Zhengfan Wu
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
CPS-MEBR: Click Feedback-Aware Web Page Summarization for Multi-Embedding-Based Retrieval
Oct 19, 2022
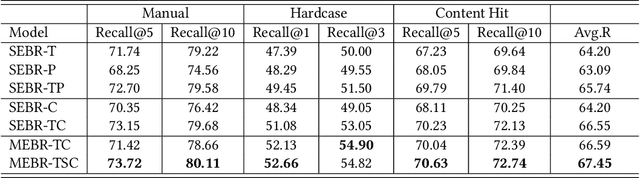
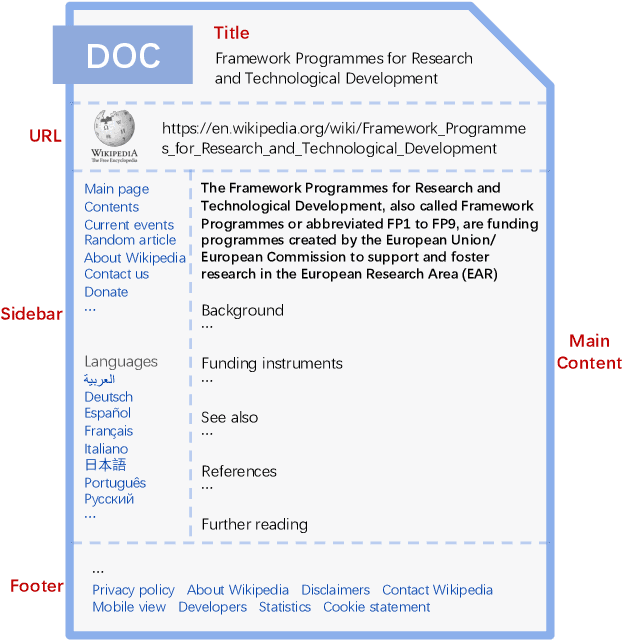
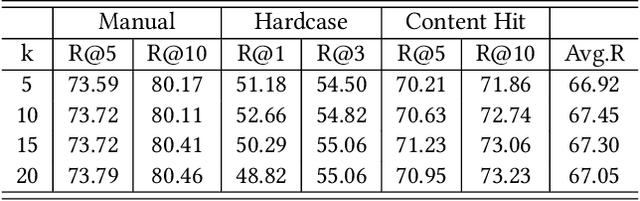
Abstract:Embedding-based retrieval (EBR) is a technique to use embeddings to represent query and document, and then convert the retrieval problem into a nearest neighbor search problem in the embedding space. Some previous works have mainly focused on representing the web page with a single embedding, but in real web search scenarios, it is difficult to represent all the information of a long and complex structured web page as a single embedding. To address this issue, we design a click feedback-aware web page summarization for multi-embedding-based retrieval (CPS-MEBR) framework which is able to generate multiple embeddings for web pages to match different potential queries. Specifically, we use the click data of users in search logs to train a summary model to extract those sentences in web pages that are frequently clicked by users, which are more likely to answer those potential queries. Meanwhile, we introduce sentence-level semantic interaction to design a multi-embedding-based retrieval (MEBR) model, which can generate multiple embeddings to deal with different potential queries by using frequently clicked sentences in web pages. Offline experiments show that it can perform high quality candidate retrieval compared to single-embedding-based retrieval (SEBR) model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge