Maksym Korablyov
Generative Active Learning for the Search of Small-molecule Protein Binders
May 02, 2024



Abstract:Despite substantial progress in machine learning for scientific discovery in recent years, truly de novo design of small molecules which exhibit a property of interest remains a significant challenge. We introduce LambdaZero, a generative active learning approach to search for synthesizable molecules. Powered by deep reinforcement learning, LambdaZero learns to search over the vast space of molecules to discover candidates with a desired property. We apply LambdaZero with molecular docking to design novel small molecules that inhibit the enzyme soluble Epoxide Hydrolase 2 (sEH), while enforcing constraints on synthesizability and drug-likeliness. LambdaZero provides an exponential speedup in terms of the number of calls to the expensive molecular docking oracle, and LambdaZero de novo designed molecules reach docking scores that would otherwise require the virtual screening of a hundred billion molecules. Importantly, LambdaZero discovers novel scaffolds of synthesizable, drug-like inhibitors for sEH. In in vitro experimental validation, a series of ligands from a generated quinazoline-based scaffold were synthesized, and the lead inhibitor N-(4,6-di(pyrrolidin-1-yl)quinazolin-2-yl)-N-methylbenzamide (UM0152893) displayed sub-micromolar enzyme inhibition of sEH.
SE(3)-Stochastic Flow Matching for Protein Backbone Generation
Oct 03, 2023Abstract:The computational design of novel protein structures has the potential to impact numerous scientific disciplines greatly. Toward this goal, we introduce $\text{FoldFlow}$ a series of novel generative models of increasing modeling power based on the flow-matching paradigm over $3\text{D}$ rigid motions -- i.e. the group $\text{SE(3)}$ -- enabling accurate modeling of protein backbones. We first introduce $\text{FoldFlow-Base}$, a simulation-free approach to learning deterministic continuous-time dynamics and matching invariant target distributions on $\text{SE(3)}$. We next accelerate training by incorporating Riemannian optimal transport to create $\text{FoldFlow-OT}$, leading to the construction of both more simple and stable flows. Finally, we design $\text{FoldFlow-SFM}$ coupling both Riemannian OT and simulation-free training to learn stochastic continuous-time dynamics over $\text{SE(3)}$. Our family of $\text{FoldFlow}$ generative models offer several key advantages over previous approaches to the generative modeling of proteins: they are more stable and faster to train than diffusion-based approaches, and our models enjoy the ability to map any invariant source distribution to any invariant target distribution over $\text{SE(3)}$. Empirically, we validate our FoldFlow models on protein backbone generation of up to $300$ amino acids leading to high-quality designable, diverse, and novel samples.
Thompson sampling for improved exploration in GFlowNets
Jun 30, 2023Abstract:Generative flow networks (GFlowNets) are amortized variational inference algorithms that treat sampling from a distribution over compositional objects as a sequential decision-making problem with a learnable action policy. Unlike other algorithms for hierarchical sampling that optimize a variational bound, GFlowNet algorithms can stably run off-policy, which can be advantageous for discovering modes of the target distribution. Despite this flexibility in the choice of behaviour policy, the optimal way of efficiently selecting trajectories for training has not yet been systematically explored. In this paper, we view the choice of trajectories for training as an active learning problem and approach it using Bayesian techniques inspired by methods for multi-armed bandits. The proposed algorithm, Thompson sampling GFlowNets (TS-GFN), maintains an approximate posterior distribution over policies and samples trajectories from this posterior for training. We show in two domains that TS-GFN yields improved exploration and thus faster convergence to the target distribution than the off-policy exploration strategies used in past work.
Learning GFlowNets from partial episodes for improved convergence and stability
Sep 30, 2022
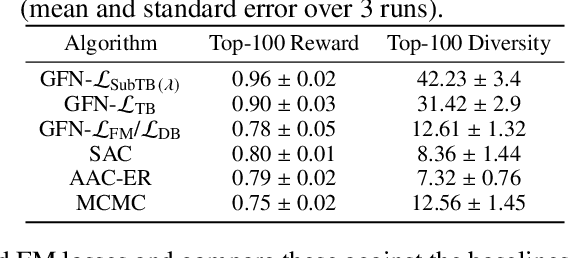

Abstract:Generative flow networks (GFlowNets) are a family of algorithms for training a sequential sampler of discrete objects under an unnormalized target density and have been successfully used for various probabilistic modeling tasks. Existing training objectives for GFlowNets are either local to states or transitions, or propagate a reward signal over an entire sampling trajectory. We argue that these alternatives represent opposite ends of a gradient bias-variance tradeoff and propose a way to exploit this tradeoff to mitigate its harmful effects. Inspired by the TD($\lambda$) algorithm in reinforcement learning, we introduce subtrajectory balance or SubTB($\lambda$), a GFlowNet training objective that can learn from partial action subsequences of varying lengths. We show that SubTB($\lambda$) accelerates sampler convergence in previously studied and new environments and enables training GFlowNets in environments with longer action sequences and sparser reward landscapes than what was possible before. We also perform a comparative analysis of stochastic gradient dynamics, shedding light on the bias-variance tradeoff in GFlowNet training and the advantages of subtrajectory balance.
RECOVER: sequential model optimization platform for combination drug repurposing identifies novel synergistic compounds in vitro
Feb 07, 2022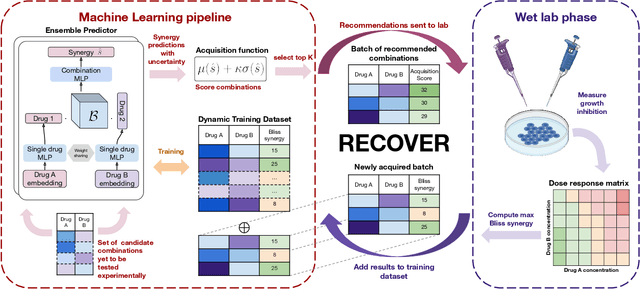
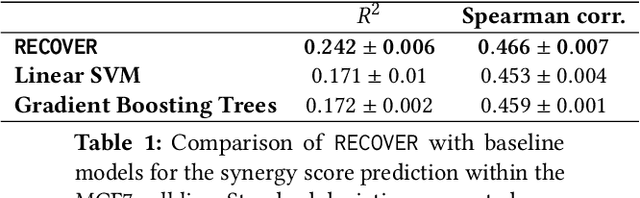


Abstract:Selecting optimal drug repurposing combinations for further preclinical development is a challenging technical feat. Due to the toxicity of many therapeutic agents (e.g., chemotherapy), practitioners have favoured selection of synergistic compounds whereby lower doses can be used whilst maintaining high efficacy. For a fixed small molecule library, an exhaustive combinatorial chemical screen becomes infeasible to perform for academic and industry laboratories alike. Deep learning models have achieved state-of-the-art results in silico for the prediction of synergy scores. However, databases of drug combinations are highly biased towards synergistic agents and these results do not necessarily generalise out of distribution. We employ a sequential model optimization search applied to a deep learning model to quickly discover highly synergistic drug combinations active against a cancer cell line, while requiring substantially less screening than an exhaustive evaluation. Through iteratively adapting the model to newly acquired data, after only 3 rounds of ML-guided experimentation (including a calibration round), we find that the set of combinations queried by our model is enriched for highly synergistic combinations. Remarkably, we rediscovered a synergistic drug combination that was later confirmed to be under study within clinical trials.
Properties of Minimizing Entropy
Dec 06, 2021


Abstract:Compact data representations are one approach for improving generalization of learned functions. We explicitly illustrate the relationship between entropy and cardinality, both measures of compactness, including how gradient descent on the former reduces the latter. Whereas entropy is distribution sensitive, cardinality is not. We propose a third compactness measure that is a compromise between the two: expected cardinality, or the expected number of unique states in any finite number of draws, which is more meaningful than standard cardinality as it discounts states with negligible probability mass. We show that minimizing entropy also minimizes expected cardinality.
Flow Network based Generative Models for Non-Iterative Diverse Candidate Generation
Jun 08, 2021



Abstract:This paper is about the problem of learning a stochastic policy for generating an object (like a molecular graph) from a sequence of actions, such that the probability of generating an object is proportional to a given positive reward for that object. Whereas standard return maximization tends to converge to a single return-maximizing sequence, there are cases where we would like to sample a diverse set of high-return solutions. These arise, for example, in black-box function optimization when few rounds are possible, each with large batches of queries, where the batches should be diverse, e.g., in the design of new molecules. One can also see this as a problem of approximately converting an energy function to a generative distribution. While MCMC methods can achieve that, they are expensive and generally only perform local exploration. Instead, training a generative policy amortizes the cost of search during training and yields to fast generation. Using insights from Temporal Difference learning, we propose GFlowNet, based on a view of the generative process as a flow network, making it possible to handle the tricky case where different trajectories can yield the same final state, e.g., there are many ways to sequentially add atoms to generate some molecular graph. We cast the set of trajectories as a flow and convert the flow consistency equations into a learning objective, akin to the casting of the Bellman equations into Temporal Difference methods. We prove that any global minimum of the proposed objectives yields a policy which samples from the desired distribution, and demonstrate the improved performance and diversity of GFlowNet on a simple domain where there are many modes to the reward function, and on a molecule synthesis task.
DEUP: Direct Epistemic Uncertainty Prediction
Feb 16, 2021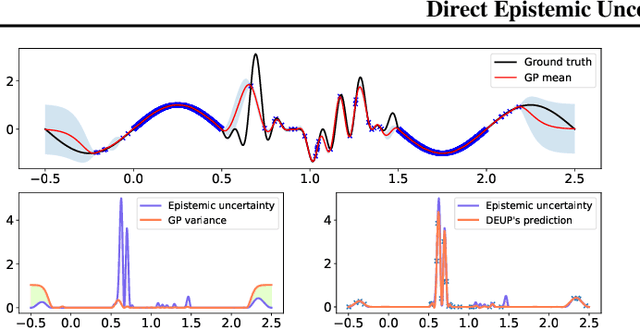
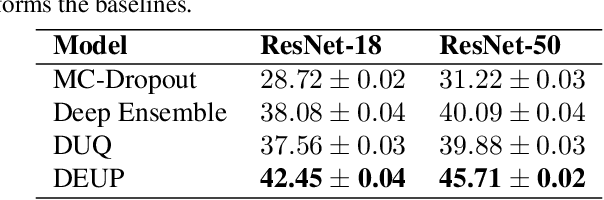
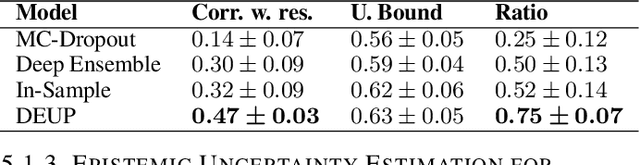
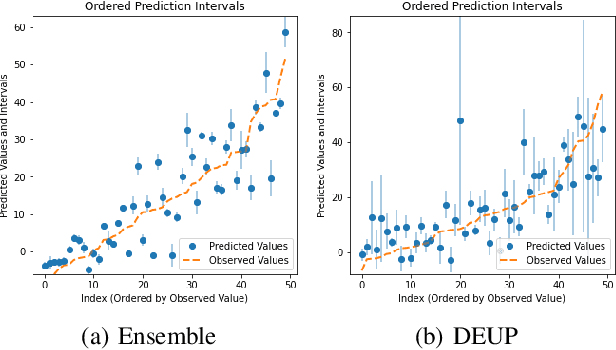
Abstract:Epistemic uncertainty is the part of out-of-sample prediction error due to the lack of knowledge of the learner. Whereas previous work was focusing on model variance, we propose a principled approach for directly estimating epistemic uncertainty by learning to predict generalization error and subtracting an estimate of aleatoric uncertainty, i.e., intrinsic unpredictability. This estimator of epistemic uncertainty includes the effect of model bias and can be applied in non-stationary learning environments arising in active learning or reinforcement learning. In addition to demonstrating these properties of Direct Epistemic Uncertainty Prediction (DEUP), we illustrate its advantage against existing methods for uncertainty estimation on downstream tasks including sequential model optimization and reinforcement learning. We also evaluate the quality of uncertainty estimates from DEUP for probabilistic classification of images and for estimating uncertainty about synergistic drug combinations.
RetroGNN: Approximating Retrosynthesis by Graph Neural Networks for De Novo Drug Design
Nov 25, 2020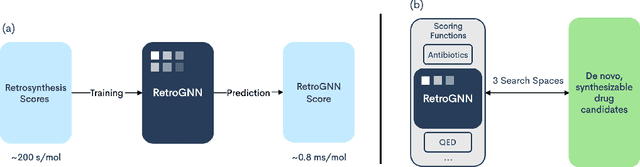
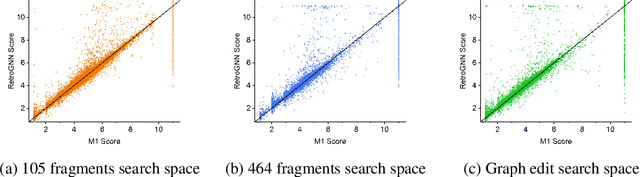
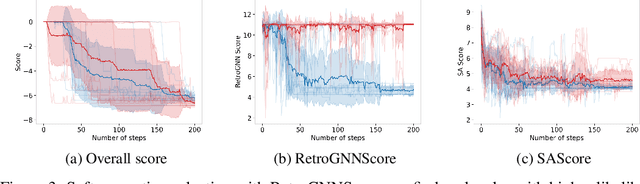
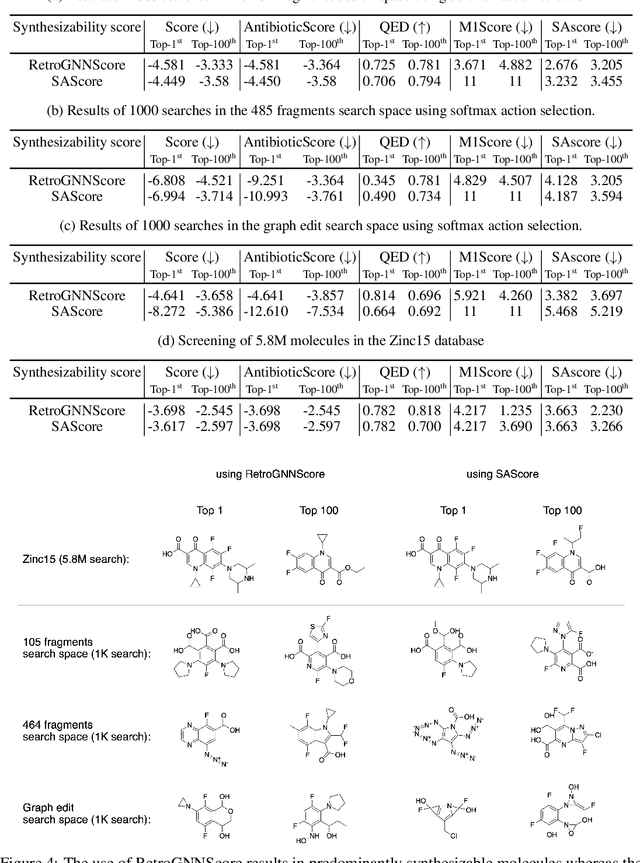
Abstract:De novo molecule generation often results in chemically unfeasible molecules. A natural idea to mitigate this problem is to bias the search process towards more easily synthesizable molecules using a proxy for synthetic accessibility. However, using currently available proxies still results in highly unrealistic compounds. We investigate the feasibility of training deep graph neural networks to approximate the outputs of a retrosynthesis planning software, and their use to bias the search process. We evaluate our method on a benchmark involving searching for drug-like molecules with antibiotic properties. Compared to enumerating over five million existing molecules from the ZINC database, our approach finds molecules predicted to be more likely to be antibiotics while maintaining good drug-like properties and being easily synthesizable. Importantly, our deep neural network can successfully filter out hard to synthesize molecules while achieving a $10^5$ times speed-up over using the retrosynthesis planning software.
Capsule networks for low-data transfer learning
Apr 26, 2018
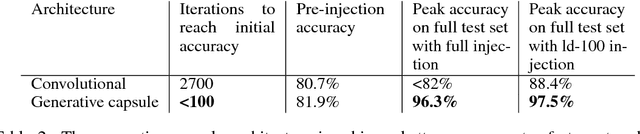
Abstract:We propose a capsule network-based architecture for generalizing learning to new data with few examples. Using both generative and non-generative capsule networks with intermediate routing, we are able to generalize to new information over 25 times faster than a similar convolutional neural network. We train the networks on the multiMNIST dataset lacking one digit. After the networks reach their maximum accuracy, we inject 1-100 examples of the missing digit into the training set, and measure the number of batches needed to return to a comparable level of accuracy. We then discuss the improvement in low-data transfer learning that capsule networks bring, and propose future directions for capsule research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge