Chenzui Li
Interactive Motion Planning for Human-Robot Collaboration Based on Human-Centric Configuration Space Ergonomic Field
Dec 16, 2025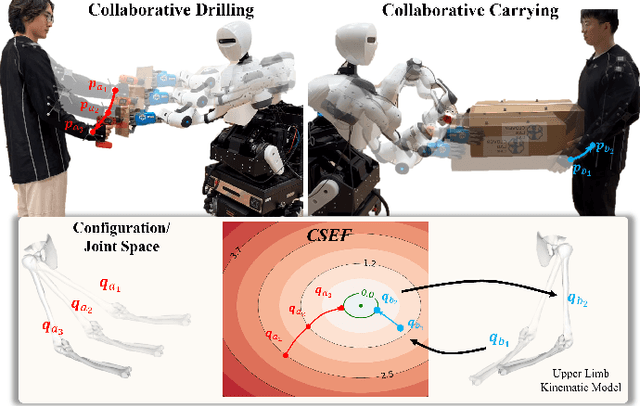
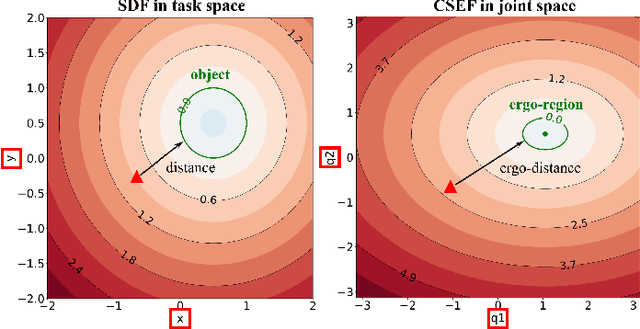
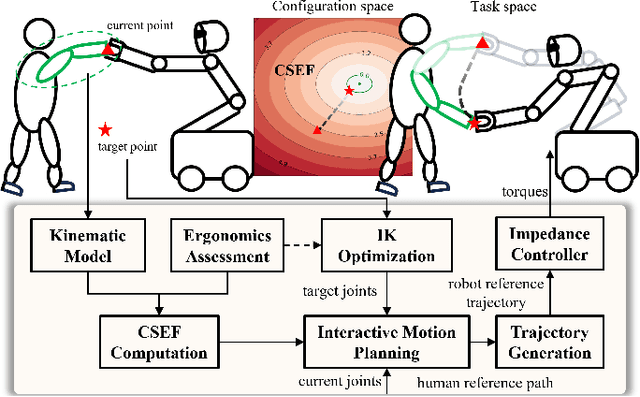
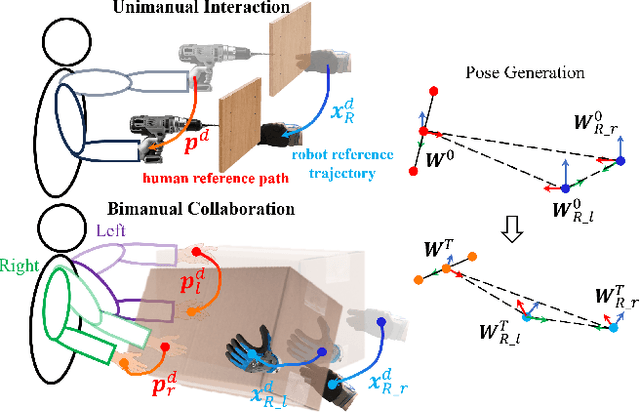
Abstract:Industrial human-robot collaboration requires motion planning that is collision-free, responsive, and ergonomically safe to reduce fatigue and musculoskeletal risk. We propose the Configuration Space Ergonomic Field (CSEF), a continuous and differentiable field over the human joint space that quantifies ergonomic quality and provides gradients for real-time ergonomics-aware planning. An efficient algorithm constructs CSEF from established metrics with joint-wise weighting and task conditioning, and we integrate it into a gradient-based planner compatible with impedance-controlled robots. In a 2-DoF benchmark, CSEF-based planning achieves higher success rates, lower ergonomic cost, and faster computation than a task-space ergonomic planner. Hardware experiments with a dual-arm robot in unimanual guidance, collaborative drilling, and bimanual cocarrying show faster ergonomic cost reduction, closer tracking to optimized joint targets, and lower muscle activation than a point-to-point baseline. CSEF-based planning method reduces average ergonomic scores by up to 10.31% for collaborative drilling tasks and 5.60% for bimanual co-carrying tasks while decreasing activation in key muscle groups, indicating practical benefits for real-world deployment.
Integrating Ergonomics and Manipulability for Upper Limb Postural Optimization in Bimanual Human-Robot Collaboration
Nov 06, 2025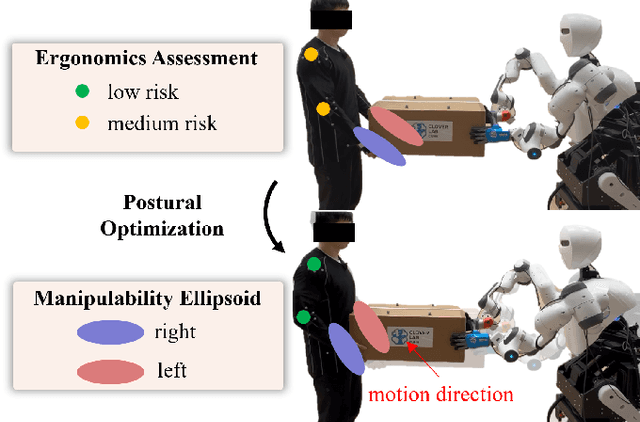
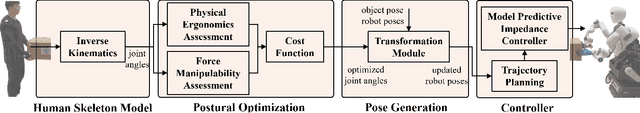
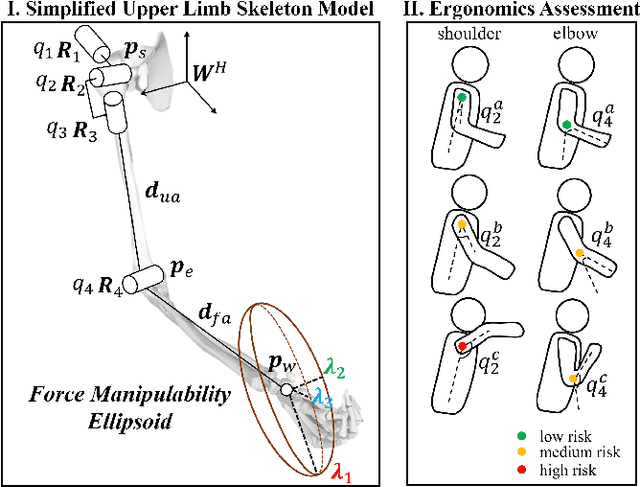
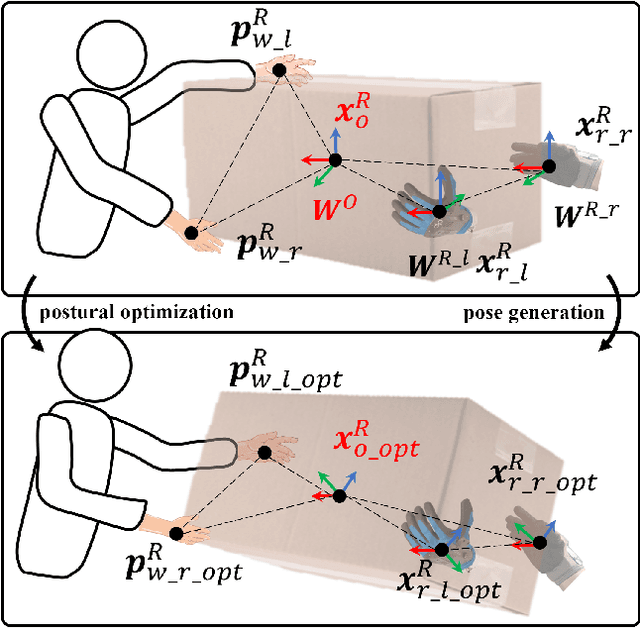
Abstract:This paper introduces an upper limb postural optimization method for enhancing physical ergonomics and force manipulability during bimanual human-robot co-carrying tasks. Existing research typically emphasizes human safety or manipulative efficiency, whereas our proposed method uniquely integrates both aspects to strengthen collaboration across diverse conditions (e.g., different grasping postures of humans, and different shapes of objects). Specifically, the joint angles of a simplified human skeleton model are optimized by minimizing the cost function to prioritize safety and manipulative capability. To guide humans towards the optimized posture, the reference end-effector poses of the robot are generated through a transformation module. A bimanual model predictive impedance controller (MPIC) is proposed for our human-like robot, CURI, to recalibrate the end effector poses through planned trajectories. The proposed method has been validated through various subjects and objects during human-human collaboration (HHC) and human-robot collaboration (HRC). The experimental results demonstrate significant improvement in muscle conditions by comparing the activation of target muscles before and after optimization.
Muscle Activation Estimation by Optimizing the Musculoskeletal Model for Personalized Strength and Conditioning Training
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:Musculoskeletal models are pivotal in the domains of rehabilitation and resistance training to analyze muscle conditions. However, individual variability in musculoskeletal parameters and the immeasurability of some internal biomechanical variables pose significant obstacles to accurate personalized modelling. Furthermore, muscle activation estimation can be challenging due to the inherent redundancy of the musculoskeletal system, where multiple muscles drive a single joint. This study develops a whole-body musculoskeletal model for strength and conditioning training and calibrates relevant muscle parameters with an electromyography-based optimization method. By utilizing the personalized musculoskeletal model, muscle activation can be subsequently estimated to analyze the performance of exercises. Bench press and deadlift are chosen for experimental verification to affirm the efficacy of this approach.
Human-Like Robot Impedance Regulation Skill Learning from Human-Human Demonstrations
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Humans are experts in collaborating with others physically by regulating compliance behaviors based on the perception of their partner states and the task requirements. Enabling robots to develop proficiency in human collaboration skills can facilitate more efficient human-robot collaboration (HRC). This paper introduces an innovative impedance regulation skill learning framework for achieving HRC in multiple physical collaborative tasks. The framework is designed to adjust the robot compliance to the human partner states while adhering to reference trajectories provided by human-human demonstrations. Specifically, electromyography (EMG) signals from human muscles are collected and analyzed to extract limb impedance, representing compliance behaviors during demonstrations. Human endpoint motions are captured and represented using a probabilistic learning method to create reference trajectories and corresponding impedance profiles. Meanwhile, an LSTMbased module is implemented to develop task-oriented impedance regulation policies by mapping the muscle synergistic contributions between two demonstrators. Finally, we propose a wholebody impedance controller for a human-like robot, coordinating joint outputs to achieve the desired impedance and reference trajectory during task execution. Experimental validation was conducted through a collaborative transportation task and two interactive Tai Chi pushing hands tasks, demonstrating superior performance from the perspective of interactive forces compared to a constant impedance control method.
BiRP: Learning Robot Generalized Bimanual Coordination using Relative Parameterization Method on Human Demonstration
Jul 12, 2023Abstract:Human bimanual manipulation can perform more complex tasks than a simple combination of two single arms, which is credited to the spatio-temporal coordination between the arms. However, the description of bimanual coordination is still an open topic in robotics. This makes it difficult to give an explainable coordination paradigm, let alone applied to robotics. In this work, we divide the main bimanual tasks in human daily activities into two types: leader-follower and synergistic coordination. Then we propose a relative parameterization method to learn these types of coordination from human demonstration. It represents coordination as Gaussian mixture models from bimanual demonstration to describe the change in the importance of coordination throughout the motions by probability. The learned coordinated representation can be generalized to new task parameters while ensuring spatio-temporal coordination. We demonstrate the method using synthetic motions and human demonstration data and deploy it to a humanoid robot to perform a generalized bimanual coordination motion. We believe that this easy-to-use bimanual learning from demonstration (LfD) method has the potential to be used as a data augmentation plugin for robot large manipulation model training. The corresponding codes are open-sourced in https://github.com/Skylark0924/Rofunc.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge