Manni Duan
DomainCQA: Crafting Expert-Level QA from Domain-Specific Charts
Mar 25, 2025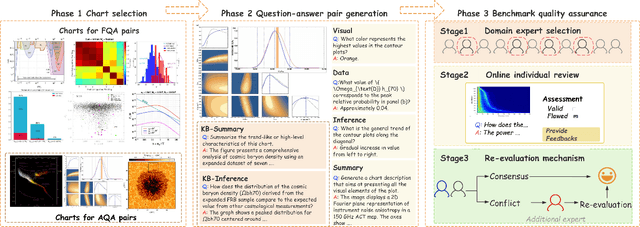
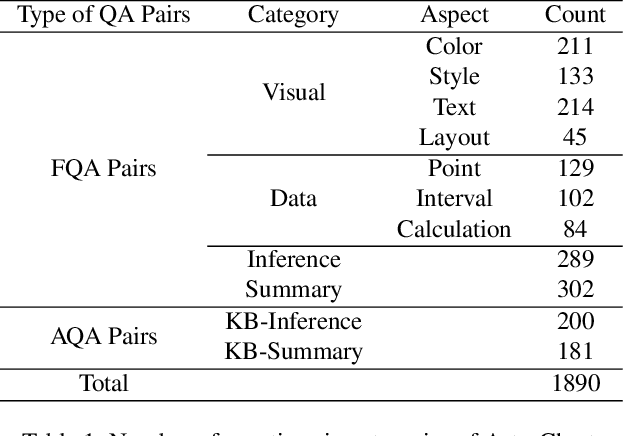
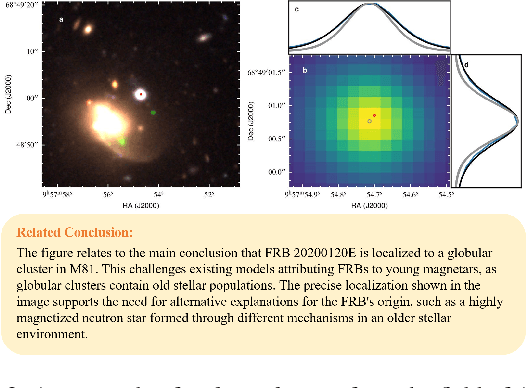
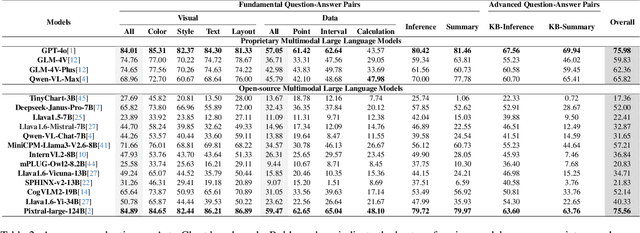
Abstract:Chart Question Answering (CQA) benchmarks are essential for evaluating the capability of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to interpret visual data. However, current benchmarks focus primarily on the evaluation of general-purpose CQA but fail to adequately capture domain-specific challenges. We introduce DomainCQA, a systematic methodology for constructing domain-specific CQA benchmarks, and demonstrate its effectiveness by developing AstroChart, a CQA benchmark in the field of astronomy. Our evaluation shows that chart reasoning and combining chart information with domain knowledge for deeper analysis and summarization, rather than domain-specific knowledge, pose the primary challenge for existing MLLMs, highlighting a critical gap in current benchmarks. By providing a scalable and rigorous framework, DomainCQA enables more precise assessment and improvement of MLLMs for domain-specific applications.
Large Language Models Understand Layouts
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate extraordinary abilities in a wide range of natural language processing (NLP) tasks. In this paper, we show that, beyond text understanding capability, LLMs are capable of processing text layouts that are denoted by spatial markers. They are able to answer questions that require explicit spatial perceiving and reasoning, while a drastic performance drop is observed when the spatial markers from the original data are excluded. We perform a series of experiments with the GPT-3.5, Baichuan2, Llama2 and ChatGLM3 models on various types of layout-sensitive datasets for further analysis. The experimental results reveal that the layout understanding ability of LLMs is mainly introduced by the coding data for pretraining, which is further enhanced at the instruction-tuning stage. In addition, layout understanding can be enhanced by integrating low-cost, auto-generated data approached by a novel text game. Finally, we show that layout understanding ability is beneficial for building efficient visual question-answering (VQA) systems.
Revisiting the Power of Prompt for Visual Tuning
Feb 04, 2024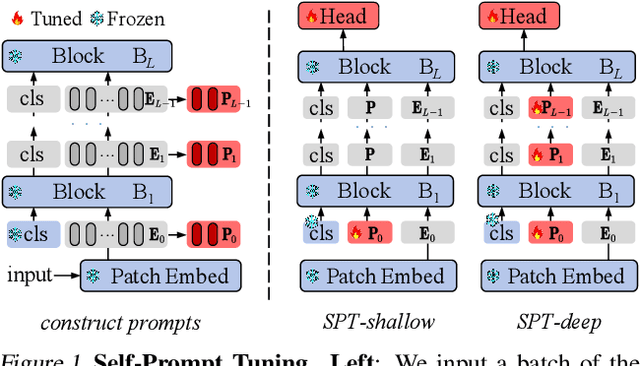
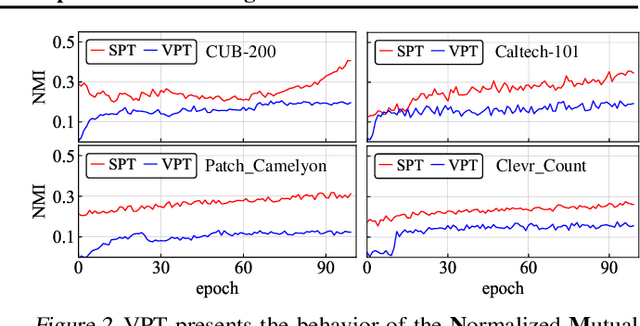
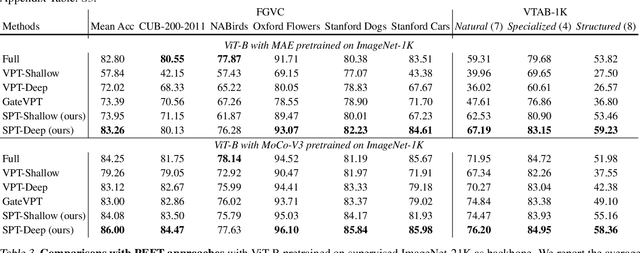
Abstract:Visual prompt tuning (VPT) is a promising solution incorporating learnable prompt tokens to customize pre-trained models for downstream tasks. However, VPT and its variants often encounter challenges like prompt initialization, prompt length, and subpar performance in self-supervised pretraining, hindering successful contextual adaptation. This study commences by exploring the correlation evolvement between prompts and patch tokens during proficient training. Inspired by the observation that the prompt tokens tend to share high mutual information with patch tokens, we propose initializing prompts with downstream token prototypes. The strategic initialization, a stand-in for the previous initialization, substantially improves performance in fine-tuning. To refine further, we optimize token construction with a streamlined pipeline that maintains excellent performance with almost no increase in computational expenses compared to VPT. Exhaustive experiments show our proposed approach outperforms existing methods by a remarkable margin. For instance, it surpasses full fine-tuning in 19 out of 24 tasks, using less than 0.4% of learnable parameters on the FGVC and VTAB-1K benchmarks. Notably, our method significantly advances the adaptation for self-supervised pretraining, achieving impressive task performance gains of at least 10% to 30%. Besides, the experimental results demonstrate the proposed SPT is robust to prompt lengths and scales well with model capacity and training data size. We finally provide an insightful exploration into the amount of target data facilitating the adaptation of pre-trained models to downstream tasks.
Improving Knowledge Distillation via Regularizing Feature Norm and Direction
May 26, 2023
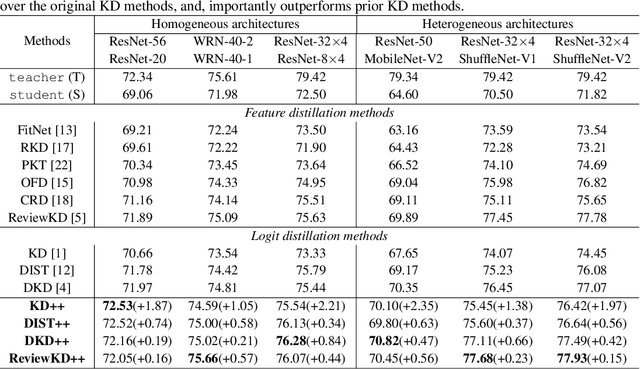
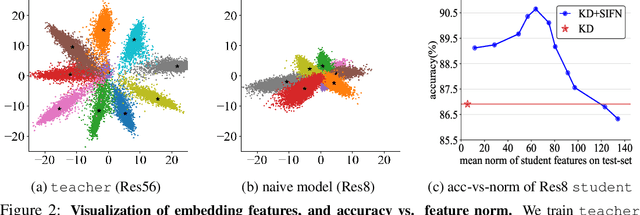

Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) exploits a large well-trained model (i.e., teacher) to train a small student model on the same dataset for the same task. Treating teacher features as knowledge, prevailing methods of knowledge distillation train student by aligning its features with the teacher's, e.g., by minimizing the KL-divergence between their logits or L2 distance between their intermediate features. While it is natural to believe that better alignment of student features to the teacher better distills teacher knowledge, simply forcing this alignment does not directly contribute to the student's performance, e.g., classification accuracy. In this work, we propose to align student features with class-mean of teacher features, where class-mean naturally serves as a strong classifier. To this end, we explore baseline techniques such as adopting the cosine distance based loss to encourage the similarity between student features and their corresponding class-means of the teacher. Moreover, we train the student to produce large-norm features, inspired by other lines of work (e.g., model pruning and domain adaptation), which find the large-norm features to be more significant. Finally, we propose a rather simple loss term (dubbed ND loss) to simultaneously (1) encourage student to produce large-\emph{norm} features, and (2) align the \emph{direction} of student features and teacher class-means. Experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate that our explored techniques help existing KD methods achieve better performance, i.e., higher classification accuracy on ImageNet and CIFAR100 datasets, and higher detection precision on COCO dataset. Importantly, our proposed ND loss helps the most, leading to the state-of-the-art performance on these benchmarks. The source code is available at \url{https://github.com/WangYZ1608/Knowledge-Distillation-via-ND}.
FocalClick: Towards Practical Interactive Image Segmentation
Apr 17, 2022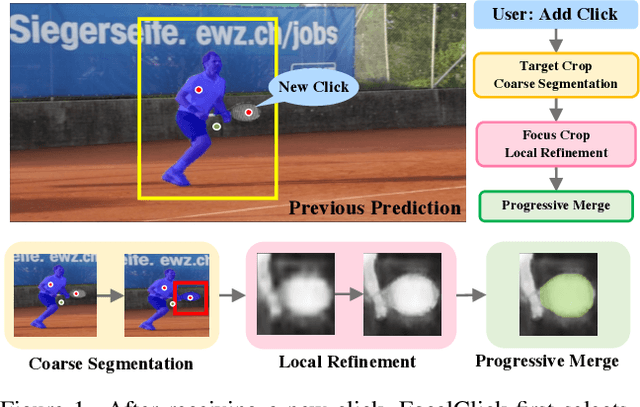

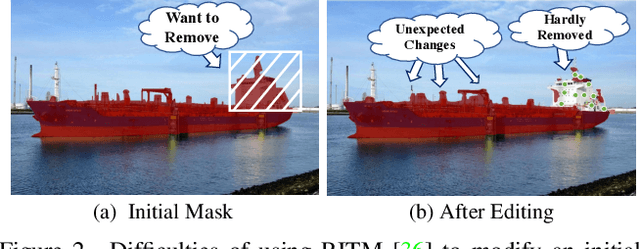
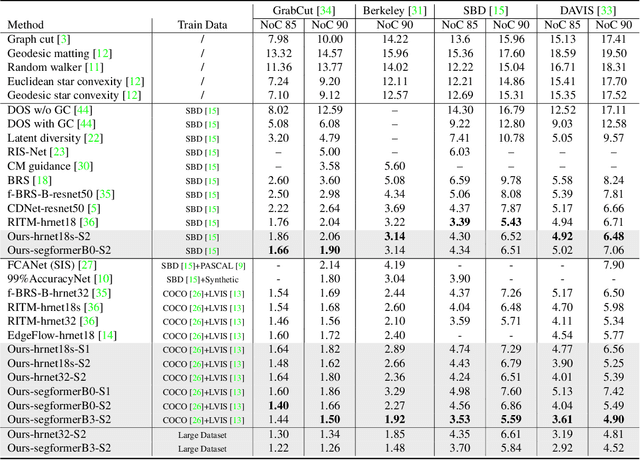
Abstract:Interactive segmentation allows users to extract target masks by making positive/negative clicks. Although explored by many previous works, there is still a gap between academic approaches and industrial needs: first, existing models are not efficient enough to work on low power devices; second, they perform poorly when used to refine preexisting masks as they could not avoid destroying the correct part. FocalClick solves both issues at once by predicting and updating the mask in localized areas. For higher efficiency, we decompose the slow prediction on the entire image into two fast inferences on small crops: a coarse segmentation on the Target Crop, and a local refinement on the Focus Crop. To make the model work with preexisting masks, we formulate a sub-task termed Interactive Mask Correction, and propose Progressive Merge as the solution. Progressive Merge exploits morphological information to decide where to preserve and where to update, enabling users to refine any preexisting mask effectively. FocalClick achieves competitive results against SOTA methods with significantly smaller FLOPs. It also shows significant superiority when making corrections on preexisting masks. Code and data will be released at github.com/XavierCHEN34/ClickSEG
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge