Berton Earnshaw
TxPert: Leveraging Biochemical Relationships for Out-of-Distribution Transcriptomic Perturbation Prediction
May 20, 2025Abstract:Accurately predicting cellular responses to genetic perturbations is essential for understanding disease mechanisms and designing effective therapies. Yet exhaustively exploring the space of possible perturbations (e.g., multi-gene perturbations or across tissues and cell types) is prohibitively expensive, motivating methods that can generalize to unseen conditions. In this work, we explore how knowledge graphs of gene-gene relationships can improve out-of-distribution (OOD) prediction across three challenging settings: unseen single perturbations; unseen double perturbations; and unseen cell lines. In particular, we present: (i) TxPert, a new state-of-the-art method that leverages multiple biological knowledge networks to predict transcriptional responses under OOD scenarios; (ii) an in-depth analysis demonstrating the impact of graphs, model architecture, and data on performance; and (iii) an expanded benchmarking framework that strengthens evaluation standards for perturbation modeling.
Virtual Cells: Predict, Explain, Discover
May 20, 2025Abstract:Drug discovery is fundamentally a process of inferring the effects of treatments on patients, and would therefore benefit immensely from computational models that can reliably simulate patient responses, enabling researchers to generate and test large numbers of therapeutic hypotheses safely and economically before initiating costly clinical trials. Even a more specific model that predicts the functional response of cells to a wide range of perturbations would be tremendously valuable for discovering safe and effective treatments that successfully translate to the clinic. Creating such virtual cells has long been a goal of the computational research community that unfortunately remains unachieved given the daunting complexity and scale of cellular biology. Nevertheless, recent advances in AI, computing power, lab automation, and high-throughput cellular profiling provide new opportunities for reaching this goal. In this perspective, we present a vision for developing and evaluating virtual cells that builds on our experience at Recursion. We argue that in order to be a useful tool to discover novel biology, virtual cells must accurately predict the functional response of a cell to perturbations and explain how the predicted response is a consequence of modifications to key biomolecular interactions. We then introduce key principles for designing therapeutically-relevant virtual cells, describe a lab-in-the-loop approach for generating novel insights with them, and advocate for biologically-grounded benchmarks to guide virtual cell development. Finally, we make the case that our approach to virtual cells provides a useful framework for building other models at higher levels of organization, including virtual patients. We hope that these directions prove useful to the research community in developing virtual models optimized for positive impact on drug discovery outcomes.
Automated Discovery of Pairwise Interactions from Unstructured Data
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:Pairwise interactions between perturbations to a system can provide evidence for the causal dependencies of the underlying underlying mechanisms of a system. When observations are low dimensional, hand crafted measurements, detecting interactions amounts to simple statistical tests, but it is not obvious how to detect interactions between perturbations affecting latent variables. We derive two interaction tests that are based on pairwise interventions, and show how these tests can be integrated into an active learning pipeline to efficiently discover pairwise interactions between perturbations. We illustrate the value of these tests in the context of biology, where pairwise perturbation experiments are frequently used to reveal interactions that are not observable from any single perturbation. Our tests can be run on unstructured data, such as the pixels in an image, which enables a more general notion of interaction than typical cell viability experiments, and can be run on cheaper experimental assays. We validate on several synthetic and real biological experiments that our tests are able to identify interacting pairs effectively. We evaluate our approach on a real biological experiment where we knocked out 50 pairs of genes and measured the effect with microscopy images. We show that we are able to recover significantly more known biological interactions than random search and standard active learning baselines.
Masked Autoencoders for Microscopy are Scalable Learners of Cellular Biology
Apr 16, 2024



Abstract:Featurizing microscopy images for use in biological research remains a significant challenge, especially for large-scale experiments spanning millions of images. This work explores the scaling properties of weakly supervised classifiers and self-supervised masked autoencoders (MAEs) when training with increasingly larger model backbones and microscopy datasets. Our results show that ViT-based MAEs outperform weakly supervised classifiers on a variety of tasks, achieving as much as a 11.5% relative improvement when recalling known biological relationships curated from public databases. Additionally, we develop a new channel-agnostic MAE architecture (CA-MAE) that allows for inputting images of different numbers and orders of channels at inference time. We demonstrate that CA-MAEs effectively generalize by inferring and evaluating on a microscopy image dataset (JUMP-CP) generated under different experimental conditions with a different channel structure than our pretraining data (RPI-93M). Our findings motivate continued research into scaling self-supervised learning on microscopy data in order to create powerful foundation models of cellular biology that have the potential to catalyze advancements in drug discovery and beyond.
Masked autoencoders are scalable learners of cellular morphology
Sep 27, 2023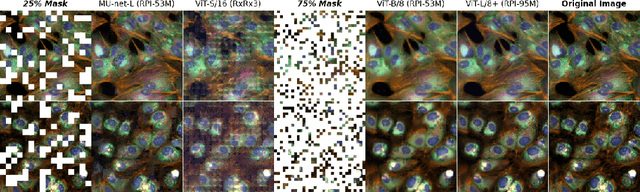
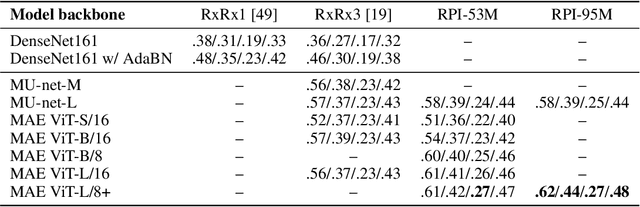
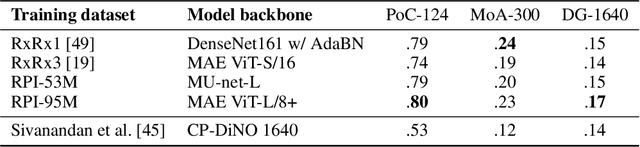
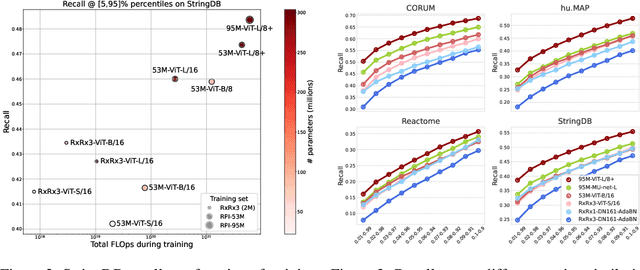
Abstract:Inferring biological relationships from cellular phenotypes in high-content microscopy screens provides significant opportunity and challenge in biological research. Prior results have shown that deep vision models can capture biological signal better than hand-crafted features. This work explores how weakly supervised and self-supervised deep learning approaches scale when training larger models on larger datasets. Our results show that both CNN- and ViT-based masked autoencoders significantly outperform weakly supervised models. At the high-end of our scale, a ViT-L/8 trained on over 3.5-billion unique crops sampled from 95-million microscopy images achieves relative improvements as high as 28% over our best weakly supervised models at inferring known biological relationships curated from public databases.
RxRx1: A Dataset for Evaluating Experimental Batch Correction Methods
Jan 13, 2023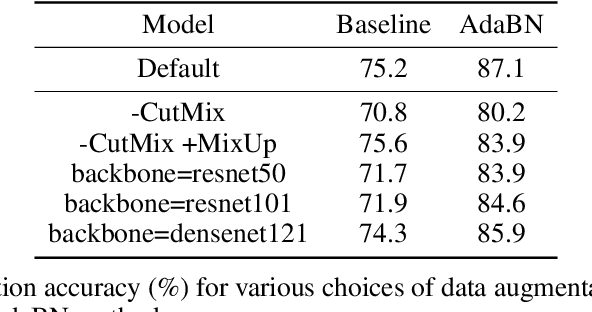



Abstract:High-throughput screening techniques are commonly used to obtain large quantities of data in many fields of biology. It is well known that artifacts arising from variability in the technical execution of different experimental batches within such screens confound these observations and can lead to invalid biological conclusions. It is therefore necessary to account for these batch effects when analyzing outcomes. In this paper we describe RxRx1, a biological dataset designed specifically for the systematic study of batch effect correction methods. The dataset consists of 125,510 high-resolution fluorescence microscopy images of human cells under 1,138 genetic perturbations in 51 experimental batches across 4 cell types. Visual inspection of the images alone clearly demonstrates significant batch effects. We propose a classification task designed to evaluate the effectiveness of experimental batch correction methods on these images and examine the performance of a number of correction methods on this task. Our goal in releasing RxRx1 is to encourage the development of effective experimental batch correction methods that generalize well to unseen experimental batches. The dataset can be downloaded at https://rxrx.ai.
MolE: a molecular foundation model for drug discovery
Nov 03, 2022



Abstract:Models that accurately predict properties based on chemical structure are valuable tools in drug discovery. However, for many properties, public and private training sets are typically small, and it is difficult for the models to generalize well outside of the training data. Recently, large language models have addressed this problem by using self-supervised pretraining on large unlabeled datasets, followed by fine-tuning on smaller, labeled datasets. In this paper, we report MolE, a molecular foundation model that adapts the DeBERTa architecture to be used on molecular graphs together with a two-step pretraining strategy. The first step of pretraining is a self-supervised approach focused on learning chemical structures, and the second step is a massive multi-task approach to learn biological information. We show that fine-tuning pretrained MolE achieves state-of-the-art results on 9 of the 22 ADMET tasks included in the Therapeutic Data Commons.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge