Linhao Zhang
WeDLM: Reconciling Diffusion Language Models with Standard Causal Attention for Fast Inference
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) generation is the standard decoding paradigm for Large Language Models (LLMs), but its token-by-token nature limits parallelism at inference time. Diffusion Language Models (DLLMs) offer parallel decoding by recovering multiple masked tokens per step; however, in practice they often fail to translate this parallelism into deployment speed gains over optimized AR engines (e.g., vLLM). A key reason is that many DLLMs rely on bidirectional attention, which breaks standard prefix KV caching and forces repeated contextualization, undermining efficiency. We propose WeDLM, a diffusion decoding framework built entirely on standard causal attention to make parallel generation prefix-cache friendly. The core idea is to let each masked position condition on all currently observed tokens while keeping a strict causal mask, achieved by Topological Reordering that moves observed tokens to the physical prefix while preserving their logical positions. Building on this property, we introduce a streaming decoding procedure that continuously commits confident tokens into a growing left-to-right prefix and maintains a fixed parallel workload, avoiding the stop-and-wait behavior common in block diffusion methods. Experiments show that WeDLM preserves the quality of strong AR backbones while delivering substantial speedups, approaching 3x on challenging reasoning benchmarks and up to 10x in low-entropy generation regimes; critically, our comparisons are against AR baselines served by vLLM under matched deployment settings, demonstrating that diffusion-style decoding can outperform an optimized AR engine in practice.
StableToken: A Noise-Robust Semantic Speech Tokenizer for Resilient SpeechLLMs
Sep 26, 2025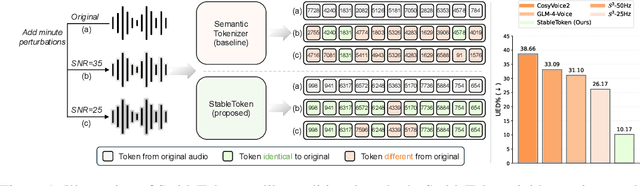
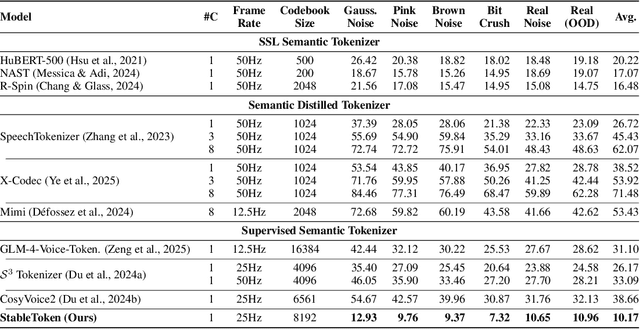
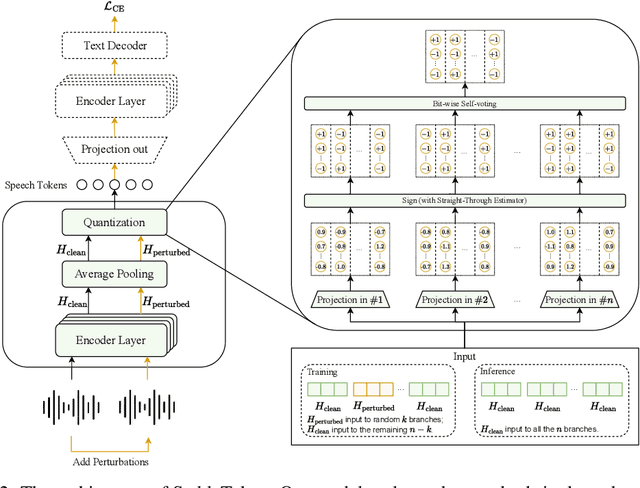
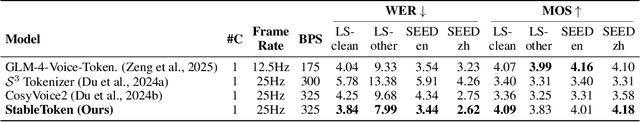
Abstract:Prevalent semantic speech tokenizers, designed to capture linguistic content, are surprisingly fragile. We find they are not robust to meaning-irrelevant acoustic perturbations; even at high Signal-to-Noise Ratios (SNRs) where speech is perfectly intelligible, their output token sequences can change drastically, increasing the learning burden for downstream LLMs. This instability stems from two flaws: a brittle single-path quantization architecture and a distant training signal indifferent to intermediate token stability. To address this, we introduce StableToken, a tokenizer that achieves stability through a consensus-driven mechanism. Its multi-branch architecture processes audio in parallel, and these representations are merged via a powerful bit-wise voting mechanism to form a single, stable token sequence. StableToken sets a new state-of-the-art in token stability, drastically reducing Unit Edit Distance (UED) under diverse noise conditions. This foundational stability translates directly to downstream benefits, significantly improving the robustness of SpeechLLMs on a variety of tasks.
Multi-SWE-bench: A Multilingual Benchmark for Issue Resolving
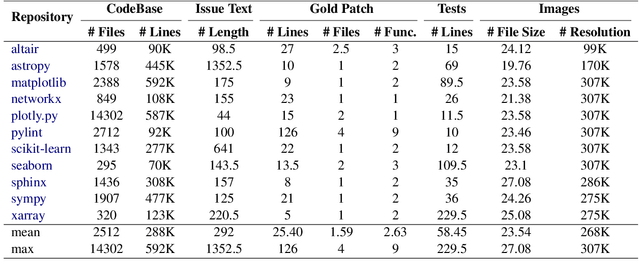
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:The task of issue resolving is to modify a codebase to generate a patch that addresses a given issue. However, existing benchmarks, such as SWE-bench, focus almost exclusively on Python, making them insufficient for evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) across diverse software ecosystems. To address this, we introduce a multilingual issue-resolving benchmark, called Multi-SWE-bench, covering Java, TypeScript, JavaScript, Go, Rust, C, and C++. It includes a total of 1,632 high-quality instances, which were carefully annotated from 2,456 candidates by 68 expert annotators, ensuring that the benchmark can provide an accurate and reliable evaluation. Based on Multi-SWE-bench, we evaluate a series of state-of-the-art models using three representative methods (Agentless, SWE-agent, and OpenHands) and present a comprehensive analysis with key empirical insights. In addition, we launch a Multi-SWE-RL open-source community, aimed at building large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) training datasets for issue-resolving tasks. As an initial contribution, we release a set of 4,723 well-structured instances spanning seven programming languages, laying a solid foundation for RL research in this domain. More importantly, we open-source our entire data production pipeline, along with detailed tutorials, encouraging the open-source community to continuously contribute and expand the dataset. We envision our Multi-SWE-bench and the ever-growing Multi-SWE-RL community as catalysts for advancing RL toward its full potential, bringing us one step closer to the dawn of AGI.
CodeV: Issue Resolving with Visual Data
Dec 23, 2024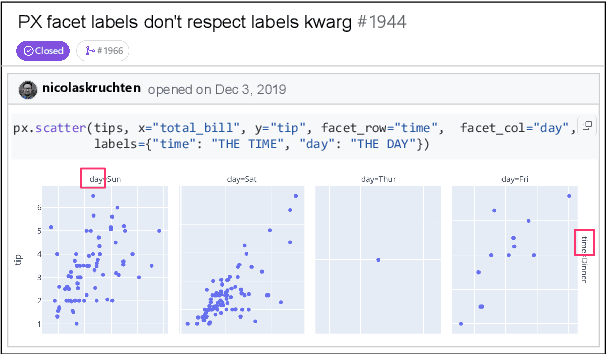


Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have advanced rapidly in recent years, with their applications in software engineering expanding to more complex repository-level tasks. GitHub issue resolving is a key challenge among these tasks. While recent approaches have made progress on this task, they focus on textual data within issues, neglecting visual data. However, this visual data is crucial for resolving issues as it conveys additional knowledge that text alone cannot. We propose CodeV, the first approach to leveraging visual data to enhance the issue-resolving capabilities of LLMs. CodeV resolves each issue by following a two-phase process: data processing and patch generation. To evaluate CodeV, we construct a benchmark for visual issue resolving, namely Visual SWE-bench. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of CodeV, as well as provide valuable insights into leveraging visual data to resolve GitHub issues.
CoFE-RAG: A Comprehensive Full-chain Evaluation Framework for Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Enhanced Data Diversity
Oct 16, 2024Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) aims to enhance large language models (LLMs) to generate more accurate and reliable answers with the help of the retrieved context from external knowledge sources, thereby reducing the incidence of hallucinations. Despite the advancements, evaluating these systems remains a crucial research area due to the following issues: (1) Limited data diversity: The insufficient diversity of knowledge sources and query types constrains the applicability of RAG systems; (2) Obscure problems location: Existing evaluation methods have difficulty in locating the stage of the RAG pipeline where problems occur; (3) Unstable retrieval evaluation: These methods often fail to effectively assess retrieval performance, particularly when the chunking strategy changes. To tackle these challenges, we propose a Comprehensive Full-chain Evaluation (CoFE-RAG) framework to facilitate thorough evaluation across the entire RAG pipeline, including chunking, retrieval, reranking, and generation. To effectively evaluate the first three phases, we introduce multi-granularity keywords, including coarse-grained and fine-grained keywords, to assess the retrieved context instead of relying on the annotation of golden chunks. Moreover, we release a holistic benchmark dataset tailored for diverse data scenarios covering a wide range of document formats and query types. We demonstrate the utility of the CoFE-RAG framework by conducting experiments to evaluate each stage of RAG systems. Our evaluation method provides unique insights into the effectiveness of RAG systems in handling diverse data scenarios, offering a more nuanced understanding of their capabilities and limitations.
COT: A Generative Approach for Hate Speech Counter-Narratives via Contrastive Optimal Transport
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Counter-narratives, which are direct responses consisting of non-aggressive fact-based arguments, have emerged as a highly effective approach to combat the proliferation of hate speech. Previous methodologies have primarily focused on fine-tuning and post-editing techniques to ensure the fluency of generated contents, while overlooking the critical aspects of individualization and relevance concerning the specific hatred targets, such as LGBT groups, immigrants, etc. This research paper introduces a novel framework based on contrastive optimal transport, which effectively addresses the challenges of maintaining target interaction and promoting diversification in generating counter-narratives. Firstly, an Optimal Transport Kernel (OTK) module is leveraged to incorporate hatred target information in the token representations, in which the comparison pairs are extracted between original and transported features. Secondly, a self-contrastive learning module is employed to address the issue of model degeneration. This module achieves this by generating an anisotropic distribution of token representations. Finally, a target-oriented search method is integrated as an improved decoding strategy to explicitly promote domain relevance and diversification in the inference process. This strategy modifies the model's confidence score by considering both token similarity and target relevance. Quantitative and qualitative experiments have been evaluated on two benchmark datasets, which demonstrate that our proposed model significantly outperforms current methods evaluated by metrics from multiple aspects.
DHA: Learning Decoupled-Head Attention from Transformer Checkpoints via Adaptive Heads Fusion
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) with billions of parameters demonstrate impressive performance. However, the widely used Multi-Head Attention (MHA) in LLMs incurs substantial computational and memory costs during inference. While some efforts have optimized attention mechanisms by pruning heads or sharing parameters among heads, these methods often lead to performance degradation or necessitate substantial continued pre-training costs to restore performance. Based on the analysis of attention redundancy, we design a Decoupled-Head Attention (DHA) mechanism. DHA adaptively configures group sharing for key heads and value heads across various layers, achieving a better balance between performance and efficiency. Inspired by the observation of clustering similar heads, we propose to progressively transform the MHA checkpoint into the DHA model through linear fusion of similar head parameters step by step, retaining the parametric knowledge of the MHA checkpoint. We construct DHA models by transforming various scales of MHA checkpoints given target head budgets. Our experiments show that DHA remarkably requires a mere 0.25\% of the original model's pre-training budgets to achieve 97.6\% of performance while saving 75\% of KV cache. Compared to Group-Query Attention (GQA), DHA achieves a 5$\times$ training acceleration, a maximum of 13.93\% performance improvement under 0.01\% pre-training budget, and 4\% relative improvement under 0.05\% pre-training budget.
TOT: Topology-Aware Optimal Transport For Multimodal Hate Detection
Feb 27, 2023



Abstract:Multimodal hate detection, which aims to identify harmful content online such as memes, is crucial for building a wholesome internet environment. Previous work has made enlightening exploration in detecting explicit hate remarks. However, most of their approaches neglect the analysis of implicit harm, which is particularly challenging as explicit text markers and demographic visual cues are often twisted or missing. The leveraged cross-modal attention mechanisms also suffer from the distributional modality gap and lack logical interpretability. To address these semantic gaps issues, we propose TOT: a topology-aware optimal transport framework to decipher the implicit harm in memes scenario, which formulates the cross-modal aligning problem as solutions for optimal transportation plans. Specifically, we leverage an optimal transport kernel method to capture complementary information from multiple modalities. The kernel embedding provides a non-linear transformation ability to reproduce a kernel Hilbert space (RKHS), which reflects significance for eliminating the distributional modality gap. Moreover, we perceive the topology information based on aligned representations to conduct bipartite graph path reasoning. The newly achieved state-of-the-art performance on two publicly available benchmark datasets, together with further visual analysis, demonstrate the superiority of TOT in capturing implicit cross-modal alignment.
PILE: Pairwise Iterative Logits Ensemble for Multi-Teacher Labeled Distillation
Nov 11, 2022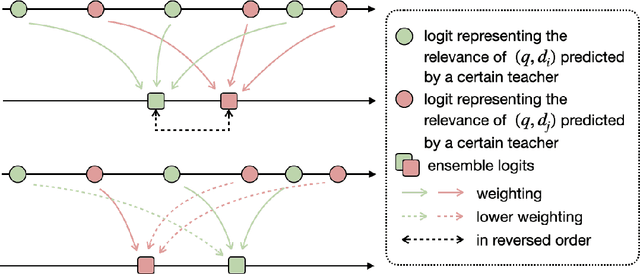
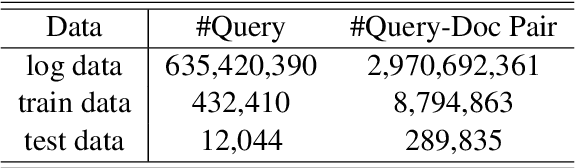

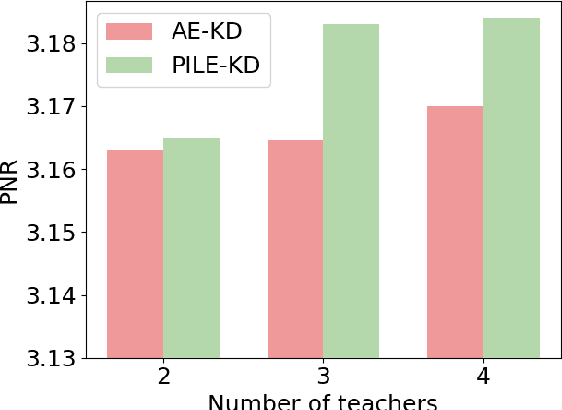
Abstract:Pre-trained language models have become a crucial part of ranking systems and achieved very impressive effects recently. To maintain high performance while keeping efficient computations, knowledge distillation is widely used. In this paper, we focus on two key questions in knowledge distillation for ranking models: 1) how to ensemble knowledge from multi-teacher; 2) how to utilize the label information of data in the distillation process. We propose a unified algorithm called Pairwise Iterative Logits Ensemble (PILE) to tackle these two questions simultaneously. PILE ensembles multi-teacher logits supervised by label information in an iterative way and achieved competitive performance in both offline and online experiments. The proposed method has been deployed in a real-world commercial search system.
Towards Controlled and Diverse Generation of Article Comments
Jul 25, 2021



Abstract:Much research in recent years has focused on automatic article commenting. However, few of previous studies focus on the controllable generation of comments. Besides, they tend to generate dull and commonplace comments, which further limits their practical application. In this paper, we make the first step towards controllable generation of comments, by building a system that can explicitly control the emotion of the generated comments. To achieve this, we associate each kind of emotion category with an embedding and adopt a dynamic fusion mechanism to fuse this embedding into the decoder. A sentence-level emotion classifier is further employed to better guide the model to generate comments expressing the desired emotion. To increase the diversity of the generated comments, we propose a hierarchical copy mechanism that allows our model to directly copy words from the input articles. We also propose a restricted beam search (RBS) algorithm to increase intra-sentence diversity. Experimental results show that our model can generate informative and diverse comments that express the desired emotions with high accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge