Hengran Zhang
Bagging-Based Model Merging for Robust General Text Embeddings
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:General-purpose text embedding models underpin a wide range of NLP and information retrieval applications, and are typically trained on large-scale multi-task corpora to encourage broad generalization. However, it remains unclear how different multi-task training strategies compare in practice, and how to efficiently adapt embedding models as new domains and data types continually emerge. In this work, we present a systematic study of multi-task training for text embeddings from two perspectives: data scheduling and model merging. We compare batch-level shuffling, sequential training variants, two-stage training, and multiple merging granularities, and find that simple batch-level shuffling consistently yields the strongest overall performance, suggesting that task conflicts are limited and training datasets are largely complementary. Despite its effectiveness, batch-level shuffling exhibits two practical limitations: suboptimal out-of-domain (OOD) generalization and poor suitability for incremental learning due to expensive full retraining. To address these issues, we propose Bagging-based rObust mOdel Merging (\modelname), which trains multiple embedding models on sampled subsets and merges them into a single model, improving robustness while retaining single-model inference efficiency. Moreover, \modelname naturally supports efficient incremental updates by training lightweight update models on new data with a small historical subset and merging them into the existing model. Experiments across diverse embedding benchmarks demonstrate that \modelname consistently improves both in-domain and OOD performance over full-corpus batch-level shuffling, while substantially reducing training cost in incremental learning settings.
Leveraging LLMs for Utility-Focused Annotation: Reducing Manual Effort for Retrieval and RAG
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Retrieval models typically rely on costly human-labeled query-document relevance annotations for training and evaluation. To reduce this cost and leverage the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) in relevance judgments, we aim to explore whether LLM-generated annotations can effectively replace human annotations in training retrieval models. Retrieval usually emphasizes relevance, which indicates "topic-relatedness" of a document to a query, while in RAG, the value of a document (or utility) depends on how it contributes to answer generation. Recognizing this mismatch, some researchers use LLM performance on downstream tasks with documents as labels, but this approach requires manual answers for specific tasks, leading to high costs and limited generalization. In another line of work, prompting LLMs to select useful documents as RAG references eliminates the need for human annotation and is not task-specific. If we leverage LLMs' utility judgments to annotate retrieval data, we may retain cross-task generalization without human annotation in large-scale corpora. Therefore, we investigate utility-focused annotation via LLMs for large-scale retriever training data across both in-domain and out-of-domain settings on the retrieval and RAG tasks. To reduce the impact of low-quality positives labeled by LLMs, we design a novel loss function, i.e., Disj-InfoNCE. Our experiments reveal that: (1) Retrievers trained on utility-focused annotations significantly outperform those trained on human annotations in the out-of-domain setting on both tasks, demonstrating superior generalization capabilities. (2) LLM annotation does not replace human annotation in the in-domain setting. However, incorporating just 20% human-annotated data enables retrievers trained with utility-focused annotations to match the performance of models trained entirely with human annotations.
Unleashing the Power of LLMs in Dense Retrieval with Query Likelihood Modeling
Apr 07, 2025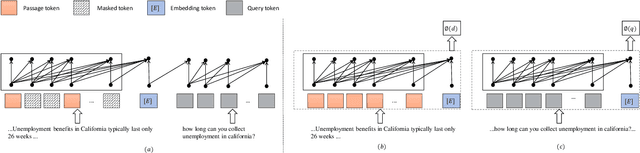
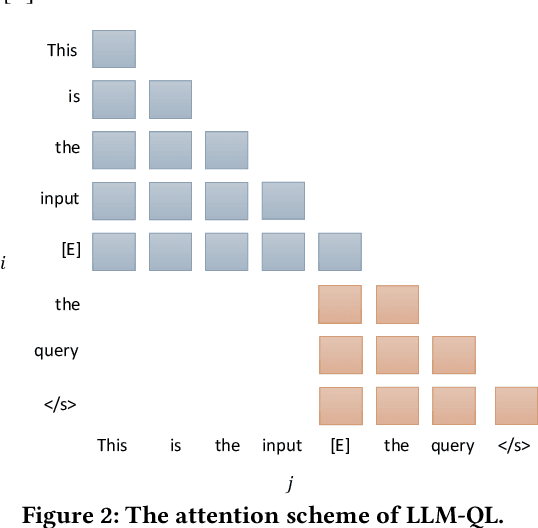
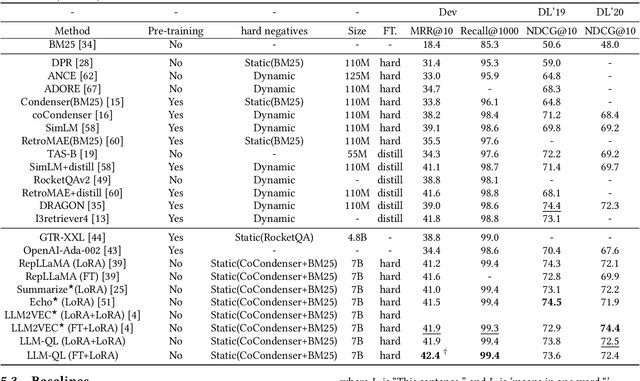
Abstract:Dense retrieval is a crucial task in Information Retrieval (IR) and is the foundation for downstream tasks such as re-ranking. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have shown compelling semantic understanding capabilities and are appealing to researchers studying dense retrieval. LLMs, as decoder-style generative models, are competent at language generation while falling short on modeling global information due to the lack of attention to tokens afterward. Inspired by the classical word-based language modeling approach for IR, i.e., the query likelihood (QL) model, we seek to sufficiently utilize LLMs' generative ability by QL maximization. However, instead of ranking documents with QL estimation, we introduce an auxiliary task of QL maximization to yield a better backbone for contrastively learning a discriminative retriever. We name our model as LLM-QL. To condense global document semantics to a single vector during QL modeling, LLM-QL has two major components, Attention Stop (AS) and Input Corruption (IC). AS stops the attention of predictive tokens to previous tokens until the ending token of the document. IC masks a portion of tokens in the input documents during prediction. Experiments on MSMARCO show that LLM-QL can achieve significantly better performance than other LLM-based retrievers and using QL estimated by LLM-QL for ranking outperforms word-based QL by a large margin.
Iterative Utility Judgment Framework via LLMs Inspired by Relevance in Philosophy
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Utility and topical relevance are critical measures in information retrieval (IR), reflecting system and user perspectives, respectively. While topical relevance has long been emphasized, utility is a higher standard of relevance and is more useful for facilitating downstream tasks, e.g., in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). When we incorporate utility judgments into RAG, we realize that the topical relevance, utility, and answering in RAG are closely related to the three types of relevance that Schutz discussed from a philosophical perspective. They are topical relevance, interpretational relevance, and motivational relevance, respectively. Inspired by the dynamic iterations of the three types of relevance, we propose an Iterative utiliTy judgmEnt fraMework (ITEM) to promote each step of the cycle of RAG. We conducted extensive experiments on multi-grade passage retrieval and factoid question-answering datasets (i.e., TREC DL, WebAP, and NQ). Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in utility judgments, ranking of topical relevance, and answer generation upon representative baselines, including multiple single-shot utility judging approaches. Our code and benchmark can be found at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ITEM-B486/.
Are Large Language Models Good at Utility Judgments?
Mar 28, 2024Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is considered to be a promising approach to alleviate the hallucination issue of large language models (LLMs), and it has received widespread attention from researchers recently. Due to the limitation in the semantic understanding of retrieval models, the success of RAG heavily lies on the ability of LLMs to identify passages with utility. Recent efforts have explored the ability of LLMs to assess the relevance of passages in retrieval, but there has been limited work on evaluating the utility of passages in supporting question answering. In this work, we conduct a comprehensive study about the capabilities of LLMs in utility evaluation for open-domain QA. Specifically, we introduce a benchmarking procedure and collection of candidate passages with different characteristics, facilitating a series of experiments with five representative LLMs. Our experiments reveal that: (i) well-instructed LLMs can distinguish between relevance and utility, and that LLMs are highly receptive to newly generated counterfactual passages. Moreover, (ii) we scrutinize key factors that affect utility judgments in the instruction design. And finally, (iii) to verify the efficacy of utility judgments in practical retrieval augmentation applications, we delve into LLMs' QA capabilities using the evidence judged with utility and direct dense retrieval results. (iv) We propose a k-sampling, listwise approach to reduce the dependency of LLMs on the sequence of input passages, thereby facilitating subsequent answer generation. We believe that the way we formalize and study the problem along with our findings contributes to a critical assessment of retrieval-augmented LLMs. Our code and benchmark can be found at \url{https://github.com/ict-bigdatalab/utility_judgments}.
From Relevance to Utility: Evidence Retrieval with Feedback for Fact Verification
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:Retrieval-enhanced methods have become a primary approach in fact verification (FV); it requires reasoning over multiple retrieved pieces of evidence to verify the integrity of a claim. To retrieve evidence, existing work often employs off-the-shelf retrieval models whose design is based on the probability ranking principle. We argue that, rather than relevance, for FV we need to focus on the utility that a claim verifier derives from the retrieved evidence. We introduce the feedback-based evidence retriever(FER) that optimizes the evidence retrieval process by incorporating feedback from the claim verifier. As a feedback signal we use the divergence in utility between how effectively the verifier utilizes the retrieved evidence and the ground-truth evidence to produce the final claim label. Empirical studies demonstrate the superiority of FER over prevailing baselines.
GCRE-GPT: A Generative Model for Comparative Relation Extraction
Mar 15, 2023Abstract:Given comparative text, comparative relation extraction aims to extract two targets (\eg two cameras) in comparison and the aspect they are compared for (\eg image quality). The extracted comparative relations form the basis of further opinion analysis.Existing solutions formulate this task as a sequence labeling task, to extract targets and aspects. However, they cannot directly extract comparative relation(s) from text. In this paper, we show that comparative relations can be directly extracted with high accuracy, by generative model. Based on GPT-2, we propose a Generation-based Comparative Relation Extractor (GCRE-GPT). Experiment results show that \modelname achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on two datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge