Ning Guo
ArenaRL: Scaling RL for Open-Ended Agents via Tournament-based Relative Ranking
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning has substantially improved the performance of LLM agents on tasks with verifiable outcomes, but it still struggles on open-ended agent tasks with vast solution spaces (e.g., complex travel planning). Due to the absence of objective ground-truth for these tasks, current RL algorithms largely rely on reward models that assign scalar scores to individual responses. We contend that such pointwise scoring suffers from an inherent discrimination collapse: the reward model struggles to distinguish subtle advantages among different trajectories, resulting in scores within a group being compressed into a narrow range. Consequently, the effective reward signal becomes dominated by noise from the reward model, leading to optimization stagnation. To address this, we propose ArenaRL, a reinforcement learning paradigm that shifts from pointwise scalar scoring to intra-group relative ranking. ArenaRL introduces a process-aware pairwise evaluation mechanism, employing multi-level rubrics to assign fine-grained relative scores to trajectories. Additionally, we construct an intra-group adversarial arena and devise a tournament-based ranking scheme to obtain stable advantage signals. Empirical results confirm that the built seeded single-elimination scheme achieves nearly equivalent advantage estimation accuracy to full pairwise comparisons with O(N^2) complexity, while operating with only O(N) complexity, striking an optimal balance between efficiency and precision. Furthermore, to address the lack of full-cycle benchmarks for open-ended agents, we build Open-Travel and Open-DeepResearch, two high-quality benchmarks featuring a comprehensive pipeline covering SFT, RL training, and multi-dimensional evaluation. Extensive experiments show that ArenaRL substantially outperforms standard RL baselines, enabling LLM agents to generate more robust solutions for complex real-world tasks.
AMAP Agentic Planning Technical Report
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:We present STAgent, an agentic large language model tailored for spatio-temporal understanding, designed to solve complex tasks such as constrained point-of-interest discovery and itinerary planning. STAgent is a specialized model capable of interacting with ten distinct tools within spatio-temporal scenarios, enabling it to explore, verify, and refine intermediate steps during complex reasoning. Notably, STAgent effectively preserves its general capabilities. We empower STAgent with these capabilities through three key contributions: (1) a stable tool environment that supports over ten domain-specific tools, enabling asynchronous rollout and training; (2) a hierarchical data curation framework that identifies high-quality data like a needle in a haystack, curating high-quality queries with a filter ratio of 1:10,000, emphasizing both diversity and difficulty; and (3) a cascaded training recipe that starts with a seed SFT stage acting as a guardian to measure query difficulty, followed by a second SFT stage fine-tuned on queries with high certainty, and an ultimate RL stage that leverages data of low certainty. Initialized with Qwen3-30B-A3B to establish a strong SFT foundation and leverage insights into sample difficulty, STAgent yields promising performance on TravelBench while maintaining its general capabilities across a wide range of general benchmarks, thereby demonstrating the effectiveness of our proposed agentic model.
Look, Zoom, Understand: The Robotic Eyeball for Embodied Perception
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:In embodied AI perception systems, visual perception should be active: the goal is not to passively process static images, but to actively acquire more informative data within pixel and spatial budget constraints. Existing vision models and fixed RGB-D camera systems fundamentally fail to reconcile wide-area coverage with fine-grained detail acquisition, severely limiting their efficacy in open-world robotic applications. To address this issue, we propose EyeVLA, a robotic eyeball for active visual perception that can take proactive actions based on instructions, enabling clear observation of fine-grained target objects and detailed information across a wide spatial extent. EyeVLA discretizes action behaviors into action tokens and integrates them with vision-language models (VLMs) that possess strong open-world understanding capabilities, enabling joint modeling of vision, language, and actions within a single autoregressive sequence. By using the 2D bounding box coordinates to guide the reasoning chain and applying reinforcement learning to refine the viewpoint selection policy, we transfer the open-world scene understanding capability of the VLM to a vision language action (VLA) policy using only minimal real-world data. Experiments show that our system efficiently performs instructed scenes in real-world environments and actively acquires more accurate visual information through instruction-driven actions of rotation and zoom, thereby achieving strong environmental perception capabilities. EyeVLA introduces a novel robotic vision system that leverages detailed and spatially rich, large-scale embodied data, and actively acquires highly informative visual observations for downstream embodied tasks.
OWT: A Foundational Organ-Wise Tokenization Framework for Medical Imaging
May 08, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in representation learning often rely on holistic, black-box embeddings that entangle multiple semantic components, limiting interpretability and generalization. These issues are especially critical in medical imaging. To address these limitations, we propose an Organ-Wise Tokenization (OWT) framework with a Token Group-based Reconstruction (TGR) training paradigm. Unlike conventional approaches that produce holistic features, OWT explicitly disentangles an image into separable token groups, each corresponding to a distinct organ or semantic entity. Our design ensures each token group encapsulates organ-specific information, boosting interpretability, generalization, and efficiency while allowing fine-grained control in downstream tasks. Experiments on CT and MRI datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of OWT in not only achieving strong image reconstruction and segmentation performance, but also enabling novel semantic-level generation and retrieval applications that are out of reach for standard holistic embedding methods. These findings underscore the potential of OWT as a foundational framework for semantically disentangled representation learning, offering broad scalability and applicability to real-world medical imaging scenarios and beyond.
MAST-Pro: Dynamic Mixture-of-Experts for Adaptive Segmentation of Pan-Tumors with Knowledge-Driven Prompts
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Accurate tumor segmentation is crucial for cancer diagnosis and treatment. While foundation models have advanced general-purpose segmentation, existing methods still struggle with: (1) limited incorporation of medical priors, (2) imbalance between generic and tumor-specific features, and (3) high computational costs for clinical adaptation. To address these challenges, we propose MAST-Pro (Mixture-of-experts for Adaptive Segmentation of pan-Tumors with knowledge-driven Prompts), a novel framework that integrates dynamic Mixture-of-Experts (D-MoE) and knowledge-driven prompts for pan-tumor segmentation. Specifically, text and anatomical prompts provide domain-specific priors, guiding tumor representation learning, while D-MoE dynamically selects experts to balance generic and tumor-specific feature learning, improving segmentation accuracy across diverse tumor types. To enhance efficiency, we employ Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT), optimizing MAST-Pro with significantly reduced computational overhead. Experiments on multi-anatomical tumor datasets demonstrate that MAST-Pro outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving up to a 5.20% improvement in average DSC while reducing trainable parameters by 91.04%, without compromising accuracy.
Developing a PET/CT Foundation Model for Cross-Modal Anatomical and Functional Imaging
Mar 04, 2025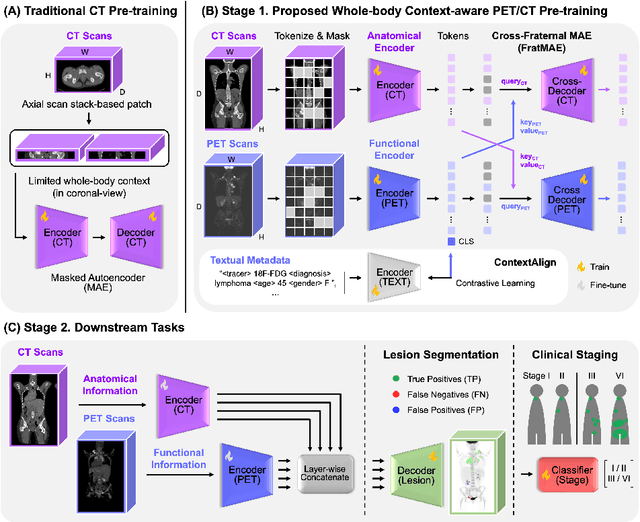
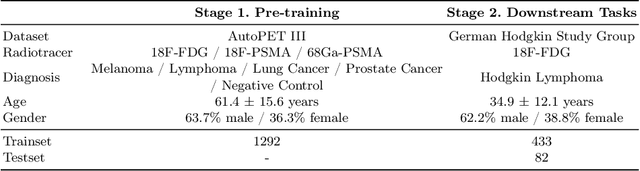
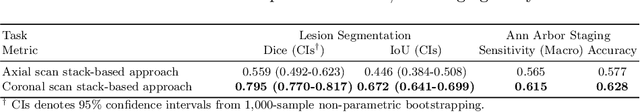
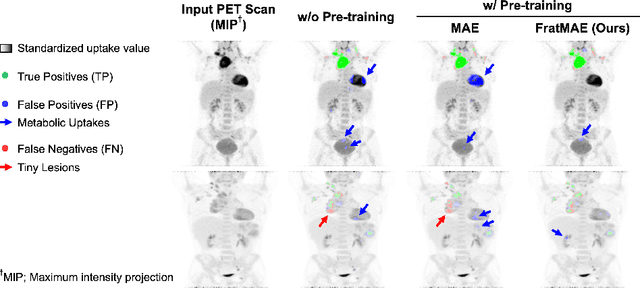
Abstract:In oncology, Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography (PET/CT) is widely used in cancer diagnosis, staging, and treatment monitoring, as it combines anatomical details from CT with functional metabolic activity and molecular marker expression information from PET. However, existing artificial intelligence-driven PET/CT analyses rely predominantly on task-specific models trained from scratch or on limited datasets, limiting their generalizability and robustness. To address this, we propose a foundation model approach specifically designed for multimodal PET/CT imaging. We introduce the Cross-Fraternal Twin Masked Autoencoder (FratMAE), a novel framework that effectively integrates whole-body anatomical and functional or molecular information. FratMAE employs separate Vision Transformer (ViT) encoders for PET and CT scans, along with cross-attention decoders that enable synergistic interactions between modalities during masked autoencoder training. Additionally, it incorporates textual metadata to enhance PET representation learning. By pre-training on PET/CT datasets, FratMAE captures intricate cross-modal relationships and global uptake patterns, achieving superior performance on downstream tasks and demonstrating its potential as a generalizable foundation model.
On Flange-based 3D Hand-Eye Calibration for Soft Robotic Tactile Welding
Jul 27, 2024



Abstract:This paper investigates the direct application of standardized designs on the robot for conducting robot hand-eye calibration by employing 3D scanners with collaborative robots. The well-established geometric features of the robot flange are exploited by directly capturing its point cloud data. In particular, an iterative method is proposed to facilitate point cloud processing toward a refined calibration outcome. Several extensive experiments are conducted over a range of collaborative robots, including Universal Robots UR5 & UR10 e-series, Franka Emika, and AUBO i5 using an industrial-grade 3D scanner Photoneo Phoxi S & M and a commercial-grade 3D scanner Microsoft Azure Kinect DK. Experimental results show that translational and rotational errors converge efficiently to less than 0.28 mm and 0.25 degrees, respectively, achieving a hand-eye calibration accuracy as high as the camera's resolution, probing the hardware limit. A welding seam tracking system is presented, combining the flange-based calibration method with soft tactile sensing. The experiment results show that the system enables the robot to adjust its motion in real-time, ensuring consistent weld quality and paving the way for more efficient and adaptable manufacturing processes.
DSFNet: Learning Disentangled Scenario Factorization for Multi-Scenario Route Ranking
Mar 30, 2024



Abstract:Multi-scenario route ranking (MSRR) is crucial in many industrial mapping systems. However, the industrial community mainly adopts interactive interfaces to encourage users to select pre-defined scenarios, which may hinder the downstream ranking performance. In addition, in the academic community, the multi-scenario ranking works only come from other fields, and there are no works specifically focusing on route data due to lacking a publicly available MSRR dataset. Moreover, all the existing multi-scenario works still fail to address the three specific challenges of MSRR simultaneously, i.e. explosion of scenario number, high entanglement, and high-capacity demand. Different from the prior, to address MSRR, our key idea is to factorize the complicated scenario in route ranking into several disentangled factor scenario patterns. Accordingly, we propose a novel method, Disentangled Scenario Factorization Network (DSFNet), which flexibly composes scenario-dependent parameters based on a high-capacity multi-factor-scenario-branch structure. Then, a novel regularization is proposed to induce the disentanglement of factor scenarios. Furthermore, two extra novel techniques, i.e. scenario-aware batch normalization and scenario-aware feature filtering, are developed to improve the network awareness of scenario representation. Additionally, to facilitate MSRR research in the academic community, we propose MSDR, the first large-scale publicly available annotated industrial Multi-Scenario Driving Route dataset. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our DSFNet, which has been successfully deployed in AMap to serve the major online traffic.
Adaptive trajectory-constrained exploration strategy for deep reinforcement learning
Dec 27, 2023
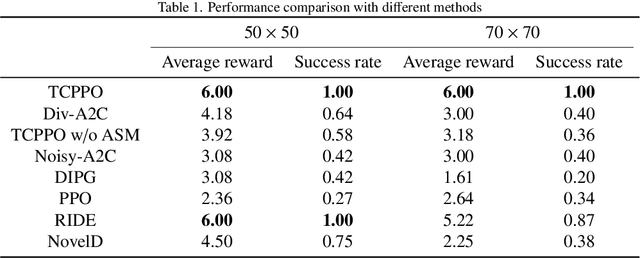


Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) faces significant challenges in addressing the hard-exploration problems in tasks with sparse or deceptive rewards and large state spaces. These challenges severely limit the practical application of DRL. Most previous exploration methods relied on complex architectures to estimate state novelty or introduced sensitive hyperparameters, resulting in instability. To mitigate these issues, we propose an efficient adaptive trajectory-constrained exploration strategy for DRL. The proposed method guides the policy of the agent away from suboptimal solutions by leveraging incomplete offline demonstrations as references. This approach gradually expands the exploration scope of the agent and strives for optimality in a constrained optimization manner. Additionally, we introduce a novel policy-gradient-based optimization algorithm that utilizes adaptively clipped trajectory-distance rewards for both single- and multi-agent reinforcement learning. We provide a theoretical analysis of our method, including a deduction of the worst-case approximation error bounds, highlighting the validity of our approach for enhancing exploration. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conducted experiments on two large 2D grid world mazes and several MuJoCo tasks. The extensive experimental results demonstrate the significant advantages of our method in achieving temporally extended exploration and avoiding myopic and suboptimal behaviors in both single- and multi-agent settings. Notably, the specific metrics and quantifiable results further support these findings. The code used in the study is available at \url{https://github.com/buaawgj/TACE}.
* 35 pages, 36 figures; accepted by Knowledge-Based Systems, not published
Proprioceptive State Estimation for Amphibious Tactile Sensing
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a novel vision-based proprioception approach for a soft robotic finger capable of estimating and reconstructing tactile interactions in terrestrial and aquatic environments. The key to this system lies in the finger's unique metamaterial structure, which facilitates omni-directional passive adaptation during grasping, protecting delicate objects across diverse scenarios. A compact in-finger camera captures high-framerate images of the finger's deformation during contact, extracting crucial tactile data in real time. We present a method of the volumetric discretized model of the soft finger and use the geometry constraints captured by the camera to find the optimal estimation of the deformed shape. The approach is benchmarked with a motion-tracking system with sparse markers and a haptic device with dense measurements. Both results show state-of-the-art accuracies, with a median error of 1.96 mm for overall body deformation, corresponding to 2.1$\%$ of the finger's length. More importantly, the state estimation is robust in both on-land and underwater environments as we demonstrate its usage for underwater object shape sensing. This combination of passive adaptation and real-time tactile sensing paves the way for amphibious robotic grasping applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge