Tian Jiang
DHGS: Decoupled Hybrid Gaussian Splatting for Driving Scene
Jul 29, 2024



Abstract:Existing Gaussian splatting methods often fall short in achieving satisfactory novel view synthesis in driving scenes, primarily due to the absence of crafty design and geometric constraints for the involved elements. This paper introduces a novel neural rendering method termed Decoupled Hybrid Gaussian Splatting (DHGS), targeting at promoting the rendering quality of novel view synthesis for static driving scenes. The novelty of this work lies in the decoupled and hybrid pixel-level blender for road and non-road layers, without the conventional unified differentiable rendering logic for the entire scene, while still maintaining consistent and continuous superimposition through the proposed depth-ordered hybrid rendering strategy. Additionally, an implicit road representation comprised of a Signed Distance Field (SDF) is trained to supervise the road surface with subtle geometric attributes. Accompanied by the use of auxiliary transmittance loss and consistency loss, novel images with imperceptible boundary and elevated fidelity are ultimately obtained. Substantial experiments on the Waymo dataset prove that DHGS outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. The project page where more video evidences are given is: https://ironbrotherstyle.github.io/dhgs_web.
Progressive Feature Fusion Network for Enhancing Image Quality Assessment
Jan 13, 2024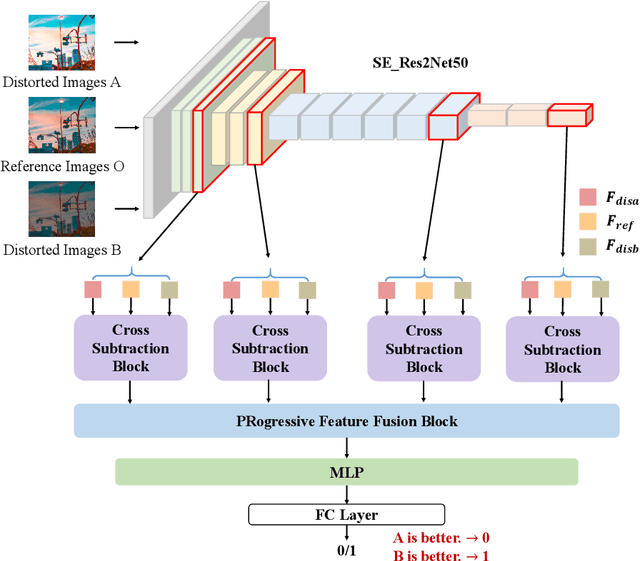
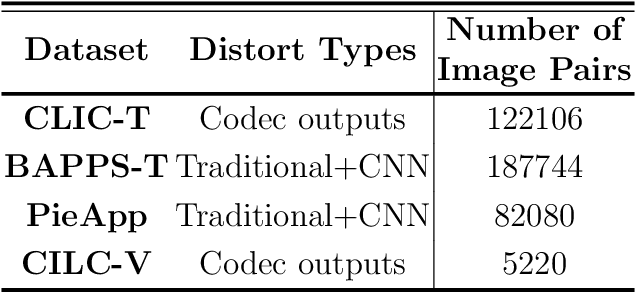
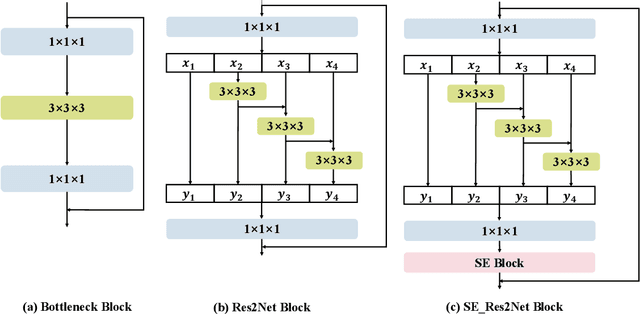
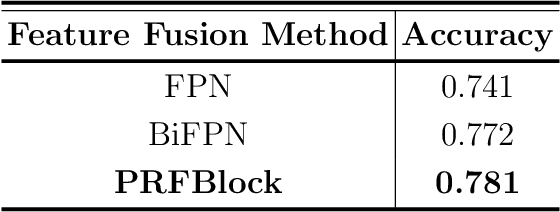
Abstract:Image compression has been applied in the fields of image storage and video broadcasting. However, it's formidably tough to distinguish the subtle quality differences between those distorted images generated by different algorithms. In this paper, we propose a new image quality assessment framework to decide which image is better in an image group. To capture the subtle differences, a fine-grained network is adopted to acquire multi-scale features. Subsequently, we design a cross subtract block for separating and gathering the information within positive and negative image pairs. Enabling image comparison in feature space. After that, a progressive feature fusion block is designed, which fuses multi-scale features in a novel progressive way. Hierarchical spatial 2D features can thus be processed gradually. Experimental results show that compared with the current mainstream image quality assessment methods, the proposed network can achieve more accurate image quality assessment and ranks second in the benchmark of CLIC in the image perceptual model track.
Evaluating the Potential of Leading Large Language Models in Reasoning Biology Questions
Nov 05, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have presented new opportunities for integrating Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) into biological research and education. This study evaluated the capabilities of leading LLMs, including GPT-4, GPT-3.5, PaLM2, Claude2, and SenseNova, in answering conceptual biology questions. The models were tested on a 108-question multiple-choice exam covering biology topics in molecular biology, biological techniques, metabolic engineering, and synthetic biology. Among the models, GPT-4 achieved the highest average score of 90 and demonstrated the greatest consistency across trials with different prompts. The results indicated GPT-4's proficiency in logical reasoning and its potential to aid biology research through capabilities like data analysis, hypothesis generation, and knowledge integration. However, further development and validation are still required before the promise of LLMs in accelerating biological discovery can be realized.
Evaluating Distribution System Reliability with Hyperstructures Graph Convolutional Nets
Nov 14, 2022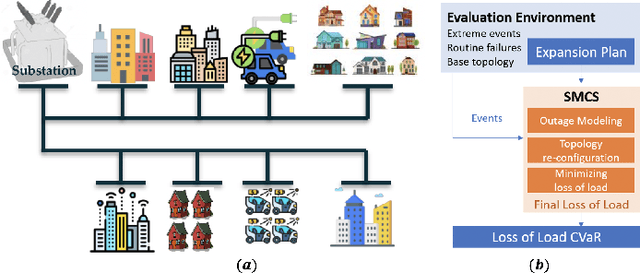
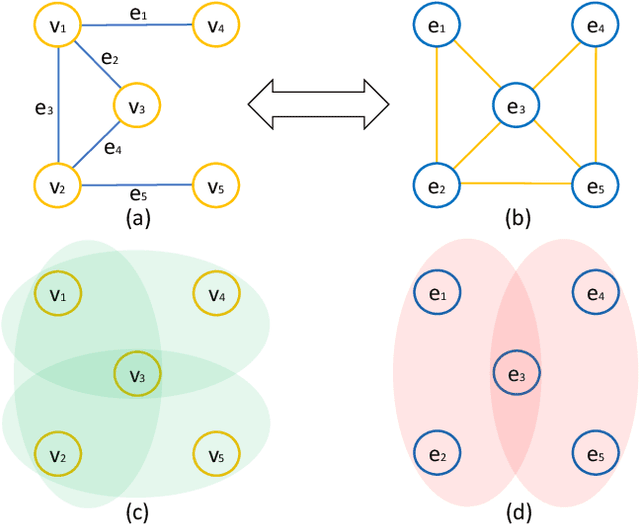
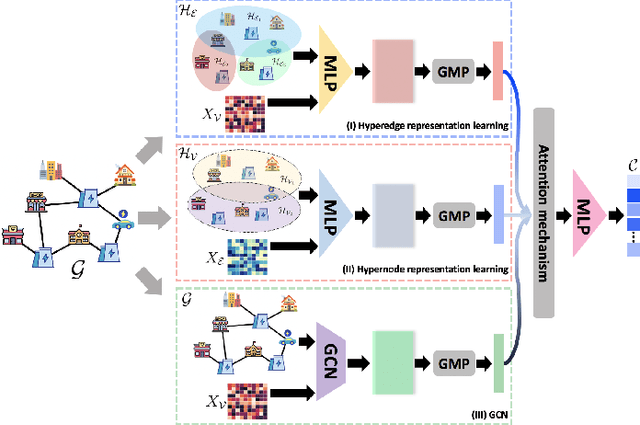
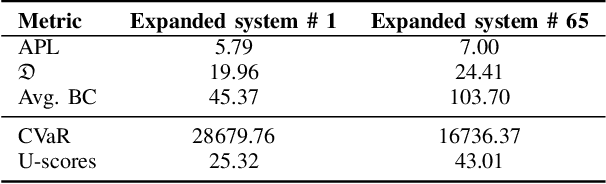
Abstract:Nowadays, it is broadly recognized in the power system community that to meet the ever expanding energy sector's needs, it is no longer possible to rely solely on physics-based models and that reliable, timely and sustainable operation of energy systems is impossible without systematic integration of artificial intelligence (AI) tools. Nevertheless, the adoption of AI in power systems is still limited, while integration of AI particularly into distribution grid investment planning is still an uncharted territory. We make the first step forward to bridge this gap by showing how graph convolutional networks coupled with the hyperstructures representation learning framework can be employed for accurate, reliable, and computationally efficient distribution grid planning with resilience objectives. We further propose a Hyperstructures Graph Convolutional Neural Networks (Hyper-GCNNs) to capture hidden higher order representations of distribution networks with attention mechanism. Our numerical experiments show that the proposed Hyper-GCNNs approach yields substantial gains in computational efficiency compared to the prevailing methodology in distribution grid planning and also noticeably outperforms seven state-of-the-art models from deep learning (DL) community.
A Minesweeper Solver Using Logic Inference, CSP and Sampling
Oct 07, 2018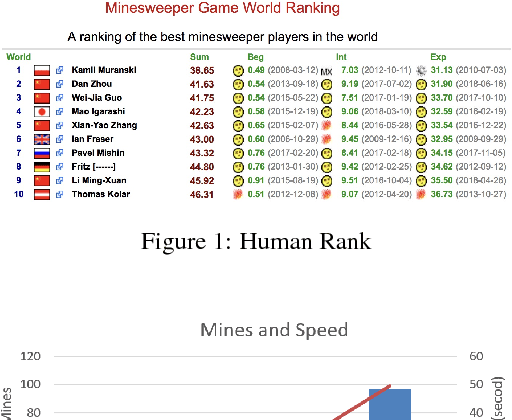
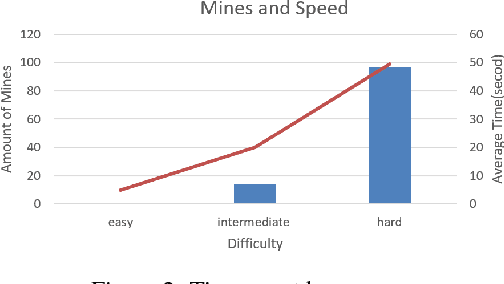
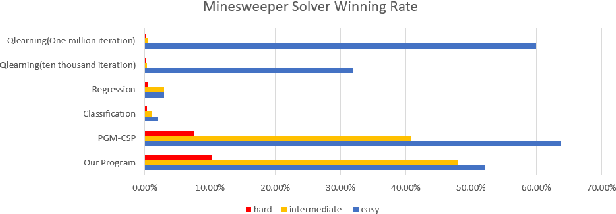
Abstract:Minesweeper as a puzzle video game and is proved that it is an NPC problem. We use CSP, Logic Inference and Sampling to make a minesweeper solver and we limit us each select in 5 seconds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge