MA4DIV: Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Search Result Diversification
Paper and Code
Mar 27, 2024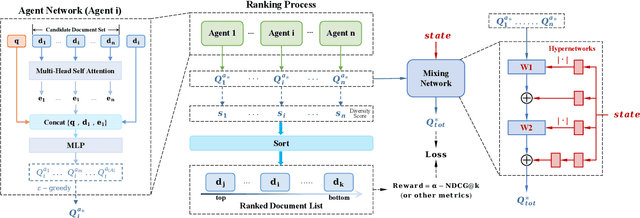

The objective of search result diversification (SRD) is to ensure that selected documents cover as many different subtopics as possible. Existing methods primarily utilize a paradigm of "greedy selection", i.e., selecting one document with the highest diversity score at a time. These approaches tend to be inefficient and are easily trapped in a suboptimal state. In addition, some other methods aim to approximately optimize the diversity metric, such as $\alpha$-NDCG, but the results still remain suboptimal. To address these challenges, we introduce Multi-Agent reinforcement learning (MARL) for search result DIVersity, which called MA4DIV. In this approach, each document is an agent and the search result diversification is modeled as a cooperative task among multiple agents. This approach allows for directly optimizing the diversity metrics, such as $\alpha$-NDCG, while achieving high training efficiency. We conducted preliminary experiments on public TREC datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness and potential of MA4DIV. Considering the limited number of queries in public TREC datasets, we construct a large-scale dataset from industry sources and show that MA4DIV achieves substantial improvements in both effectiveness and efficiency than existing baselines on a industrial scale dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge