Wonduk Seo
Toward Culturally Aligned LLMs through Ontology-Guided Multi-Agent Reasoning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) increasingly support culturally sensitive decision making, yet often exhibit misalignment due to skewed pretraining data and the absence of structured value representations. Existing methods can steer outputs, but often lack demographic grounding and treat values as independent, unstructured signals, reducing consistency and interpretability. We propose OG-MAR, an Ontology-Guided Multi-Agent Reasoning framework. OG-MAR summarizes respondent-specific values from the World Values Survey (WVS) and constructs a global cultural ontology by eliciting relations over a fixed taxonomy via competency questions. At inference time, it retrieves ontology-consistent relations and demographically similar profiles to instantiate multiple value-persona agents, whose outputs are synthesized by a judgment agent that enforces ontology consistency and demographic proximity. Experiments on regional social-survey benchmarks across four LLM backbones show that OG-MAR improves cultural alignment and robustness over competitive baselines, while producing more transparent reasoning traces.
MARIC: Multi-Agent Reasoning for Image Classification
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Image classification has traditionally relied on parameter-intensive model training, requiring large-scale annotated datasets and extensive fine tuning to achieve competitive performance. While recent vision language models (VLMs) alleviate some of these constraints, they remain limited by their reliance on single pass representations, often failing to capture complementary aspects of visual content. In this paper, we introduce Multi Agent based Reasoning for Image Classification (MARIC), a multi agent framework that reformulates image classification as a collaborative reasoning process. MARIC first utilizes an Outliner Agent to analyze the global theme of the image and generate targeted prompts. Based on these prompts, three Aspect Agents extract fine grained descriptions along distinct visual dimensions. Finally, a Reasoning Agent synthesizes these complementary outputs through integrated reflection step, producing a unified representation for classification. By explicitly decomposing the task into multiple perspectives and encouraging reflective synthesis, MARIC mitigates the shortcomings of both parameter-heavy training and monolithic VLM reasoning. Experiments on 4 diverse image classification benchmark datasets demonstrate that MARIC significantly outperforms baselines, highlighting the effectiveness of multi-agent visual reasoning for robust and interpretable image classification.
SPIO: Ensemble and Selective Strategies via LLM-Based Multi-Agent Planning in Automated Data Science
Mar 30, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized automated data analytics and machine learning by enabling dynamic reasoning and adaptability. While recent approaches have advanced multi-stage pipelines through multi-agent systems, they typically rely on rigid, single-path workflows that limit the exploration and integration of diverse strategies, often resulting in suboptimal predictions. To address these challenges, we propose SPIO (Sequential Plan Integration and Optimization), a novel framework that leverages LLM-driven decision-making to orchestrate multi-agent planning across four key modules: data preprocessing, feature engineering, modeling, and hyperparameter tuning. In each module, dedicated planning agents independently generate candidate strategies that cascade into subsequent stages, fostering comprehensive exploration. A plan optimization agent refines these strategies by suggesting several optimized plans. We further introduce two variants: SPIO-S, which selects a single best solution path as determined by the LLM, and SPIO-E, which selects the top k candidate plans and ensembles them to maximize predictive performance. Extensive experiments on Kaggle and OpenML datasets demonstrate that SPIO significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, providing a robust and scalable solution for automated data science task.
QA-Expand: Multi-Question Answer Generation for Enhanced Query Expansion in Information Retrieval
Feb 12, 2025
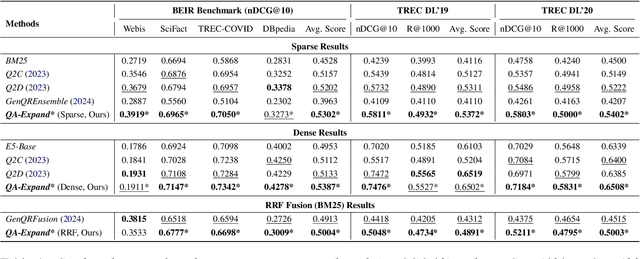
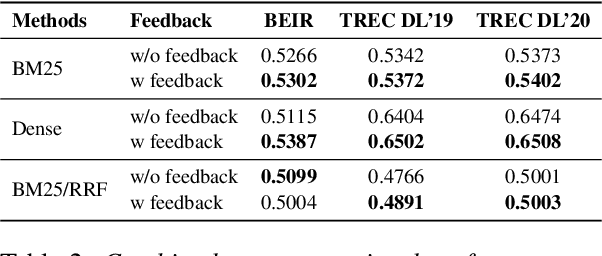
Abstract:Query expansion is widely used in Information Retrieval (IR) to improve search outcomes by enriching queries with additional contextual information. Although recent Large Language Model (LLM) based methods generate pseudo-relevant content and expanded terms via multiple prompts, they often yield repetitive, narrow expansions that lack the diverse context needed to retrieve all relevant information. In this paper, we introduce QA-Expand, a novel and effective framework for query expansion. It first generates multiple relevant questions from the initial query and subsequently produces corresponding pseudo-answers as surrogate documents. A feedback model further rewrites and filters these answers to ensure only the most informative augmentations are incorporated. Extensive experiments on benchmarks such as BEIR and TREC demonstrate that QA-Expand enhances retrieval performance by up to 13% over state-of-the-art methods, offering a robust solution for modern retrieval challenges.
Pesti-Gen: Unleashing a Generative Molecule Approach for Toxicity Aware Pesticide Design
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Global climate change has reduced crop resilience and pesticide efficacy, making reliance on synthetic pesticides inevitable, even though their widespread use poses significant health and environmental risks. While these pesticides remain a key tool in pest management, previous machine-learning applications in pesticide and agriculture have focused on classification or regression, leaving the fundamental challenge of generating new molecular structures or designing novel candidates unaddressed. In this paper, we propose Pesti-Gen, a novel generative model based on variational auto-encoders, designed to create pesticide candidates with optimized properties for the first time. Specifically, Pesti-Gen leverages a two-stage learning process: an initial pre-training phase that captures a generalized chemical structure representation, followed by a fine-tuning stage that incorporates toxicity-specific information. The model simultaneously optimizes over multiple toxicity metrics, such as (1) livestock toxicity and (2) aqua toxicity to generate environmentally friendly pesticide candidates. Notably, Pesti-Gen achieves approximately 68\% structural validity in generating new molecular structures, demonstrating the model's effectiveness in producing optimized and feasible pesticide candidates, thereby providing a new way for safer and more sustainable pest management solutions.
ValuesRAG: Enhancing Cultural Alignment Through Retrieval-Augmented Contextual Learning
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Cultural values alignment in Large Language Models (LLMs) is a critical challenge due to their tendency to embed Western-centric biases from training data, leading to misrepresentations and fairness issues in cross-cultural contexts. Recent approaches, such as role-assignment and few-shot learning, often struggle with reliable cultural alignment as they heavily rely on pre-trained knowledge, lack scalability, and fail to capture nuanced cultural values effectively. To address these issues, we propose ValuesRAG, a novel and effective framework that applies Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with in-context learning to integrate cultural and demographic knowledge dynamically during text generation. Leveraging the World Values Survey (WVS) dataset, ValuesRAG first generates summaries of values for each individual. Subsequently, we curated several representative regional datasets to serve as test datasets and retrieve relevant summaries of values based on demographic features, followed by a reranking step to select the top-k relevant summaries. ValuesRAG consistently outperforms baseline methods, both in the main experiment and in the ablation study where only the values summary was provided, highlighting ValuesRAG's potential to foster culturally aligned AI systems and enhance the inclusivity of AI-driven applications.
GenCRF: Generative Clustering and Reformulation Framework for Enhanced Intent-Driven Information Retrieval
Sep 17, 2024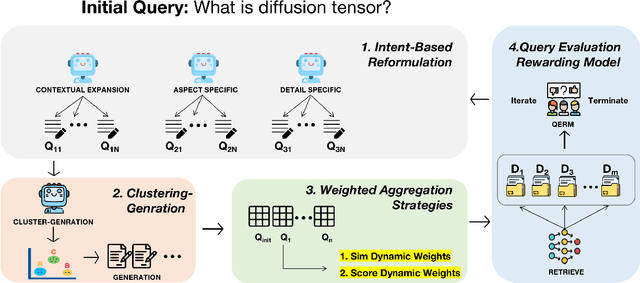
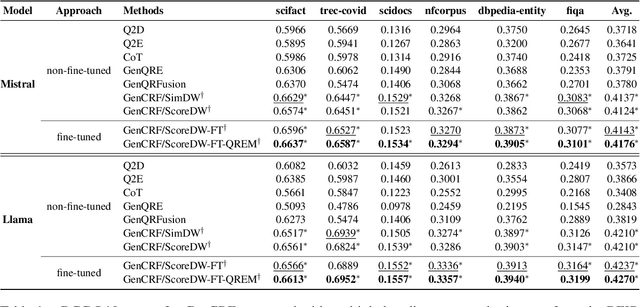
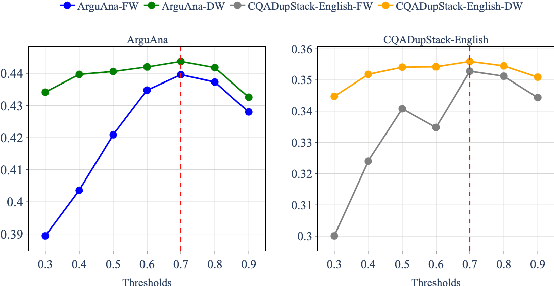
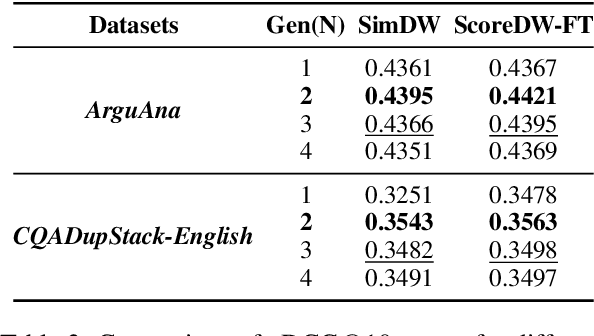
Abstract:Query reformulation is a well-known problem in Information Retrieval (IR) aimed at enhancing single search successful completion rate by automatically modifying user's input query. Recent methods leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve query reformulation, but often generate limited and redundant expansions, potentially constraining their effectiveness in capturing diverse intents. In this paper, we propose GenCRF: a Generative Clustering and Reformulation Framework to capture diverse intentions adaptively based on multiple differentiated, well-generated queries in the retrieval phase for the first time. GenCRF leverages LLMs to generate variable queries from the initial query using customized prompts, then clusters them into groups to distinctly represent diverse intents. Furthermore, the framework explores to combine diverse intents query with innovative weighted aggregation strategies to optimize retrieval performance and crucially integrates a novel Query Evaluation Rewarding Model (QERM) to refine the process through feedback loops. Empirical experiments on the BEIR benchmark demonstrate that GenCRF achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing previous query reformulation SOTAs by up to 12% on nDCG@10. These techniques can be adapted to various LLMs, significantly boosting retriever performance and advancing the field of Information Retrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge