Moona Mazher
SegRap2025: A Benchmark of Gross Tumor Volume and Lymph Node Clinical Target Volume Segmentation for Radiotherapy Planning of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Accurate delineation of Gross Tumor Volume (GTV), Lymph Node Clinical Target Volume (LN CTV), and Organ-at-Risk (OAR) from Computed Tomography (CT) scans is essential for precise radiotherapy planning in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC). Building upon SegRap2023, which focused on OAR and GTV segmentation using single-center paired non-contrast CT (ncCT) and contrast-enhanced CT (ceCT) scans, the SegRap2025 challenge aims to enhance the generalizability and robustness of segmentation models across imaging centers and modalities. SegRap2025 comprises two tasks: Task01 addresses GTV segmentation using paired CT from the SegRap2023 dataset, with an additional external testing set to evaluate cross-center generalization, and Task02 focuses on LN CTV segmentation using multi-center training data and an unseen external testing set, where each case contains paired CT scans or a single modality, emphasizing both cross-center and cross-modality robustness. This paper presents the challenge setup and provides a comprehensive analysis of the solutions submitted by ten participating teams. For GTV segmentation task, the top-performing models achieved average Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 74.61% and 56.79% on the internal and external testing cohorts, respectively. For LN CTV segmentation task, the highest average DSC values reached 60.24%, 60.50%, and 57.23% on paired CT, ceCT-only, and ncCT-only subsets, respectively. SegRap2025 establishes a large-scale multi-center, multi-modality benchmark for evaluating the generalization and robustness in radiotherapy target segmentation, providing valuable insights toward clinically applicable automated radiotherapy planning systems. The benchmark is available at: https://hilab-git.github.io/SegRap2025_Challenge.
Calibration and Uncertainty for multiRater Volume Assessment in multiorgan Segmentation (CURVAS) challenge results
May 13, 2025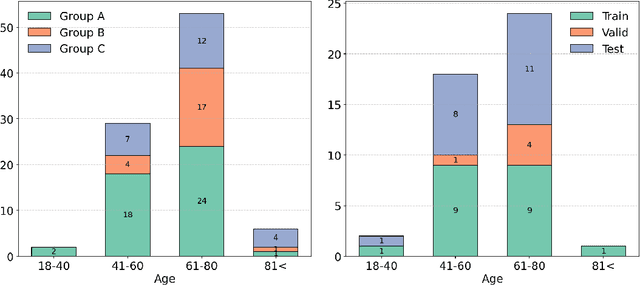
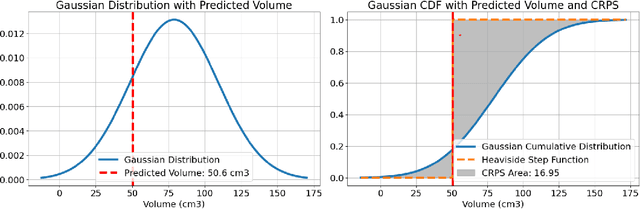

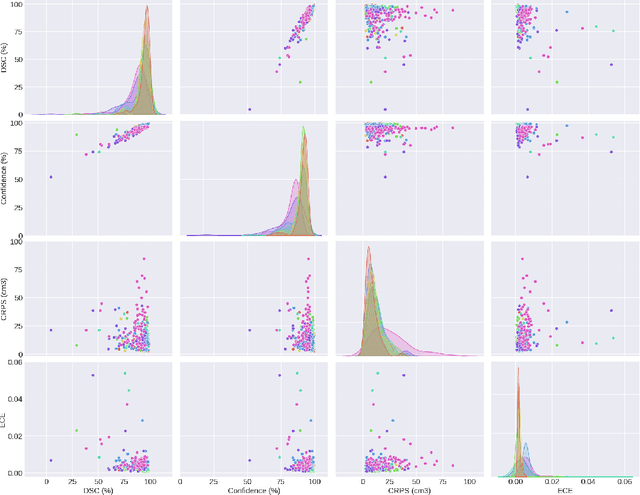
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) has become the dominant approach for medical image segmentation, yet ensuring the reliability and clinical applicability of these models requires addressing key challenges such as annotation variability, calibration, and uncertainty estimation. This is why we created the Calibration and Uncertainty for multiRater Volume Assessment in multiorgan Segmentation (CURVAS), which highlights the critical role of multiple annotators in establishing a more comprehensive ground truth, emphasizing that segmentation is inherently subjective and that leveraging inter-annotator variability is essential for robust model evaluation. Seven teams participated in the challenge, submitting a variety of DL models evaluated using metrics such as Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), Expected Calibration Error (ECE), and Continuous Ranked Probability Score (CRPS). By incorporating consensus and dissensus ground truth, we assess how DL models handle uncertainty and whether their confidence estimates align with true segmentation performance. Our findings reinforce the importance of well-calibrated models, as better calibration is strongly correlated with the quality of the results. Furthermore, we demonstrate that segmentation models trained on diverse datasets and enriched with pre-trained knowledge exhibit greater robustness, particularly in cases deviating from standard anatomical structures. Notably, the best-performing models achieved high DSC and well-calibrated uncertainty estimates. This work underscores the need for multi-annotator ground truth, thorough calibration assessments, and uncertainty-aware evaluations to develop trustworthy and clinically reliable DL-based medical image segmentation models.
Advances in Automated Fetal Brain MRI Segmentation and Biometry: Insights from the FeTA 2024 Challenge
May 05, 2025



Abstract:Accurate fetal brain tissue segmentation and biometric analysis are essential for studying brain development in utero. The FeTA Challenge 2024 advanced automated fetal brain MRI analysis by introducing biometry prediction as a new task alongside tissue segmentation. For the first time, our diverse multi-centric test set included data from a new low-field (0.55T) MRI dataset. Evaluation metrics were also expanded to include the topology-specific Euler characteristic difference (ED). Sixteen teams submitted segmentation methods, most of which performed consistently across both high- and low-field scans. However, longitudinal trends indicate that segmentation accuracy may be reaching a plateau, with results now approaching inter-rater variability. The ED metric uncovered topological differences that were missed by conventional metrics, while the low-field dataset achieved the highest segmentation scores, highlighting the potential of affordable imaging systems when paired with high-quality reconstruction. Seven teams participated in the biometry task, but most methods failed to outperform a simple baseline that predicted measurements based solely on gestational age, underscoring the challenge of extracting reliable biometric estimates from image data alone. Domain shift analysis identified image quality as the most significant factor affecting model generalization, with super-resolution pipelines also playing a substantial role. Other factors, such as gestational age, pathology, and acquisition site, had smaller, though still measurable, effects. Overall, FeTA 2024 offers a comprehensive benchmark for multi-class segmentation and biometry estimation in fetal brain MRI, underscoring the need for data-centric approaches, improved topological evaluation, and greater dataset diversity to enable clinically robust and generalizable AI tools.
Foundation Model for Whole-Heart Segmentation: Leveraging Student-Teacher Learning in Multi-Modal Medical Imaging
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:Whole-heart segmentation from CT and MRI scans is crucial for cardiovascular disease analysis, yet existing methods struggle with modality-specific biases and the need for extensive labeled datasets. To address these challenges, we propose a foundation model for whole-heart segmentation using a self-supervised learning (SSL) framework based on a student-teacher architecture. Our model is pretrained on a large, unlabeled dataset of CT and MRI scans, leveraging the xLSTM backbone to capture long-range spatial dependencies and complex anatomical structures in 3D medical images. By incorporating multi-modal pretraining, our approach ensures strong generalization across both CT and MRI modalities, mitigating modality-specific variations and improving segmentation accuracy in diverse clinical settings. The use of large-scale unlabeled data significantly reduces the dependency on manual annotations, enabling robust performance even with limited labeled data. We further introduce an xLSTM-UNet-based architecture for downstream whole-heart segmentation tasks, demonstrating its effectiveness on few-label CT and MRI datasets. Our results validate the robustness and adaptability of the proposed model, highlighting its potential for advancing automated whole-heart segmentation in medical imaging.
Multi-Class Segmentation of Aortic Branches and Zones in Computed Tomography Angiography: The AortaSeg24 Challenge
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:Multi-class segmentation of the aorta in computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans is essential for diagnosing and planning complex endovascular treatments for patients with aortic dissections. However, existing methods reduce aortic segmentation to a binary problem, limiting their ability to measure diameters across different branches and zones. Furthermore, no open-source dataset is currently available to support the development of multi-class aortic segmentation methods. To address this gap, we organized the AortaSeg24 MICCAI Challenge, introducing the first dataset of 100 CTA volumes annotated for 23 clinically relevant aortic branches and zones. This dataset was designed to facilitate both model development and validation. The challenge attracted 121 teams worldwide, with participants leveraging state-of-the-art frameworks such as nnU-Net and exploring novel techniques, including cascaded models, data augmentation strategies, and custom loss functions. We evaluated the submitted algorithms using the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and Normalized Surface Distance (NSD), highlighting the approaches adopted by the top five performing teams. This paper presents the challenge design, dataset details, evaluation metrics, and an in-depth analysis of the top-performing algorithms. The annotated dataset, evaluation code, and implementations of the leading methods are publicly available to support further research. All resources can be accessed at https://aortaseg24.grand-challenge.org.
Tumor Detection, Segmentation and Classification Challenge on Automated 3D Breast Ultrasound: The TDSC-ABUS Challenge
Jan 26, 2025



Abstract:Breast cancer is one of the most common causes of death among women worldwide. Early detection helps in reducing the number of deaths. Automated 3D Breast Ultrasound (ABUS) is a newer approach for breast screening, which has many advantages over handheld mammography such as safety, speed, and higher detection rate of breast cancer. Tumor detection, segmentation, and classification are key components in the analysis of medical images, especially challenging in the context of 3D ABUS due to the significant variability in tumor size and shape, unclear tumor boundaries, and a low signal-to-noise ratio. The lack of publicly accessible, well-labeled ABUS datasets further hinders the advancement of systems for breast tumor analysis. Addressing this gap, we have organized the inaugural Tumor Detection, Segmentation, and Classification Challenge on Automated 3D Breast Ultrasound 2023 (TDSC-ABUS2023). This initiative aims to spearhead research in this field and create a definitive benchmark for tasks associated with 3D ABUS image analysis. In this paper, we summarize the top-performing algorithms from the challenge and provide critical analysis for ABUS image examination. We offer the TDSC-ABUS challenge as an open-access platform at https://tdsc-abus2023.grand-challenge.org/ to benchmark and inspire future developments in algorithmic research.
SMILE-UHURA Challenge -- Small Vessel Segmentation at Mesoscopic Scale from Ultra-High Resolution 7T Magnetic Resonance Angiograms
Nov 14, 2024Abstract:The human brain receives nutrients and oxygen through an intricate network of blood vessels. Pathology affecting small vessels, at the mesoscopic scale, represents a critical vulnerability within the cerebral blood supply and can lead to severe conditions, such as Cerebral Small Vessel Diseases. The advent of 7 Tesla MRI systems has enabled the acquisition of higher spatial resolution images, making it possible to visualise such vessels in the brain. However, the lack of publicly available annotated datasets has impeded the development of robust, machine learning-driven segmentation algorithms. To address this, the SMILE-UHURA challenge was organised. This challenge, held in conjunction with the ISBI 2023, in Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, aimed to provide a platform for researchers working on related topics. The SMILE-UHURA challenge addresses the gap in publicly available annotated datasets by providing an annotated dataset of Time-of-Flight angiography acquired with 7T MRI. This dataset was created through a combination of automated pre-segmentation and extensive manual refinement. In this manuscript, sixteen submitted methods and two baseline methods are compared both quantitatively and qualitatively on two different datasets: held-out test MRAs from the same dataset as the training data (with labels kept secret) and a separate 7T ToF MRA dataset where both input volumes and labels are kept secret. The results demonstrate that most of the submitted deep learning methods, trained on the provided training dataset, achieved reliable segmentation performance. Dice scores reached up to 0.838 $\pm$ 0.066 and 0.716 $\pm$ 0.125 on the respective datasets, with an average performance of up to 0.804 $\pm$ 0.15.
PitVis-2023 Challenge: Workflow Recognition in videos of Endoscopic Pituitary Surgery
Sep 02, 2024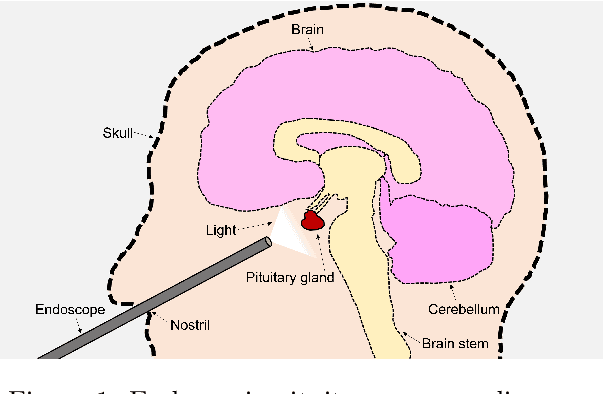
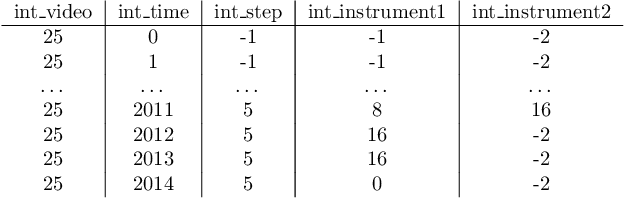
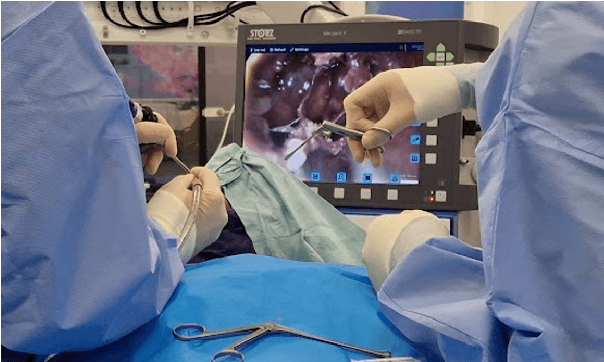
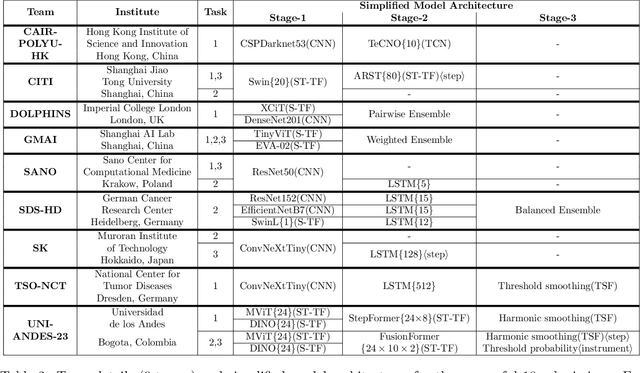
Abstract:The field of computer vision applied to videos of minimally invasive surgery is ever-growing. Workflow recognition pertains to the automated recognition of various aspects of a surgery: including which surgical steps are performed; and which surgical instruments are used. This information can later be used to assist clinicians when learning the surgery; during live surgery; and when writing operation notes. The Pituitary Vision (PitVis) 2023 Challenge tasks the community to step and instrument recognition in videos of endoscopic pituitary surgery. This is a unique task when compared to other minimally invasive surgeries due to the smaller working space, which limits and distorts vision; and higher frequency of instrument and step switching, which requires more precise model predictions. Participants were provided with 25-videos, with results presented at the MICCAI-2023 conference as part of the Endoscopic Vision 2023 Challenge in Vancouver, Canada, on 08-Oct-2023. There were 18-submissions from 9-teams across 6-countries, using a variety of deep learning models. A commonality between the top performing models was incorporating spatio-temporal and multi-task methods, with greater than 50% and 10% macro-F1-score improvement over purely spacial single-task models in step and instrument recognition respectively. The PitVis-2023 Challenge therefore demonstrates state-of-the-art computer vision models in minimally invasive surgery are transferable to a new dataset, with surgery specific techniques used to enhance performance, progressing the field further. Benchmark results are provided in the paper, and the dataset is publicly available at: https://doi.org/10.5522/04/26531686.
Assessment of Left Atrium Motion Deformation Through Full Cardiac Cycle
May 27, 2024Abstract:Unlike Right Atrium (RA), Left Atrium (LA) presents distinctive challenges, including much thinner myocardial walls, complex and irregular morphology, as well as diversity in individual's structure, making off-the-shelf methods designed for the Left Ventricle (LV) may not work in the context of the left atrium. To overcome aforementioned challenges, we are the first to present comprehensive technical workflow designed for 4D registration modeling to automatically analyze LA motion using high-resolution 3D Cine MR images. We integrate segmentation network and 4D registration process to precisely delineate LA segmentation throughout the full cardiac cycle. Additionally, an image 4D registration network is employed to extract LA displacement vector fields (DVFs). Our findings show the potential of proposed end to end framework in providing clinicians with novel regional biomarkers for left atrium motion tracking and deformation, carrying significant clinical implications.
A Robust Ensemble Algorithm for Ischemic Stroke Lesion Segmentation: Generalizability and Clinical Utility Beyond the ISLES Challenge
Apr 03, 2024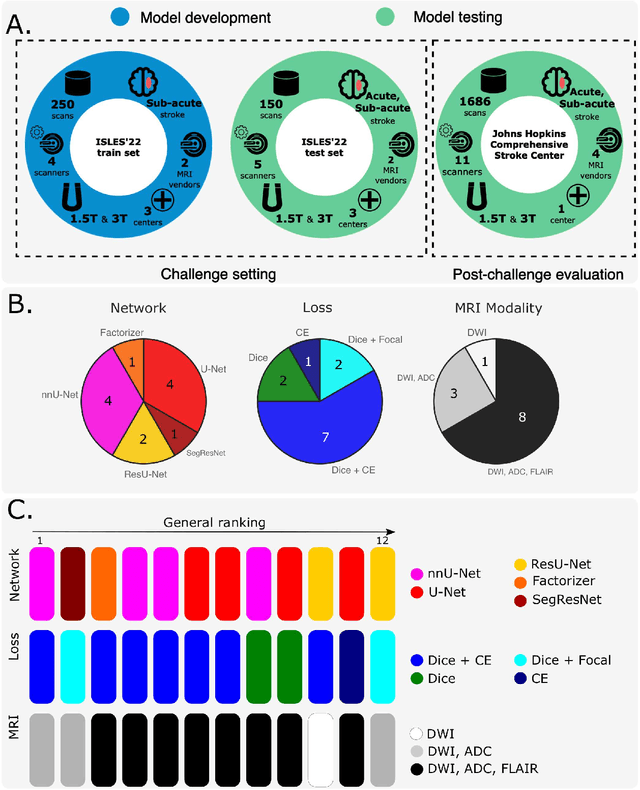
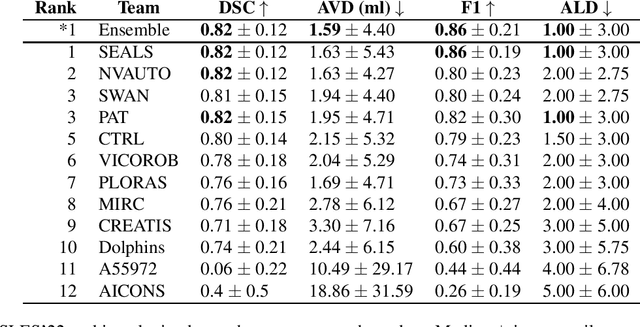
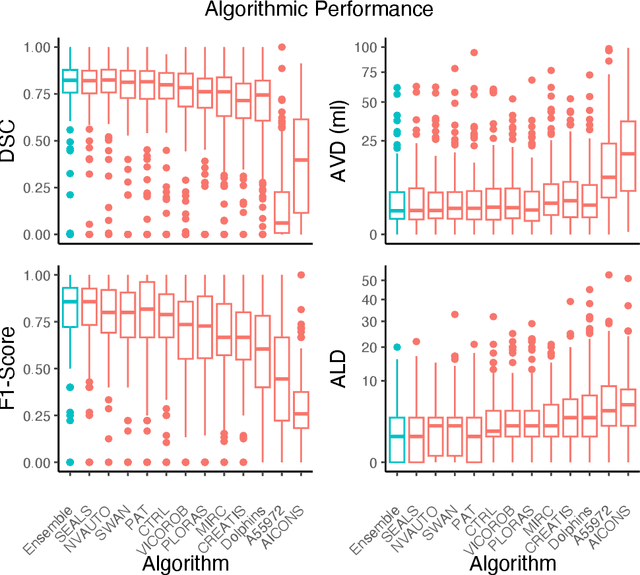
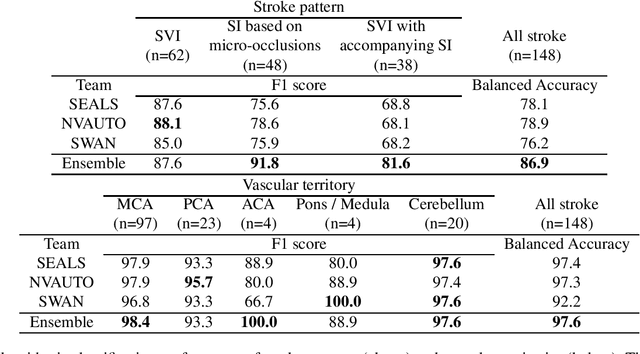
Abstract:Diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI) is essential for stroke diagnosis, treatment decisions, and prognosis. However, image and disease variability hinder the development of generalizable AI algorithms with clinical value. We address this gap by presenting a novel ensemble algorithm derived from the 2022 Ischemic Stroke Lesion Segmentation (ISLES) challenge. ISLES'22 provided 400 patient scans with ischemic stroke from various medical centers, facilitating the development of a wide range of cutting-edge segmentation algorithms by the research community. Through collaboration with leading teams, we combined top-performing algorithms into an ensemble model that overcomes the limitations of individual solutions. Our ensemble model achieved superior ischemic lesion detection and segmentation accuracy on our internal test set compared to individual algorithms. This accuracy generalized well across diverse image and disease variables. Furthermore, the model excelled in extracting clinical biomarkers. Notably, in a Turing-like test, neuroradiologists consistently preferred the algorithm's segmentations over manual expert efforts, highlighting increased comprehensiveness and precision. Validation using a real-world external dataset (N=1686) confirmed the model's generalizability. The algorithm's outputs also demonstrated strong correlations with clinical scores (admission NIHSS and 90-day mRS) on par with or exceeding expert-derived results, underlining its clinical relevance. This study offers two key findings. First, we present an ensemble algorithm (https://github.com/Tabrisrei/ISLES22_Ensemble) that detects and segments ischemic stroke lesions on DWI across diverse scenarios on par with expert (neuro)radiologists. Second, we show the potential for biomedical challenge outputs to extend beyond the challenge's initial objectives, demonstrating their real-world clinical applicability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge