Moksh Jain
A Comedy of Estimators: On KL Regularization in RL Training of LLMs
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:The reasoning performance of large language models (LLMs) can be substantially improved by training them with reinforcement learning (RL). The RL objective for LLM training involves a regularization term, which is the reverse Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between the trained policy and the reference policy. Since computing the KL divergence exactly is intractable, various estimators are used in practice to estimate it from on-policy samples. Despite its wide adoption, including in several open-source libraries, there is no systematic study analyzing the numerous ways of incorporating KL estimators in the objective and their effect on the downstream performance of RL-trained models. Recent works show that prevailing practices for incorporating KL regularization do not provide correct gradients for stated objectives, creating a discrepancy between the objective and its implementation. In this paper, we further analyze these practices and study the gradients of several estimators configurations, revealing how design choices shape gradient bias. We substantiate these findings with empirical observations by RL fine-tuning \texttt{Qwen2.5-7B}, \texttt{Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct} and \texttt{Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507} with different configurations and evaluating their performance on both in- and out-of-distribution tasks. Through our analysis, we observe that, in on-policy settings: (1) estimator configurations with biased gradients can result in training instabilities; and (2) using estimator configurations resulting in unbiased gradients leads to better performance on in-domain as well as out-of-domain tasks. We also investigate the performance resulting from different KL configurations in off-policy settings and observe that KL regularization can help stabilize off-policy RL training resulting from asynchronous setups.
Recursive Self-Aggregation Unlocks Deep Thinking in Large Language Models
Sep 30, 2025Abstract:Test-time scaling methods improve the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by increasing the amount of compute used during inference to make a prediction. Inference-time compute can be scaled in parallel by choosing among multiple independent solutions or sequentially through self-refinement. We propose Recursive Self-Aggregation (RSA), a test-time scaling method inspired by evolutionary methods that combines the benefits of both parallel and sequential scaling. Each step of RSA refines a population of candidate reasoning chains through aggregation of subsets to yield a population of improved solutions, which are then used as the candidate pool for the next iteration. RSA exploits the rich information embedded in the reasoning chains -- not just the final answers -- and enables bootstrapping from partially correct intermediate steps within different chains of thought. Empirically, RSA delivers substantial performance gains with increasing compute budgets across diverse tasks, model families and sizes. Notably, RSA enables Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507 to achieve competitive performance with larger reasoning models, including DeepSeek-R1 and o3-mini (high), while outperforming purely parallel and sequential scaling strategies across AIME-25, HMMT-25, Reasoning Gym, LiveCodeBench-v6, and SuperGPQA. We further demonstrate that training the model to combine solutions via a novel aggregation-aware reinforcement learning approach yields significant performance gains. Code available at https://github.com/HyperPotatoNeo/RSA.
Search-Based Correction of Reasoning Chains for Language Models
May 17, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning has advanced the capabilities and transparency of language models (LMs); however, reasoning chains can contain inaccurate statements that reduce performance and trustworthiness. To address this, we introduce a new self-correction framework that augments each reasoning step in a CoT with a latent variable indicating its veracity, enabling modeling of all possible truth assignments rather than assuming correctness throughout. To efficiently explore this expanded space, we introduce Search Corrector, a discrete search algorithm over boolean-valued veracity assignments. It efficiently performs otherwise intractable inference in the posterior distribution over veracity assignments by leveraging the LM's joint likelihood over veracity and the final answer as a proxy reward. This efficient inference-time correction method facilitates supervised fine-tuning of an Amortized Corrector by providing pseudo-labels for veracity. The Amortized Corrector generalizes self-correction, enabling accurate zero-shot veracity inference in novel contexts. Empirical results demonstrate that Search Corrector reliably identifies errors in logical (ProntoQA) and mathematical reasoning (GSM8K) benchmarks. The Amortized Corrector achieves comparable zero-shot accuracy and improves final answer accuracy by up to 25%.
Trajectory Balance with Asynchrony: Decoupling Exploration and Learning for Fast, Scalable LLM Post-Training
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is a critical component of large language model (LLM) post-training. However, existing on-policy algorithms used for post-training are inherently incompatible with the use of experience replay buffers, which can be populated scalably by distributed off-policy actors to enhance exploration as compute increases. We propose efficiently obtaining this benefit of replay buffers via Trajectory Balance with Asynchrony (TBA), a massively scalable LLM RL system. In contrast to existing approaches, TBA uses a larger fraction of compute on search, constantly generating off-policy data for a central replay buffer. A training node simultaneously samples data from this buffer based on reward or recency to update the policy using Trajectory Balance (TB), a diversity-seeking RL objective introduced for GFlowNets. TBA offers three key advantages: (1) decoupled training and search, speeding up training wall-clock time by 4x or more; (2) improved diversity through large-scale off-policy sampling; and (3) scalable search for sparse reward settings. On mathematical reasoning, preference-tuning, and automated red-teaming (diverse and representative post-training tasks), TBA produces speed and performance improvements over strong baselines.
Solving Bayesian inverse problems with diffusion priors and off-policy RL
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a practical application of Relative Trajectory Balance (RTB), a recently introduced off-policy reinforcement learning (RL) objective that can asymptotically solve Bayesian inverse problems optimally. We extend the original work by using RTB to train conditional diffusion model posteriors from pretrained unconditional priors for challenging linear and non-linear inverse problems in vision, and science. We use the objective alongside techniques such as off-policy backtracking exploration to improve training. Importantly, our results show that existing training-free diffusion posterior methods struggle to perform effective posterior inference in latent space due to inherent biases.
Action abstractions for amortized sampling
Oct 19, 2024Abstract:As trajectories sampled by policies used by reinforcement learning (RL) and generative flow networks (GFlowNets) grow longer, credit assignment and exploration become more challenging, and the long planning horizon hinders mode discovery and generalization. The challenge is particularly pronounced in entropy-seeking RL methods, such as generative flow networks, where the agent must learn to sample from a structured distribution and discover multiple high-reward states, each of which take many steps to reach. To tackle this challenge, we propose an approach to incorporate the discovery of action abstractions, or high-level actions, into the policy optimization process. Our approach involves iteratively extracting action subsequences commonly used across many high-reward trajectories and `chunking' them into a single action that is added to the action space. In empirical evaluation on synthetic and real-world environments, our approach demonstrates improved sample efficiency performance in discovering diverse high-reward objects, especially on harder exploration problems. We also observe that the abstracted high-order actions are interpretable, capturing the latent structure of the reward landscape of the action space. This work provides a cognitively motivated approach to action abstraction in RL and is the first demonstration of hierarchical planning in amortized sequential sampling.
Proof Flow: Preliminary Study on Generative Flow Network Language Model Tuning for Formal Reasoning
Oct 17, 2024


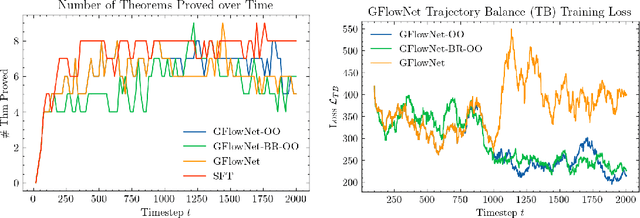
Abstract:Reasoning is a fundamental substrate for solving novel and complex problems. Deliberate efforts in learning and developing frameworks around System 2 reasoning have made great strides, yet problems of sufficient complexity remain largely out of reach for open models. To address this gap, we examine the potential of Generative Flow Networks as a fine-tuning method for LLMs to unlock advanced reasoning capabilities. In this paper, we present a proof of concept in the domain of formal reasoning, specifically in the Neural Theorem Proving (NTP) setting, where proofs specified in a formal language such as Lean can be deterministically and objectively verified. Unlike classical reward-maximization reinforcement learning, which frequently over-exploits high-reward actions and fails to effectively explore the state space, GFlowNets have emerged as a promising approach for sampling compositional objects, improving generalization, and enabling models to maintain diverse hypotheses. Our early results demonstrate GFlowNet fine-tuning's potential for enhancing model performance in a search setting, which is especially relevant given the paradigm shift towards inference time compute scaling and "thinking slowly."
Automated Discovery of Pairwise Interactions from Unstructured Data
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:Pairwise interactions between perturbations to a system can provide evidence for the causal dependencies of the underlying underlying mechanisms of a system. When observations are low dimensional, hand crafted measurements, detecting interactions amounts to simple statistical tests, but it is not obvious how to detect interactions between perturbations affecting latent variables. We derive two interaction tests that are based on pairwise interventions, and show how these tests can be integrated into an active learning pipeline to efficiently discover pairwise interactions between perturbations. We illustrate the value of these tests in the context of biology, where pairwise perturbation experiments are frequently used to reveal interactions that are not observable from any single perturbation. Our tests can be run on unstructured data, such as the pixels in an image, which enables a more general notion of interaction than typical cell viability experiments, and can be run on cheaper experimental assays. We validate on several synthetic and real biological experiments that our tests are able to identify interacting pairs effectively. We evaluate our approach on a real biological experiment where we knocked out 50 pairs of genes and measured the effect with microscopy images. We show that we are able to recover significantly more known biological interactions than random search and standard active learning baselines.
Amortizing intractable inference in diffusion models for vision, language, and control
May 31, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have emerged as effective distribution estimators in vision, language, and reinforcement learning, but their use as priors in downstream tasks poses an intractable posterior inference problem. This paper studies amortized sampling of the posterior over data, $\mathbf{x}\sim p^{\rm post}(\mathbf{x})\propto p(\mathbf{x})r(\mathbf{x})$, in a model that consists of a diffusion generative model prior $p(\mathbf{x})$ and a black-box constraint or likelihood function $r(\mathbf{x})$. We state and prove the asymptotic correctness of a data-free learning objective, relative trajectory balance, for training a diffusion model that samples from this posterior, a problem that existing methods solve only approximately or in restricted cases. Relative trajectory balance arises from the generative flow network perspective on diffusion models, which allows the use of deep reinforcement learning techniques to improve mode coverage. Experiments illustrate the broad potential of unbiased inference of arbitrary posteriors under diffusion priors: in vision (classifier guidance), language (infilling under a discrete diffusion LLM), and multimodal data (text-to-image generation). Beyond generative modeling, we apply relative trajectory balance to the problem of continuous control with a score-based behavior prior, achieving state-of-the-art results on benchmarks in offline reinforcement learning.
Learning diverse attacks on large language models for robust red-teaming and safety tuning
May 28, 2024Abstract:Red-teaming, or identifying prompts that elicit harmful responses, is a critical step in ensuring the safe and responsible deployment of large language models (LLMs). Developing effective protection against many modes of attack prompts requires discovering diverse attacks. Automated red-teaming typically uses reinforcement learning to fine-tune an attacker language model to generate prompts that elicit undesirable responses from a target LLM, as measured, for example, by an auxiliary toxicity classifier. We show that even with explicit regularization to favor novelty and diversity, existing approaches suffer from mode collapse or fail to generate effective attacks. As a flexible and probabilistically principled alternative, we propose to use GFlowNet fine-tuning, followed by a secondary smoothing phase, to train the attacker model to generate diverse and effective attack prompts. We find that the attacks generated by our method are effective against a wide range of target LLMs, both with and without safety tuning, and transfer well between target LLMs. Finally, we demonstrate that models safety-tuned using a dataset of red-teaming prompts generated by our method are robust to attacks from other RL-based red-teaming approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge