Daiting Shi
Bagging-Based Model Merging for Robust General Text Embeddings
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:General-purpose text embedding models underpin a wide range of NLP and information retrieval applications, and are typically trained on large-scale multi-task corpora to encourage broad generalization. However, it remains unclear how different multi-task training strategies compare in practice, and how to efficiently adapt embedding models as new domains and data types continually emerge. In this work, we present a systematic study of multi-task training for text embeddings from two perspectives: data scheduling and model merging. We compare batch-level shuffling, sequential training variants, two-stage training, and multiple merging granularities, and find that simple batch-level shuffling consistently yields the strongest overall performance, suggesting that task conflicts are limited and training datasets are largely complementary. Despite its effectiveness, batch-level shuffling exhibits two practical limitations: suboptimal out-of-domain (OOD) generalization and poor suitability for incremental learning due to expensive full retraining. To address these issues, we propose Bagging-based rObust mOdel Merging (\modelname), which trains multiple embedding models on sampled subsets and merges them into a single model, improving robustness while retaining single-model inference efficiency. Moreover, \modelname naturally supports efficient incremental updates by training lightweight update models on new data with a small historical subset and merging them into the existing model. Experiments across diverse embedding benchmarks demonstrate that \modelname consistently improves both in-domain and OOD performance over full-corpus batch-level shuffling, while substantially reducing training cost in incremental learning settings.
TRE: Encouraging Exploration in the Trust Region
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Entropy regularization is a standard technique in reinforcement learning (RL) to enhance exploration, yet it yields negligible effects or even degrades performance in Large Language Models (LLMs). We attribute this failure to the cumulative tail risk inherent to LLMs with massive vocabularies and long generation horizons. In such environments, standard global entropy maximization indiscriminately dilutes probability mass into the vast tail of invalid tokens rather than focusing on plausible candidates, thereby disrupting coherent reasoning. To address this, we propose Trust Region Entropy (TRE), a method that encourages exploration strictly within the model's trust region. Extensive experiments across mathematical reasoning (MATH), combinatorial search (Countdown), and preference alignment (HH) tasks demonstrate that TRE consistently outperforms vanilla PPO, standard entropy regularization, and other exploration baselines. Our code is available at https://github.com/WhyChaos/TRE-Encouraging-Exploration-in-the-Trust-Region.
Advancing General-Purpose Reasoning Models with Modular Gradient Surgery
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has played a central role in recent advances in large reasoning models (LRMs), yielding strong gains in verifiable and open-ended reasoning. However, training a single general-purpose LRM across diverse domains remains challenging due to pronounced domain heterogeneity. Through a systematic study of two widely used strategies, Sequential RL and Mixed RL, we find that both incur substantial cross-domain interference at the behavioral and gradient levels, resulting in limited overall gains. To address these challenges, we introduce **M**odular **G**radient **S**urgery (**MGS**), which resolves gradient conflicts at the module level within the transformer. When applied to Llama and Qwen models, MGS achieves average improvements of 4.3 (16.6\%) and 4.5 (11.1\%) points, respectively, over standard multi-task RL across three representative domains (math, general chat, and instruction following). Further analysis demonstrates that MGS remains effective under prolonged training. Overall, our study clarifies the sources of interference in multi-domain RL and presents an effective solution for training general-purpose LRMs.
Agentic-R: Learning to Retrieve for Agentic Search
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Agentic search has recently emerged as a powerful paradigm, where an agent interleaves multi-step reasoning with on-demand retrieval to solve complex questions. Despite its success, how to design a retriever for agentic search remains largely underexplored. Existing search agents typically rely on similarity-based retrievers, while similar passages are not always useful for final answer generation. In this paper, we propose a novel retriever training framework tailored for agentic search. Unlike retrievers designed for single-turn retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) that only rely on local passage utility, we propose to use both local query-passage relevance and global answer correctness to measure passage utility in a multi-turn agentic search. We further introduce an iterative training strategy, where the search agent and the retriever are optimized bidirectionally and iteratively. Different from RAG retrievers that are only trained once with fixed questions, our retriever is continuously improved using evolving and higher-quality queries from the agent. Extensive experiments on seven single-hop and multi-hop QA benchmarks demonstrate that our retriever, termed \ours{}, consistently outperforms strong baselines across different search agents. Our codes are available at: https://github.com/8421BCD/Agentic-R.
Reinforced Efficient Reasoning via Semantically Diverse Exploration
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has proven effective in enhancing the reasoning of large language models (LLMs). Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS)-based extensions improve upon vanilla RLVR (e.g., GRPO) by providing tree-based reasoning rollouts that enable fine-grained and segment-level credit assignment. However, existing methods still suffer from limited exploration diversity and inefficient reasoning. To address the above challenges, we propose reinforced efficient reasoning via semantically diverse explorations, i.e., ROSE, for LLMs. To encourage more diverse reasoning exploration, our method incorporates a semantic-entropy-based branching strategy and an $\varepsilon$-exploration mechanism. The former operates on already sampled reasoning rollouts to capture semantic uncertainty and select branching points with high semantic divergence to generate new successive reasoning paths, whereas the latter stochastically initiates reasoning rollouts from the root, preventing the search process from becoming overly local. To improve efficiency, we design a length-aware segment-level advantage estimator that rewards concise and correct reasoning while penalizing unnecessarily long reasoning chains. Extensive experiments on various mathematical reasoning benchmarks with Qwen and Llama models validate the effectiveness and efficiency of ROSE. Codes are available at https://github.com/ZiqiZhao1/ROSE-rl.
Leveraging LLMs for Utility-Focused Annotation: Reducing Manual Effort for Retrieval and RAG
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Retrieval models typically rely on costly human-labeled query-document relevance annotations for training and evaluation. To reduce this cost and leverage the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) in relevance judgments, we aim to explore whether LLM-generated annotations can effectively replace human annotations in training retrieval models. Retrieval usually emphasizes relevance, which indicates "topic-relatedness" of a document to a query, while in RAG, the value of a document (or utility) depends on how it contributes to answer generation. Recognizing this mismatch, some researchers use LLM performance on downstream tasks with documents as labels, but this approach requires manual answers for specific tasks, leading to high costs and limited generalization. In another line of work, prompting LLMs to select useful documents as RAG references eliminates the need for human annotation and is not task-specific. If we leverage LLMs' utility judgments to annotate retrieval data, we may retain cross-task generalization without human annotation in large-scale corpora. Therefore, we investigate utility-focused annotation via LLMs for large-scale retriever training data across both in-domain and out-of-domain settings on the retrieval and RAG tasks. To reduce the impact of low-quality positives labeled by LLMs, we design a novel loss function, i.e., Disj-InfoNCE. Our experiments reveal that: (1) Retrievers trained on utility-focused annotations significantly outperform those trained on human annotations in the out-of-domain setting on both tasks, demonstrating superior generalization capabilities. (2) LLM annotation does not replace human annotation in the in-domain setting. However, incorporating just 20% human-annotated data enables retrievers trained with utility-focused annotations to match the performance of models trained entirely with human annotations.
Unleashing the Power of LLMs in Dense Retrieval with Query Likelihood Modeling
Apr 07, 2025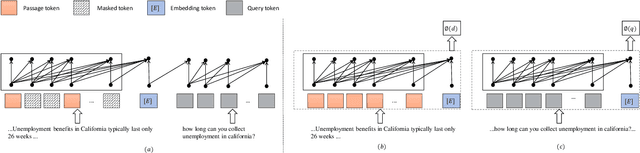
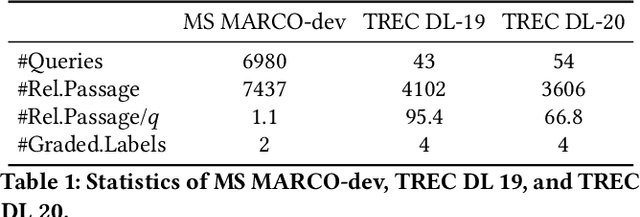
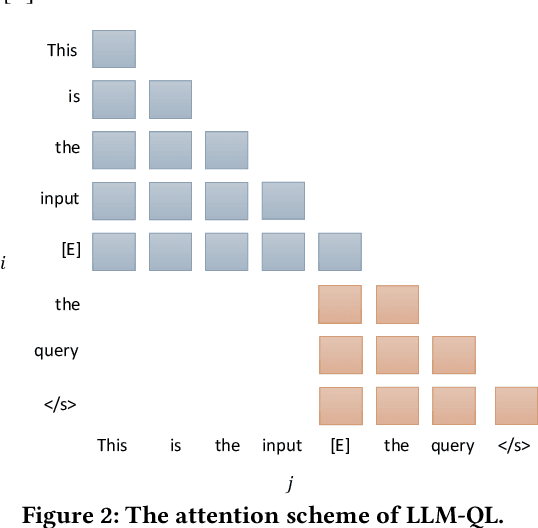
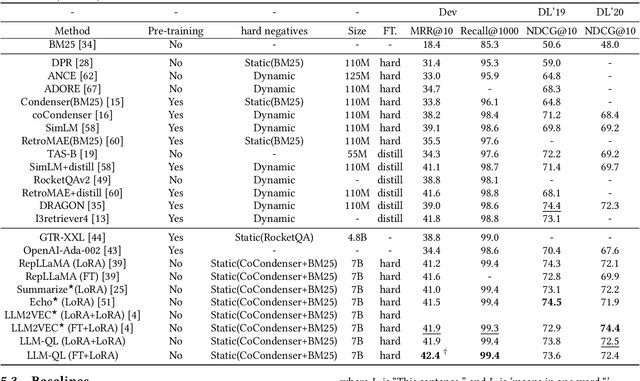
Abstract:Dense retrieval is a crucial task in Information Retrieval (IR) and is the foundation for downstream tasks such as re-ranking. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have shown compelling semantic understanding capabilities and are appealing to researchers studying dense retrieval. LLMs, as decoder-style generative models, are competent at language generation while falling short on modeling global information due to the lack of attention to tokens afterward. Inspired by the classical word-based language modeling approach for IR, i.e., the query likelihood (QL) model, we seek to sufficiently utilize LLMs' generative ability by QL maximization. However, instead of ranking documents with QL estimation, we introduce an auxiliary task of QL maximization to yield a better backbone for contrastively learning a discriminative retriever. We name our model as LLM-QL. To condense global document semantics to a single vector during QL modeling, LLM-QL has two major components, Attention Stop (AS) and Input Corruption (IC). AS stops the attention of predictive tokens to previous tokens until the ending token of the document. IC masks a portion of tokens in the input documents during prediction. Experiments on MSMARCO show that LLM-QL can achieve significantly better performance than other LLM-based retrievers and using QL estimated by LLM-QL for ranking outperforms word-based QL by a large margin.
GenCRF: Generative Clustering and Reformulation Framework for Enhanced Intent-Driven Information Retrieval
Sep 17, 2024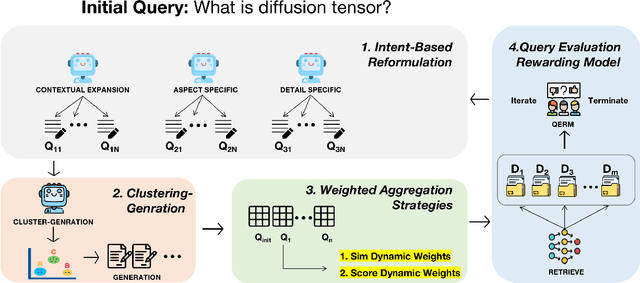
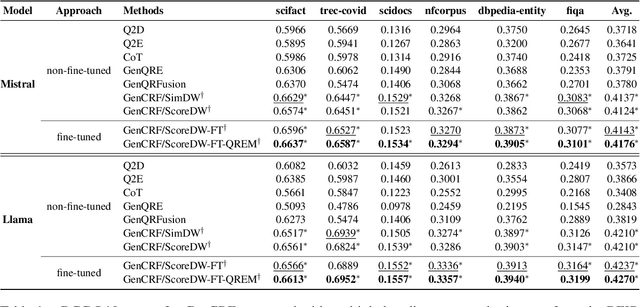
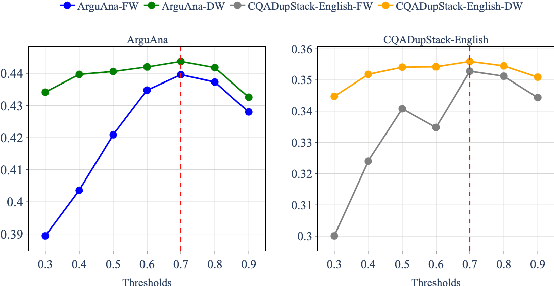
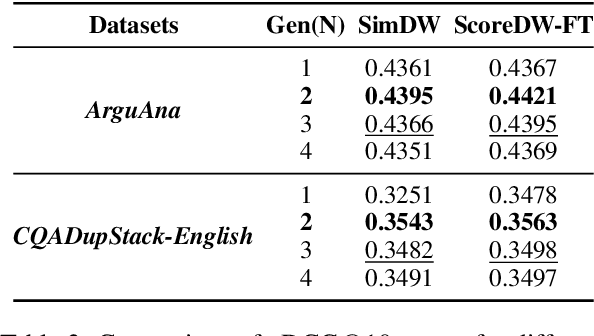
Abstract:Query reformulation is a well-known problem in Information Retrieval (IR) aimed at enhancing single search successful completion rate by automatically modifying user's input query. Recent methods leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve query reformulation, but often generate limited and redundant expansions, potentially constraining their effectiveness in capturing diverse intents. In this paper, we propose GenCRF: a Generative Clustering and Reformulation Framework to capture diverse intentions adaptively based on multiple differentiated, well-generated queries in the retrieval phase for the first time. GenCRF leverages LLMs to generate variable queries from the initial query using customized prompts, then clusters them into groups to distinctly represent diverse intents. Furthermore, the framework explores to combine diverse intents query with innovative weighted aggregation strategies to optimize retrieval performance and crucially integrates a novel Query Evaluation Rewarding Model (QERM) to refine the process through feedback loops. Empirical experiments on the BEIR benchmark demonstrate that GenCRF achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing previous query reformulation SOTAs by up to 12% on nDCG@10. These techniques can be adapted to various LLMs, significantly boosting retriever performance and advancing the field of Information Retrieval.
TourRank: Utilizing Large Language Models for Documents Ranking with a Tournament-Inspired Strategy
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly employed in zero-shot documents ranking, yielding commendable results. However, several significant challenges still persist in LLMs for ranking: (1) LLMs are constrained by limited input length, precluding them from processing a large number of documents simultaneously; (2) The output document sequence is influenced by the input order of documents, resulting in inconsistent ranking outcomes; (3) Achieving a balance between cost and ranking performance is quite challenging. To tackle these issues, we introduce a novel documents ranking method called TourRank, which is inspired by the tournament mechanism. This approach alleviates the impact of LLM's limited input length through intelligent grouping, while the tournament-like points system ensures robust ranking, mitigating the influence of the document input sequence. We test TourRank with different LLMs on the TREC DL datasets and the BEIR benchmark. Experimental results show that TourRank achieves state-of-the-art performance at a reasonable cost.
MA4DIV: Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Search Result Diversification
Mar 27, 2024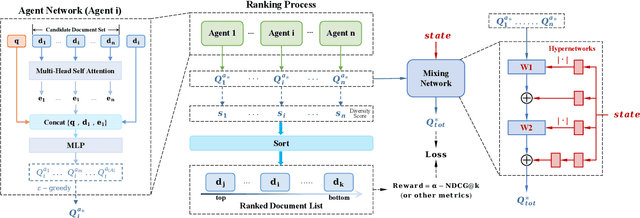

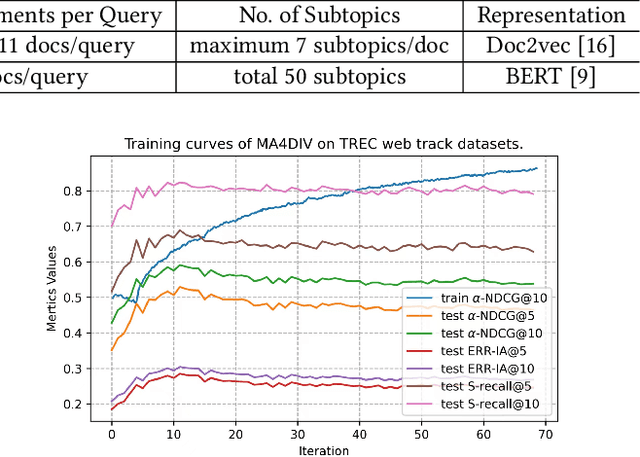
Abstract:The objective of search result diversification (SRD) is to ensure that selected documents cover as many different subtopics as possible. Existing methods primarily utilize a paradigm of "greedy selection", i.e., selecting one document with the highest diversity score at a time. These approaches tend to be inefficient and are easily trapped in a suboptimal state. In addition, some other methods aim to approximately optimize the diversity metric, such as $\alpha$-NDCG, but the results still remain suboptimal. To address these challenges, we introduce Multi-Agent reinforcement learning (MARL) for search result DIVersity, which called MA4DIV. In this approach, each document is an agent and the search result diversification is modeled as a cooperative task among multiple agents. This approach allows for directly optimizing the diversity metrics, such as $\alpha$-NDCG, while achieving high training efficiency. We conducted preliminary experiments on public TREC datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness and potential of MA4DIV. Considering the limited number of queries in public TREC datasets, we construct a large-scale dataset from industry sources and show that MA4DIV achieves substantial improvements in both effectiveness and efficiency than existing baselines on a industrial scale dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge