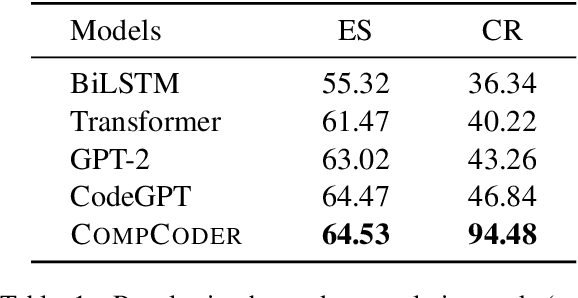
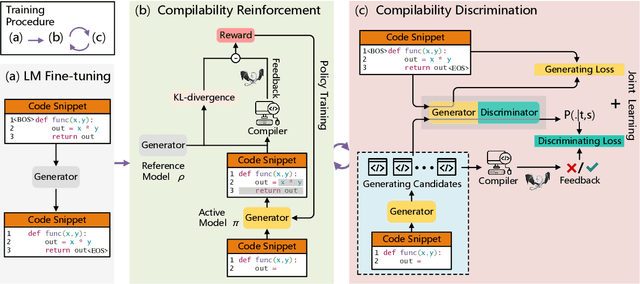
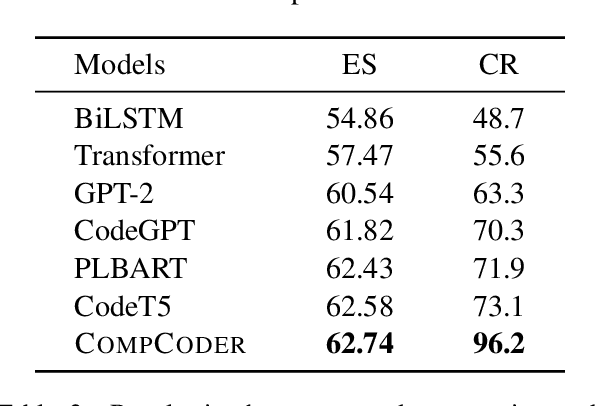
Abstract:Automatically generating compilable programs with (or without) natural language descriptions has always been a touchstone problem for computational linguistics and automated software engineering. Existing deep-learning approaches model code generation as text generation, either constrained by grammar structures in decoder, or driven by pre-trained language models on large-scale code corpus (e.g., CodeGPT, PLBART, and CodeT5). However, few of them account for compilability of the generated programs. To improve compilability of the generated programs, this paper proposes COMPCODER, a three-stage pipeline utilizing compiler feedback for compilable code generation, including language model fine-tuning, compilability reinforcement, and compilability discrimination. Comprehensive experiments on two code generation tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach, improving the success rate of compilation from 44.18 to 89.18 in code completion on average and from 70.3 to 96.2 in text-to-code generation, respectively, when comparing with the state-of-the-art CodeGPT.
Pan More Gold from the Sand: Refining Open-domain Dialogue Training with Noisy Self-Retrieval Generation
Jan 27, 2022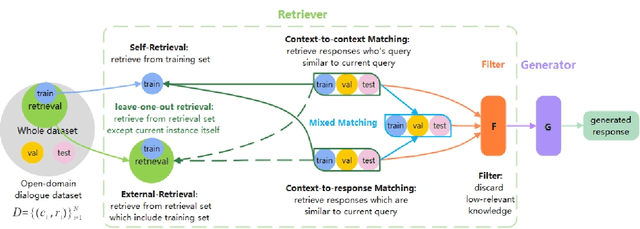
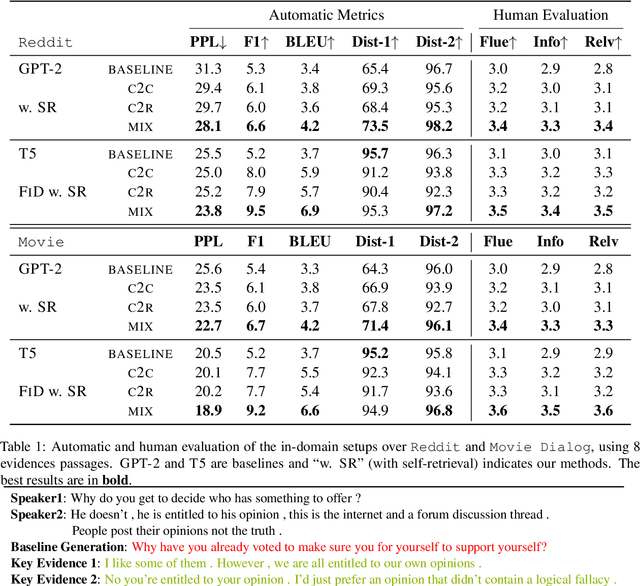
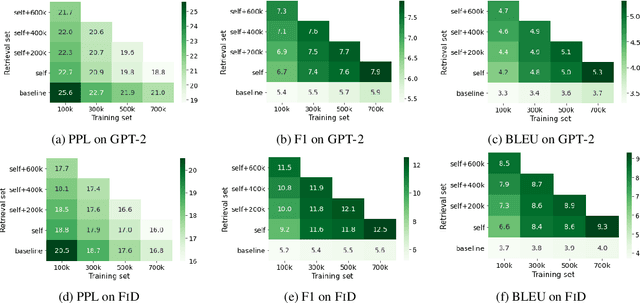
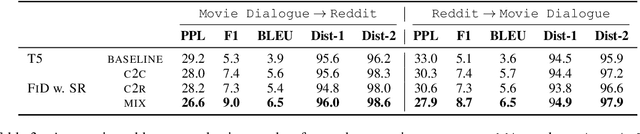
Abstract:Real human conversation data are complicated, heterogeneous, and noisy, from whom building open-domain dialogue systems remains a challenging task. In fact, such dialogue data can still contain a wealth of information and knowledge, however, they are not fully explored. In this paper, we show existing open-domain dialogue generation methods by memorizing context-response paired data with causal or encode-decode language models underutilize the training data. Different from current approaches, using external knowledge, we explore a retrieval-generation training framework that can increase the usage of training data by directly considering the heterogeneous and noisy training data as the "evidence". Experiments over publicly available datasets demonstrate that our method can help models generate better responses, even such training data are usually impressed as low-quality data. Such performance gain is comparable with those improved by enlarging the training set, even better. We also found that the model performance has a positive correlation with the relevance of the retrieved evidence. Moreover, our method performed well on zero-shot experiments, which indicates that our method can be more robust to real-world data.
SynCoBERT: Syntax-Guided Multi-Modal Contrastive Pre-Training for Code Representation
Sep 09, 2021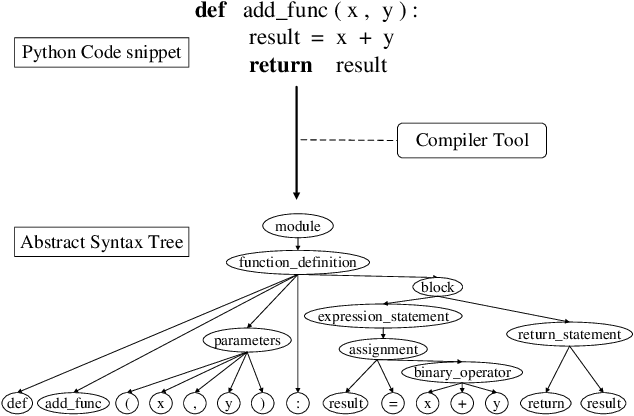
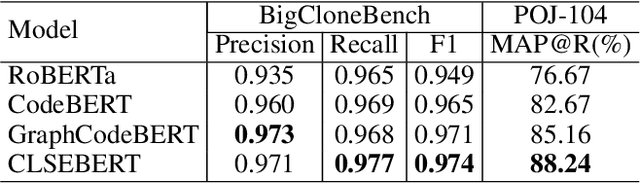

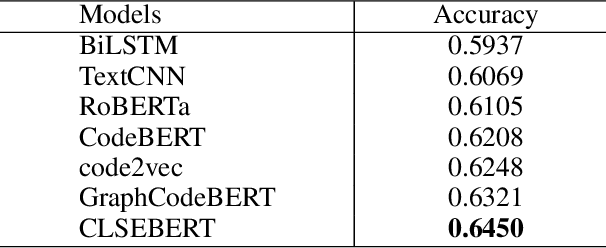
Abstract:Code representation learning, which aims to encode the semantics of source code into distributed vectors, plays an important role in recent deep-learning-based models for code intelligence. Recently, many pre-trained language models for source code (e.g., CuBERT and CodeBERT) have been proposed to model the context of code and serve as a basis for downstream code intelligence tasks such as code search, code clone detection, and program translation. Current approaches typically consider the source code as a plain sequence of tokens, or inject the structure information (e.g., AST and data-flow) into the sequential model pre-training. To further explore the properties of programming languages, this paper proposes SynCoBERT, a syntax-guided multi-modal contrastive pre-training approach for better code representations. Specially, we design two novel pre-training objectives originating from the symbolic and syntactic properties of source code, i.e., Identifier Prediction (IP) and AST Edge Prediction (TEP), which are designed to predict identifiers, and edges between two nodes of AST, respectively. Meanwhile, to exploit the complementary information in semantically equivalent modalities (i.e., code, comment, AST) of the code, we propose a multi-modal contrastive learning strategy to maximize the mutual information among different modalities. Extensive experiments on four downstream tasks related to code intelligence show that SynCoBERT advances the state-of-the-art with the same pre-training corpus and model size.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge