Peng Wei
WebClipper: Efficient Evolution of Web Agents with Graph-based Trajectory Pruning
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Deep Research systems based on web agents have shown strong potential in solving complex information-seeking tasks, yet their search efficiency remains underexplored. We observe that many state-of-the-art open-source web agents rely on long tool-call trajectories with cyclic reasoning loops and exploration of unproductive branches. To address this, we propose WebClipper, a framework that compresses web agent trajectories via graph-based pruning. Concretely, we model the agent's search process as a state graph and cast trajectory optimization as a minimum-necessary Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) mining problem, yielding pruned trajectories that preserve essential reasoning while eliminating redundant steps. Continued training on these refined trajectories enables the agent to evolve toward more efficient search patterns and reduces tool-call rounds by about 20% while improving accuracy. Furthermore, we introduce a new metric called F-AE Score to measure the model's overall performance in balancing accuracy and efficiency. Experiments demonstrate that WebClipper compresses tool-call rounds under excellent performance, providing practical insight into balancing effectiveness and efficiency in web agent design.
Relative Wasserstein Angle and the Problem of the $W_2$-Nearest Gaussian Distribution
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:We study the problem of quantifying how far an empirical distribution deviates from Gaussianity under the framework of optimal transport. By exploiting the cone geometry of the relative translation invariant quadratic Wasserstein space, we introduce two novel geometric quantities, the relative Wasserstein angle and the orthogonal projection distance, which provide meaningful measures of non-Gaussianity. We prove that the filling cone generated by any two rays in this space is flat, ensuring that angles, projections, and inner products are rigorously well-defined. This geometric viewpoint recasts Gaussian approximation as a projection problem onto the Gaussian cone and reveals that the commonly used moment-matching Gaussian can \emph{not} be the \(W_2\)-nearest Gaussian for a given empirical distribution. In one dimension, we derive closed-form expressions for the proposed quantities and extend them to several classical distribution families, including uniform, Laplace, and logistic distributions; while in high dimensions, we develop an efficient stochastic manifold optimization algorithm based on a semi-discrete dual formulation. Experiments on synthetic data and real-world feature distributions demonstrate that the relative Wasserstein angle is more robust than the Wasserstein distance and that the proposed nearest Gaussian provides a better approximation than moment matching in the evaluation of Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) scores.
Transformer-based Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning for Separation Assurance in Structured and Unstructured Airspaces
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Conventional optimization-based metering depends on strict adherence to precomputed schedules, which limits the flexibility required for the stochastic operations of Advanced Air Mobility (AAM). In contrast, multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) offers a decentralized, adaptive framework that can better handle uncertainty, required for safe aircraft separation assurance. Despite this advantage, current MARL approaches often overfit to specific airspace structures, limiting their adaptability to new configurations. To improve generalization, we recast the MARL problem in a relative polar state space and train a transformer encoder model across diverse traffic patterns and intersection angles. The learned model provides speed advisories to resolve conflicts while maintaining aircraft near their desired cruising speeds. In our experiments, we evaluated encoder depths of 1, 2, and 3 layers in both structured and unstructured airspaces, and found that a single encoder configuration outperformed deeper variants, yielding near-zero near mid-air collision rates and shorter loss-of-separation infringements than the deeper configurations. Additionally, we showed that the same configuration outperforms a baseline model designed purely with attention. Together, our results suggest that the newly formulated state representation, novel design of neural network architecture, and proposed training strategy provide an adaptable and scalable decentralized solution for aircraft separation assurance in both structured and unstructured airspaces.
MedDialogRubrics: A Comprehensive Benchmark and Evaluation Framework for Multi-turn Medical Consultations in Large Language Models
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Medical conversational AI (AI) plays a pivotal role in the development of safer and more effective medical dialogue systems. However, existing benchmarks and evaluation frameworks for assessing the information-gathering and diagnostic reasoning abilities of medical large language models (LLMs) have not been rigorously evaluated. To address these gaps, we present MedDialogRubrics, a novel benchmark comprising 5,200 synthetically constructed patient cases and over 60,000 fine-grained evaluation rubrics generated by LLMs and subsequently refined by clinical experts, specifically designed to assess the multi-turn diagnostic capabilities of LLM. Our framework employs a multi-agent system to synthesize realistic patient records and chief complaints from underlying disease knowledge without accessing real-world electronic health records, thereby mitigating privacy and data-governance concerns. We design a robust Patient Agent that is limited to a set of atomic medical facts and augmented with a dynamic guidance mechanism that continuously detects and corrects hallucinations throughout the dialogue, ensuring internal coherence and clinical plausibility of the simulated cases. Furthermore, we propose a structured LLM-based and expert-annotated rubric-generation pipeline that retrieves Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM) guidelines and utilizes the reject sampling to derive a prioritized set of rubric items ("must-ask" items) for each case. We perform a comprehensive evaluation of state-of-the-art models and demonstrate that, across multiple assessment dimensions, current models face substantial challenges. Our results indicate that improving medical dialogue will require advances in dialogue management architectures, not just incremental tuning of the base-model.
Multi-Agent Deep Research: Training Multi-Agent Systems with M-GRPO
Nov 18, 2025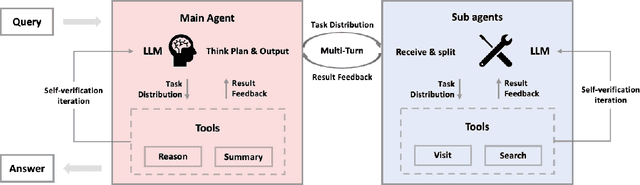
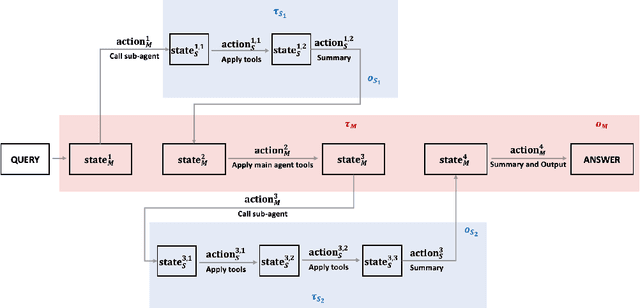
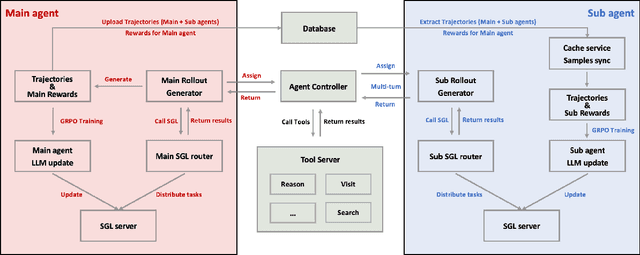
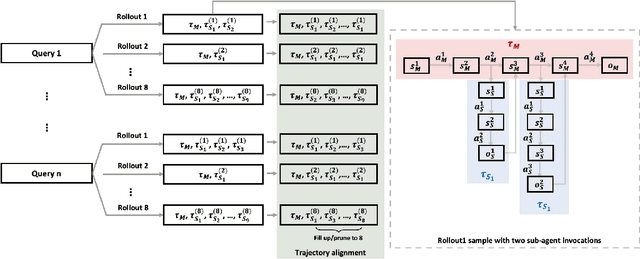
Abstract:Multi-agent systems perform well on general reasoning tasks. However, the lack of training in specialized areas hinders their accuracy. Current training methods train a unified large language model (LLM) for all agents in the system. This may limit the performances due to different distributions underlying for different agents. Therefore, training multi-agent systems with distinct LLMs should be the next step to solve. However, this approach introduces optimization challenges. For example, agents operate at different frequencies, rollouts involve varying sub-agent invocations, and agents are often deployed across separate servers, disrupting end-to-end gradient flow. To address these issues, we propose M-GRPO, a hierarchical extension of Group Relative Policy Optimization designed for vertical Multi-agent systems with a main agent (planner) and multiple sub-agents (multi-turn tool executors). M-GRPO computes group-relative advantages for both main and sub-agents, maintaining hierarchical credit assignment. It also introduces a trajectory-alignment scheme that generates fixed-size batches despite variable sub-agent invocations. We deploy a decoupled training pipeline in which agents run on separate servers and exchange minimal statistics via a shared store. This enables scalable training without cross-server backpropagation. In experiments on real-world benchmarks (e.g., GAIA, XBench-DeepSearch, and WebWalkerQA), M-GRPO consistently outperforms both single-agent GRPO and multi-agent GRPO with frozen sub-agents, demonstrating improved stability and sample efficiency. These results show that aligning heterogeneous trajectories and decoupling optimization across specialized agents enhances tool-augmented reasoning tasks.
GroupRank: A Groupwise Reranking Paradigm Driven by Reinforcement Learning
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models have shown strong potential as rerankers to enhance the overall performance of RAG systems. However, existing reranking paradigms are constrained by a core theoretical and practical dilemma: Pointwise methods, while simple and highly flexible, evaluate documents independently, making them prone to the Ranking Myopia Trap, overlooking the relative importance between documents. In contrast, Listwise methods can perceive the global ranking context, but suffer from inherent List Rigidity, leading to severe scalability and flexibility issues when handling large candidate sets. To address these challenges, we propose Groupwise, a novel reranking paradigm. In this approach, the query and a group of candidate documents are jointly fed into the model, which performs within-group comparisons to assign individual relevance scores to each document. This design retains the flexibility of Pointwise methods while enabling the comparative capability of Listwise methods. We further adopt GRPO for model training, equipped with a heterogeneous reward function that integrates ranking metrics with a distributional reward aimed at aligning score distributions across groups. To overcome the bottleneck caused by the scarcity of high quality labeled data, we further propose an innovative pipeline for synthesizing high quality retrieval and ranking data. The resulting data can be leveraged not only for training the reranker but also for training the retriever. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach. On two reasoning intensive retrieval benchmarks, BRIGHT and R2MED.
MedReseacher-R1: Expert-Level Medical Deep Researcher via A Knowledge-Informed Trajectory Synthesis Framework
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Recent developments in Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have shown impressive capabilities spanning multiple domains, exemplified by deep research systems that demonstrate superior performance on complex information-seeking and synthesis tasks. While general-purpose deep research agents have shown impressive capabilities, they struggle significantly with medical domain challenges, as evidenced by leading proprietary systems achieving limited accuracy on complex medical benchmarks. The key limitations are: (1) the model lacks sufficient dense medical knowledge for clinical reasoning, and (2) the framework is constrained by the absence of specialized retrieval tools tailored for medical contexts.We present a medical deep research agent that addresses these challenges through two core innovations. First, we develop a novel data synthesis framework using medical knowledge graphs, extracting the longest chains from subgraphs around rare medical entities to generate complex multi-hop question-answer pairs. Second, we integrate a custom-built private medical retrieval engine alongside general-purpose tools, enabling accurate medical information synthesis. Our approach generates 2100+ diverse trajectories across 12 medical specialties, each averaging 4.2 tool interactions.Through a two-stage training paradigm combining supervised fine-tuning and online reinforcement learning with composite rewards, our MedResearcher-R1-32B model demonstrates exceptional performance, establishing new state-of-the-art results on medical benchmarks while maintaining competitive performance on general deep research tasks. Our work demonstrates that strategic domain-specific innovations in architecture, tool design, and training data construction can enable smaller open-source models to outperform much larger proprietary systems in specialized domains.
DIVER: A Multi-Stage Approach for Reasoning-intensive Information Retrieval
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation has achieved strong performance on knowledge-intensive tasks where query-document relevance can be identified through direct lexical or semantic matches. However, many real-world queries involve abstract reasoning, analogical thinking, or multi-step inference, which existing retrievers often struggle to capture. To address this challenge, we present \textbf{DIVER}, a retrieval pipeline tailored for reasoning-intensive information retrieval. DIVER consists of four components: document processing to improve input quality, LLM-driven query expansion via iterative document interaction, a reasoning-enhanced retriever fine-tuned on synthetic multi-domain data with hard negatives, and a pointwise reranker that combines LLM-assigned helpfulness scores with retrieval scores. On the BRIGHT benchmark, DIVER achieves state-of-the-art nDCG@10 scores of 41.6 and 28.9 on original queries, consistently outperforming competitive reasoning-aware models. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of reasoning-aware retrieval strategies in complex real-world tasks. Our code and retrieval model will be released soon.
Learning to Align, Aligning to Learn: A Unified Approach for Self-Optimized Alignment
Aug 11, 2025



Abstract:Alignment methodologies have emerged as a critical pathway for enhancing language model alignment capabilities. While SFT (supervised fine-tuning) accelerates convergence through direct token-level loss intervention, its efficacy is constrained by offline policy trajectory. In contrast, RL(reinforcement learning) facilitates exploratory policy optimization, but suffers from low sample efficiency and stringent dependency on high-quality base models. To address these dual challenges, we propose GRAO (Group Relative Alignment Optimization), a unified framework that synergizes the respective strengths of SFT and RL through three key innovations: 1) A multi-sample generation strategy enabling comparative quality assessment via reward feedback; 2) A novel Group Direct Alignment Loss formulation leveraging intra-group relative advantage weighting; 3) Reference-aware parameter updates guided by pairwise preference dynamics. Our theoretical analysis establishes GRAO's convergence guarantees and sample efficiency advantages over conventional approaches. Comprehensive evaluations across complex human alignment tasks demonstrate GRAO's superior performance, achieving 57.70\%,17.65\% 7.95\% and 5.18\% relative improvements over SFT, DPO, PPO and GRPO baselines respectively. This work provides both a theoretically grounded alignment framework and empirical evidence for efficient capability evolution in language models.
Towards provable probabilistic safety for scalable embodied AI systems
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Embodied AI systems, comprising AI models and physical plants, are increasingly prevalent across various applications. Due to the rarity of system failures, ensuring their safety in complex operating environments remains a major challenge, which severely hinders their large-scale deployment in safety-critical domains, such as autonomous vehicles, medical devices, and robotics. While achieving provable deterministic safety--verifying system safety across all possible scenarios--remains theoretically ideal, the rarity and complexity of corner cases make this approach impractical for scalable embodied AI systems. To address this challenge, we introduce provable probabilistic safety, which aims to ensure that the residual risk of large-scale deployment remains below a predefined threshold. Instead of attempting exhaustive safety proof across all corner cases, this paradigm establishes a probabilistic safety boundary on overall system performance, leveraging statistical methods to enhance feasibility and scalability. A well-defined probabilistic safety boundary enables embodied AI systems to be deployed at scale while allowing for continuous refinement of safety guarantees. Our work focuses on three core questions: what is provable probabilistic safety, how to prove the probabilistic safety, and how to achieve the provable probabilistic safety. By bridging the gap between theoretical safety assurance and practical deployment, our work offers a pathway toward safer, large-scale adoption of embodied AI systems in safety-critical applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge