Yujing Lu
TRE: Encouraging Exploration in the Trust Region
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Entropy regularization is a standard technique in reinforcement learning (RL) to enhance exploration, yet it yields negligible effects or even degrades performance in Large Language Models (LLMs). We attribute this failure to the cumulative tail risk inherent to LLMs with massive vocabularies and long generation horizons. In such environments, standard global entropy maximization indiscriminately dilutes probability mass into the vast tail of invalid tokens rather than focusing on plausible candidates, thereby disrupting coherent reasoning. To address this, we propose Trust Region Entropy (TRE), a method that encourages exploration strictly within the model's trust region. Extensive experiments across mathematical reasoning (MATH), combinatorial search (Countdown), and preference alignment (HH) tasks demonstrate that TRE consistently outperforms vanilla PPO, standard entropy regularization, and other exploration baselines. Our code is available at https://github.com/WhyChaos/TRE-Encouraging-Exploration-in-the-Trust-Region.
DomainCQA: Crafting Expert-Level QA from Domain-Specific Charts
Mar 25, 2025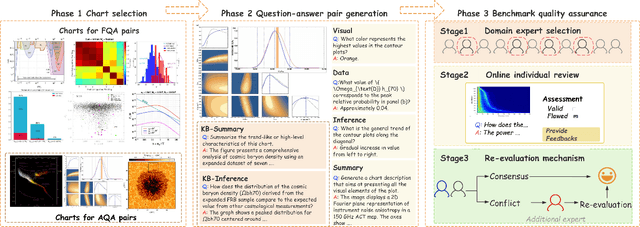
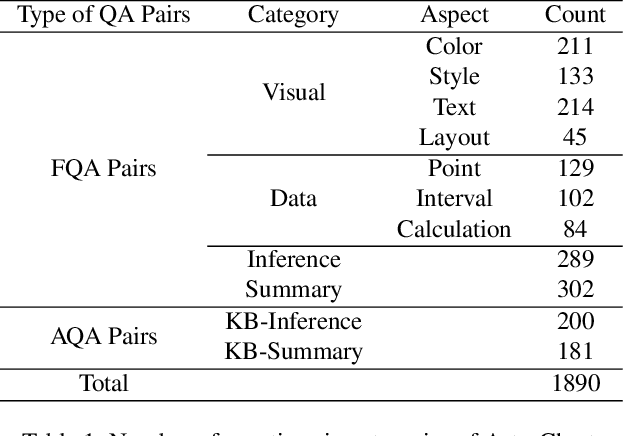
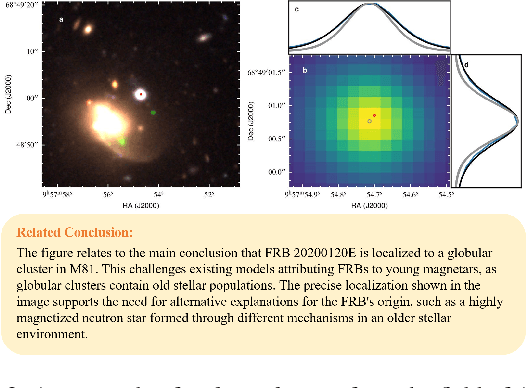
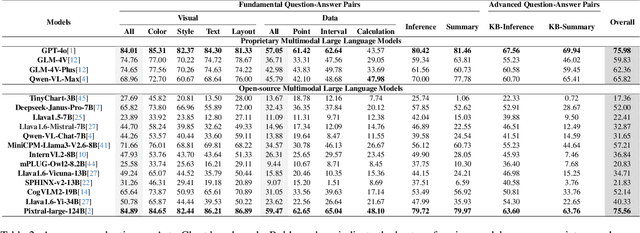
Abstract:Chart Question Answering (CQA) benchmarks are essential for evaluating the capability of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to interpret visual data. However, current benchmarks focus primarily on the evaluation of general-purpose CQA but fail to adequately capture domain-specific challenges. We introduce DomainCQA, a systematic methodology for constructing domain-specific CQA benchmarks, and demonstrate its effectiveness by developing AstroChart, a CQA benchmark in the field of astronomy. Our evaluation shows that chart reasoning and combining chart information with domain knowledge for deeper analysis and summarization, rather than domain-specific knowledge, pose the primary challenge for existing MLLMs, highlighting a critical gap in current benchmarks. By providing a scalable and rigorous framework, DomainCQA enables more precise assessment and improvement of MLLMs for domain-specific applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge