Minghua Zhang
A Structured Review of Underwater Object Detection Challenges and Solutions: From Traditional to Large Vision Language Models
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Underwater object detection (UOD) is vital to diverse marine applications, including oceanographic research, underwater robotics, and marine conservation. However, UOD faces numerous challenges that compromise its performance. Over the years, various methods have been proposed to address these issues, but they often fail to fully capture the complexities of underwater environments. This review systematically categorizes UOD challenges into five key areas: Image quality degradation, target-related issues, data-related challenges, computational and processing constraints, and limitations in detection methodologies. To address these challenges, we analyze the progression from traditional image processing and object detection techniques to modern approaches. Additionally, we explore the potential of large vision-language models (LVLMs) in UOD, leveraging their multi-modal capabilities demonstrated in other domains. We also present case studies, including synthetic dataset generation using DALL-E 3 and fine-tuning Florence-2 LVLM for UOD. This review identifies three key insights: (i) Current UOD methods are insufficient to fully address challenges like image degradation and small object detection in dynamic underwater environments. (ii) Synthetic data generation using LVLMs shows potential for augmenting datasets but requires further refinement to ensure realism and applicability. (iii) LVLMs hold significant promise for UOD, but their real-time application remains under-explored, requiring further research on optimization techniques.
DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:We present DeepSeek-V3, a strong Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model with 671B total parameters with 37B activated for each token. To achieve efficient inference and cost-effective training, DeepSeek-V3 adopts Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) and DeepSeekMoE architectures, which were thoroughly validated in DeepSeek-V2. Furthermore, DeepSeek-V3 pioneers an auxiliary-loss-free strategy for load balancing and sets a multi-token prediction training objective for stronger performance. We pre-train DeepSeek-V3 on 14.8 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens, followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning stages to fully harness its capabilities. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that DeepSeek-V3 outperforms other open-source models and achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models. Despite its excellent performance, DeepSeek-V3 requires only 2.788M H800 GPU hours for its full training. In addition, its training process is remarkably stable. Throughout the entire training process, we did not experience any irrecoverable loss spikes or perform any rollbacks. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3.
DeepSeek LLM: Scaling Open-Source Language Models with Longtermism
Jan 05, 2024



Abstract:The rapid development of open-source large language models (LLMs) has been truly remarkable. However, the scaling law described in previous literature presents varying conclusions, which casts a dark cloud over scaling LLMs. We delve into the study of scaling laws and present our distinctive findings that facilitate scaling of large scale models in two commonly used open-source configurations, 7B and 67B. Guided by the scaling laws, we introduce DeepSeek LLM, a project dedicated to advancing open-source language models with a long-term perspective. To support the pre-training phase, we have developed a dataset that currently consists of 2 trillion tokens and is continuously expanding. We further conduct supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) on DeepSeek LLM Base models, resulting in the creation of DeepSeek Chat models. Our evaluation results demonstrate that DeepSeek LLM 67B surpasses LLaMA-2 70B on various benchmarks, particularly in the domains of code, mathematics, and reasoning. Furthermore, open-ended evaluations reveal that DeepSeek LLM 67B Chat exhibits superior performance compared to GPT-3.5.
CPS-MEBR: Click Feedback-Aware Web Page Summarization for Multi-Embedding-Based Retrieval
Oct 19, 2022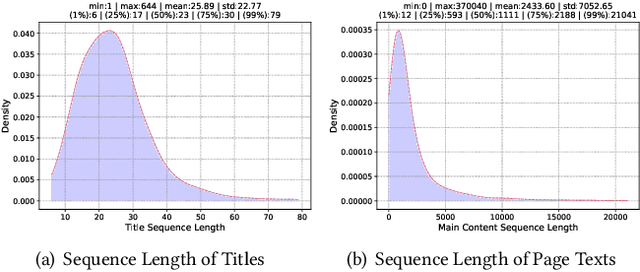
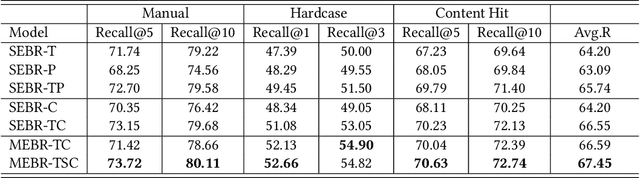
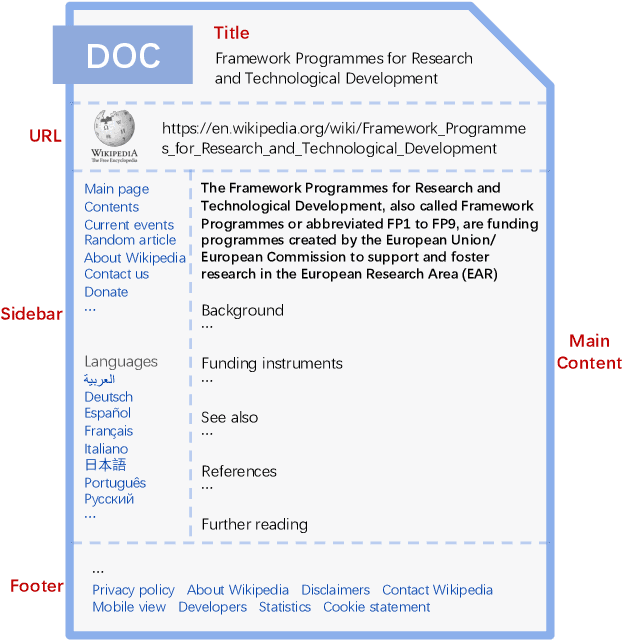
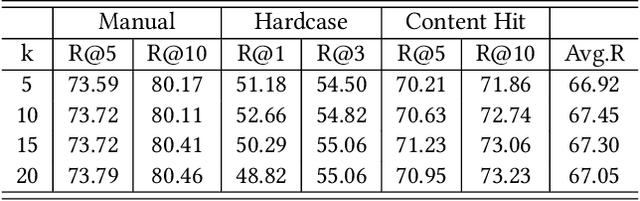
Abstract:Embedding-based retrieval (EBR) is a technique to use embeddings to represent query and document, and then convert the retrieval problem into a nearest neighbor search problem in the embedding space. Some previous works have mainly focused on representing the web page with a single embedding, but in real web search scenarios, it is difficult to represent all the information of a long and complex structured web page as a single embedding. To address this issue, we design a click feedback-aware web page summarization for multi-embedding-based retrieval (CPS-MEBR) framework which is able to generate multiple embeddings for web pages to match different potential queries. Specifically, we use the click data of users in search logs to train a summary model to extract those sentences in web pages that are frequently clicked by users, which are more likely to answer those potential queries. Meanwhile, we introduce sentence-level semantic interaction to design a multi-embedding-based retrieval (MEBR) model, which can generate multiple embeddings to deal with different potential queries by using frequently clicked sentences in web pages. Offline experiments show that it can perform high quality candidate retrieval compared to single-embedding-based retrieval (SEBR) model.
Question-type Driven Question Generation
Aug 31, 2019



Abstract:Question generation is a challenging task which aims to ask a question based on an answer and relevant context. The existing works suffer from the mismatching between question type and answer, i.e. generating a question with type $how$ while the answer is a personal name. We propose to automatically predict the question type based on the input answer and context. Then, the question type is fused into a seq2seq model to guide the question generation, so as to deal with the mismatching problem. We achieve significant improvement on the accuracy of question type prediction and finally obtain state-of-the-art results for question generation on both SQuAD and MARCO datasets.
Multi-Task Learning with Language Modeling for Question Generation
Aug 30, 2019



Abstract:This paper explores the task of answer-aware questions generation. Based on the attention-based pointer generator model, we propose to incorporate an auxiliary task of language modeling to help question generation in a hierarchical multi-task learning structure. Our joint-learning model enables the encoder to learn a better representation of the input sequence, which will guide the decoder to generate more coherent and fluent questions. On both SQuAD and MARCO datasets, our multi-task learning model boosts the performance, achieving state-of-the-art results. Moreover, human evaluation further proves the high quality of our generated questions.
Learning Universal Sentence Representations with Mean-Max Attention Autoencoder
Sep 18, 2018



Abstract:In order to learn universal sentence representations, previous methods focus on complex recurrent neural networks or supervised learning. In this paper, we propose a mean-max attention autoencoder (mean-max AAE) within the encoder-decoder framework. Our autoencoder rely entirely on the MultiHead self-attention mechanism to reconstruct the input sequence. In the encoding we propose a mean-max strategy that applies both mean and max pooling operations over the hidden vectors to capture diverse information of the input. To enable the information to steer the reconstruction process dynamically, the decoder performs attention over the mean-max representation. By training our model on a large collection of unlabelled data, we obtain high-quality representations of sentences. Experimental results on a broad range of 10 transfer tasks demonstrate that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art unsupervised single methods, including the classical skip-thoughts and the advanced skip-thoughts+LN model. Furthermore, compared with the traditional recurrent neural network, our mean-max AAE greatly reduce the training time.
An Unsupervised Model with Attention Autoencoders for Question Retrieval
Mar 09, 2018



Abstract:Question retrieval is a crucial subtask for community question answering. Previous research focus on supervised models which depend heavily on training data and manual feature engineering. In this paper, we propose a novel unsupervised framework, namely reduced attentive matching network (RAMN), to compute semantic matching between two questions. Our RAMN integrates together the deep semantic representations, the shallow lexical mismatching information and the initial rank produced by an external search engine. For the first time, we propose attention autoencoders to generate semantic representations of questions. In addition, we employ lexical mismatching to capture surface matching between two questions, which is derived from the importance of each word in a question. We conduct experiments on the open CQA datasets of SemEval-2016 and SemEval-2017. The experimental results show that our unsupervised model obtains comparable performance with the state-of-the-art supervised methods in SemEval-2016 Task 3, and outperforms the best system in SemEval-2017 Task 3 by a wide margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge