Xi Wu
Interactive Motion Planning for Human-Robot Collaboration Based on Human-Centric Configuration Space Ergonomic Field
Dec 16, 2025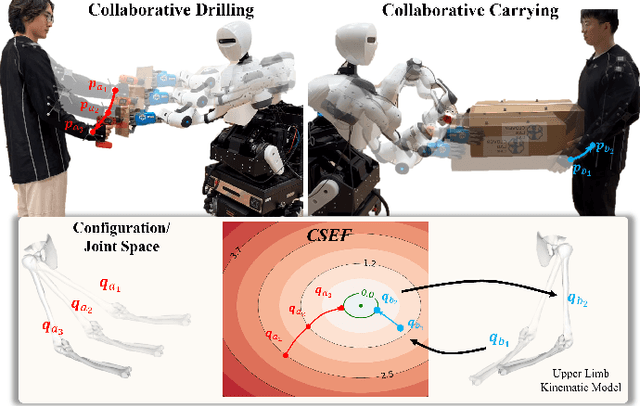
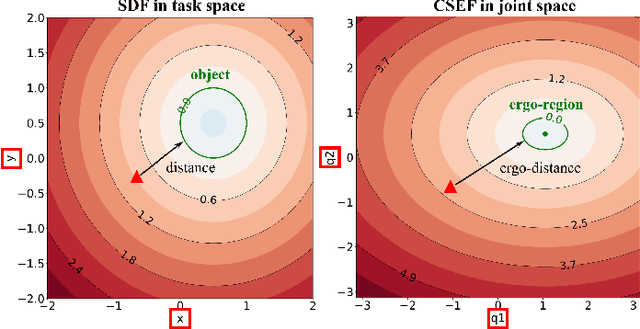
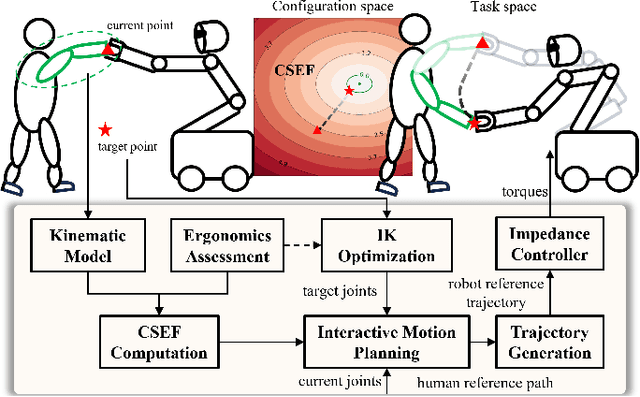
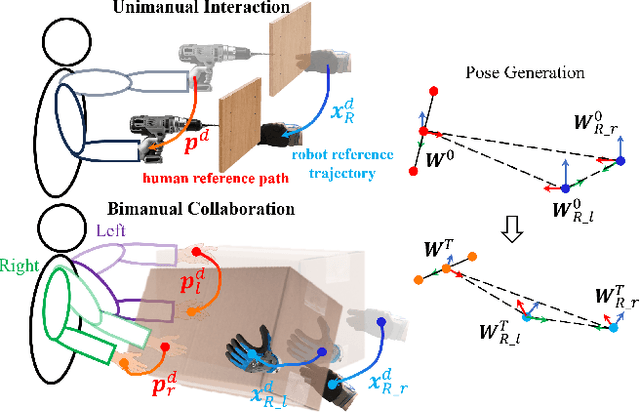
Abstract:Industrial human-robot collaboration requires motion planning that is collision-free, responsive, and ergonomically safe to reduce fatigue and musculoskeletal risk. We propose the Configuration Space Ergonomic Field (CSEF), a continuous and differentiable field over the human joint space that quantifies ergonomic quality and provides gradients for real-time ergonomics-aware planning. An efficient algorithm constructs CSEF from established metrics with joint-wise weighting and task conditioning, and we integrate it into a gradient-based planner compatible with impedance-controlled robots. In a 2-DoF benchmark, CSEF-based planning achieves higher success rates, lower ergonomic cost, and faster computation than a task-space ergonomic planner. Hardware experiments with a dual-arm robot in unimanual guidance, collaborative drilling, and bimanual cocarrying show faster ergonomic cost reduction, closer tracking to optimized joint targets, and lower muscle activation than a point-to-point baseline. CSEF-based planning method reduces average ergonomic scores by up to 10.31% for collaborative drilling tasks and 5.60% for bimanual co-carrying tasks while decreasing activation in key muscle groups, indicating practical benefits for real-world deployment.
Advancing Ocean State Estimation with efficient and scalable AI
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Accurate and efficient global ocean state estimation remains a grand challenge for Earth system science, hindered by the dual bottlenecks of computational scalability and degraded data fidelity in traditional data assimilation (DA) and deep learning (DL) approaches. Here we present an AI-driven Data Assimilation Framework for Ocean (ADAF-Ocean) that directly assimilates multi-source and multi-scale observations, ranging from sparse in-situ measurements to 4 km satellite swaths, without any interpolation or data thinning. Inspired by Neural Processes, ADAF-Ocean learns a continuous mapping from heterogeneous inputs to ocean states, preserving native data fidelity. Through AI-driven super-resolution, it reconstructs 0.25$^\circ$ mesoscale dynamics from coarse 1$^\circ$ fields, which ensures both efficiency and scalability, with just 3.7\% more parameters than the 1$^\circ$ configuration. When coupled with a DL forecasting system, ADAF-Ocean extends global forecast skill by up to 20 days compared to baselines without assimilation. This framework establishes a computationally viable and scientifically rigorous pathway toward real-time, high-resolution Earth system monitoring.
Integrating Ergonomics and Manipulability for Upper Limb Postural Optimization in Bimanual Human-Robot Collaboration
Nov 06, 2025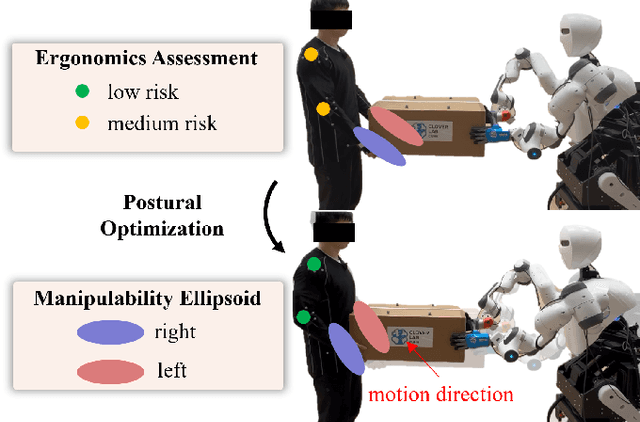
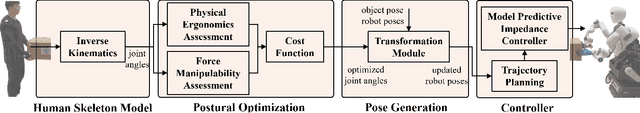
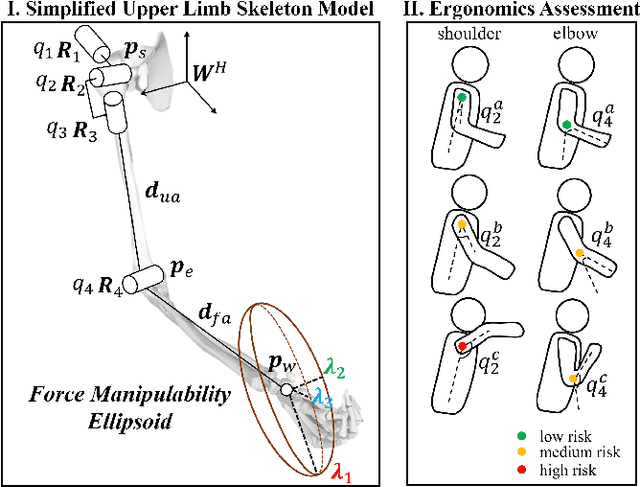
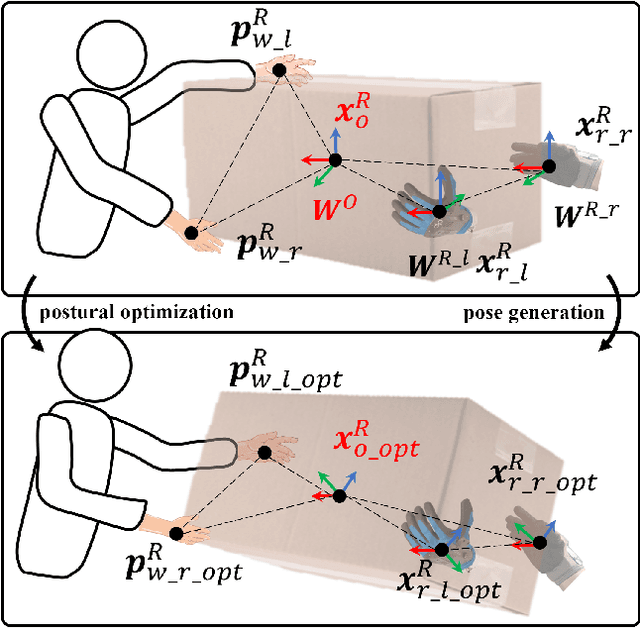
Abstract:This paper introduces an upper limb postural optimization method for enhancing physical ergonomics and force manipulability during bimanual human-robot co-carrying tasks. Existing research typically emphasizes human safety or manipulative efficiency, whereas our proposed method uniquely integrates both aspects to strengthen collaboration across diverse conditions (e.g., different grasping postures of humans, and different shapes of objects). Specifically, the joint angles of a simplified human skeleton model are optimized by minimizing the cost function to prioritize safety and manipulative capability. To guide humans towards the optimized posture, the reference end-effector poses of the robot are generated through a transformation module. A bimanual model predictive impedance controller (MPIC) is proposed for our human-like robot, CURI, to recalibrate the end effector poses through planned trajectories. The proposed method has been validated through various subjects and objects during human-human collaboration (HHC) and human-robot collaboration (HRC). The experimental results demonstrate significant improvement in muscle conditions by comparing the activation of target muscles before and after optimization.
RLMiniStyler: Light-weight RL Style Agent for Arbitrary Sequential Neural Style Generation
May 07, 2025Abstract:Arbitrary style transfer aims to apply the style of any given artistic image to another content image. Still, existing deep learning-based methods often require significant computational costs to generate diverse stylized results. Motivated by this, we propose a novel reinforcement learning-based framework for arbitrary style transfer RLMiniStyler. This framework leverages a unified reinforcement learning policy to iteratively guide the style transfer process by exploring and exploiting stylization feedback, generating smooth sequences of stylized results while achieving model lightweight. Furthermore, we introduce an uncertainty-aware multi-task learning strategy that automatically adjusts loss weights to adapt to the content and style balance requirements at different training stages, thereby accelerating model convergence. Through a series of experiments across image various resolutions, we have validated the advantages of RLMiniStyler over other state-of-the-art methods in generating high-quality, diverse artistic image sequences at a lower cost. Codes are available at https://github.com/fengxiaoming520/RLMiniStyler.
Real-Time Animatable 2DGS-Avatars with Detail Enhancement from Monocular Videos
May 01, 2025Abstract:High-quality, animatable 3D human avatar reconstruction from monocular videos offers significant potential for reducing reliance on complex hardware, making it highly practical for applications in game development, augmented reality, and social media. However, existing methods still face substantial challenges in capturing fine geometric details and maintaining animation stability, particularly under dynamic or complex poses. To address these issues, we propose a novel real-time framework for animatable human avatar reconstruction based on 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS). By leveraging 2DGS and global SMPL pose parameters, our framework not only aligns positional and rotational discrepancies but also enables robust and natural pose-driven animation of the reconstructed avatars. Furthermore, we introduce a Rotation Compensation Network (RCN) that learns rotation residuals by integrating local geometric features with global pose parameters. This network significantly improves the handling of non-rigid deformations and ensures smooth, artifact-free pose transitions during animation. Experimental results demonstrate that our method successfully reconstructs realistic and highly animatable human avatars from monocular videos, effectively preserving fine-grained details while ensuring stable and natural pose variation. Our approach surpasses current state-of-the-art methods in both reconstruction quality and animation robustness on public benchmarks.
Muscle Activation Estimation by Optimizing the Musculoskeletal Model for Personalized Strength and Conditioning Training
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:Musculoskeletal models are pivotal in the domains of rehabilitation and resistance training to analyze muscle conditions. However, individual variability in musculoskeletal parameters and the immeasurability of some internal biomechanical variables pose significant obstacles to accurate personalized modelling. Furthermore, muscle activation estimation can be challenging due to the inherent redundancy of the musculoskeletal system, where multiple muscles drive a single joint. This study develops a whole-body musculoskeletal model for strength and conditioning training and calibrates relevant muscle parameters with an electromyography-based optimization method. By utilizing the personalized musculoskeletal model, muscle activation can be subsequently estimated to analyze the performance of exercises. Bench press and deadlift are chosen for experimental verification to affirm the efficacy of this approach.
Human-Like Robot Impedance Regulation Skill Learning from Human-Human Demonstrations
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Humans are experts in collaborating with others physically by regulating compliance behaviors based on the perception of their partner states and the task requirements. Enabling robots to develop proficiency in human collaboration skills can facilitate more efficient human-robot collaboration (HRC). This paper introduces an innovative impedance regulation skill learning framework for achieving HRC in multiple physical collaborative tasks. The framework is designed to adjust the robot compliance to the human partner states while adhering to reference trajectories provided by human-human demonstrations. Specifically, electromyography (EMG) signals from human muscles are collected and analyzed to extract limb impedance, representing compliance behaviors during demonstrations. Human endpoint motions are captured and represented using a probabilistic learning method to create reference trajectories and corresponding impedance profiles. Meanwhile, an LSTMbased module is implemented to develop task-oriented impedance regulation policies by mapping the muscle synergistic contributions between two demonstrators. Finally, we propose a wholebody impedance controller for a human-like robot, coordinating joint outputs to achieve the desired impedance and reference trajectory during task execution. Experimental validation was conducted through a collaborative transportation task and two interactive Tai Chi pushing hands tasks, demonstrating superior performance from the perspective of interactive forces compared to a constant impedance control method.
Teacher Encoder-Student Decoder Denoising Guided Segmentation Network for Anomaly Detection
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:Visual anomaly detection is a highly challenging task, often categorized as a one-class classification and segmentation problem. Recent studies have demonstrated that the student-teacher (S-T) framework effectively addresses this challenge. However, most S-T frameworks rely solely on pre-trained teacher networks to guide student networks in learning multi-scale similar features, overlooking the potential of the student networks to enhance learning through multi-scale feature fusion. In this study, we propose a novel model named PFADSeg, which integrates a pre-trained teacher network, a denoising student network with multi-scale feature fusion, and a guided anomaly segmentation network into a unified framework. By adopting a unique teacher-encoder and student-decoder denoising mode, the model improves the student network's ability to learn from teacher network features. Furthermore, an adaptive feature fusion mechanism is introduced to train a self-supervised segmentation network that synthesizes anomaly masks autonomously, significantly increasing detection performance. Evaluated on the MVTec AD dataset, PFADSeg achieves state-of-the-art results with an image-level AUC of 98.9%, a pixel-level mean precision of 76.4%, and an instance-level mean precision of 78.7%.
BASIC: Semi-supervised Multi-organ Segmentation with Balanced Subclass Regularization and Semantic-conflict Penalty
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has shown notable potential in relieving the heavy demand of dense prediction tasks on large-scale well-annotated datasets, especially for the challenging multi-organ segmentation (MoS). However, the prevailing class-imbalance problem in MoS caused by the substantial variations in organ size exacerbates the learning difficulty of the SSL network. To address this issue, in this paper, we propose an innovative semi-supervised network with BAlanced Subclass regularIzation and semantic-Conflict penalty mechanism (BASIC) to effectively learn the unbiased knowledge for semi-supervised MoS. Concretely, we construct a novel auxiliary subclass segmentation (SCS) task based on priorly generated balanced subclasses, thus deeply excavating the unbiased information for the main MoS task with the fashion of multi-task learning. Additionally, based on a mean teacher framework, we elaborately design a balanced subclass regularization to utilize the teacher predictions of SCS task to supervise the student predictions of MoS task, thus effectively transferring unbiased knowledge to the MoS subnetwork and alleviating the influence of the class-imbalance problem. Considering the similar semantic information inside the subclasses and their corresponding original classes (i.e., parent classes), we devise a semantic-conflict penalty mechanism to give heavier punishments to the conflicting SCS predictions with wrong parent classes and provide a more accurate constraint to the MoS predictions. Extensive experiments conducted on two publicly available datasets, i.e., the WORD dataset and the MICCAI FLARE 2022 dataset, have verified the superior performance of our proposed BASIC compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
A Self-Learning Multimodal Approach for Fake News Detection
Dec 08, 2024



Abstract:The rapid growth of social media has resulted in an explosion of online news content, leading to a significant increase in the spread of misleading or false information. While machine learning techniques have been widely applied to detect fake news, the scarcity of labeled datasets remains a critical challenge. Misinformation frequently appears as paired text and images, where a news article or headline is accompanied by a related visuals. In this paper, we introduce a self-learning multimodal model for fake news classification. The model leverages contrastive learning, a robust method for feature extraction that operates without requiring labeled data, and integrates the strengths of Large Language Models (LLMs) to jointly analyze both text and image features. LLMs are excel at this task due to their ability to process diverse linguistic data drawn from extensive training corpora. Our experimental results on a public dataset demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms several state-of-the-art classification approaches, achieving over 85% accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. These findings highlight the model's effectiveness in tackling the challenges of multimodal fake news detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge