Stanisław Jastrzębski
Molecule-Edit Templates for Efficient and Accurate Retrosynthesis Prediction
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:Retrosynthesis involves determining a sequence of reactions to synthesize complex molecules from simpler precursors. As this poses a challenge in organic chemistry, machine learning has offered solutions, particularly for predicting possible reaction substrates for a given target molecule. These solutions mainly fall into template-based and template-free categories. The former is efficient but relies on a vast set of predefined reaction patterns, while the latter, though more flexible, can be computationally intensive and less interpretable. To address these issues, we introduce METRO (Molecule-Edit Templates for RetrOsynthesis), a machine-learning model that predicts reactions using minimal templates - simplified reaction patterns capturing only essential molecular changes - reducing computational overhead and achieving state-of-the-art results on standard benchmarks.
3D-GMIC: an efficient deep neural network to find small objects in large 3D images
Oct 16, 2022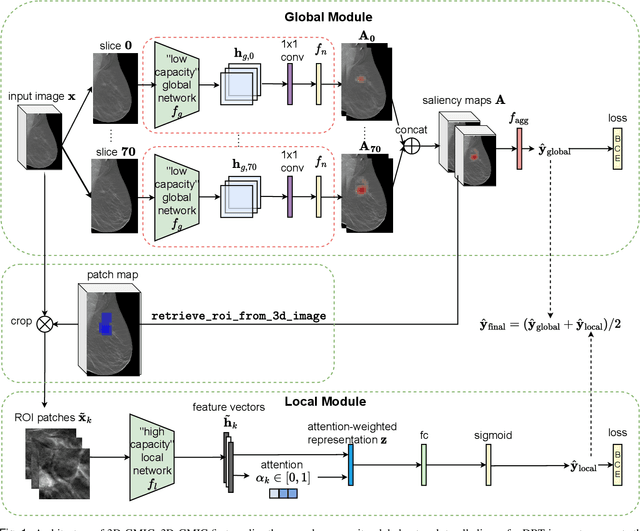
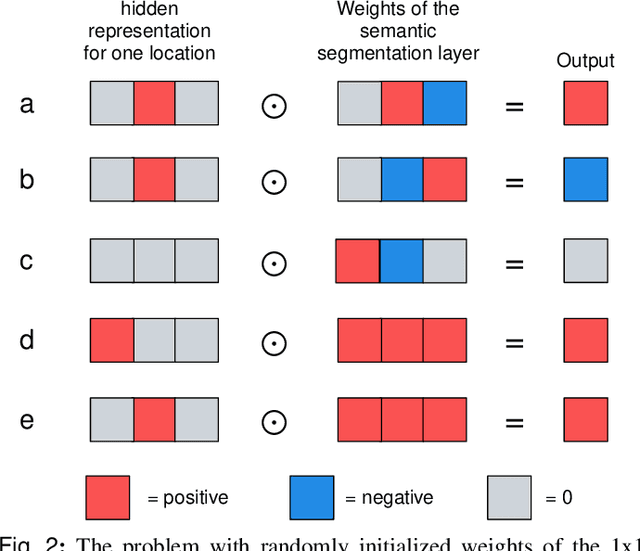
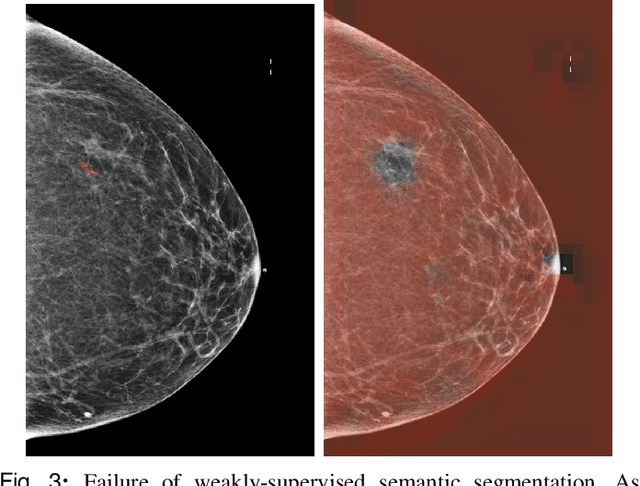
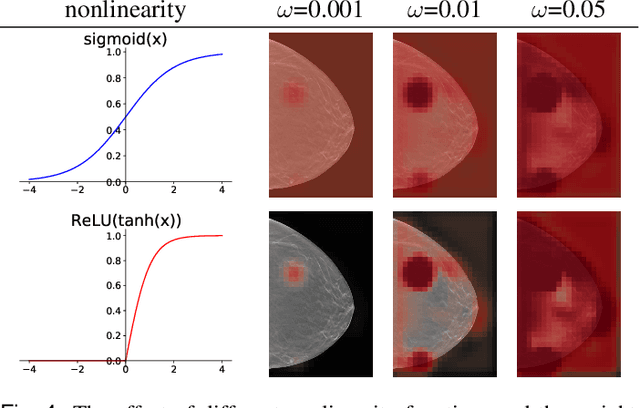
Abstract:3D imaging enables a more accurate diagnosis by providing spatial information about organ anatomy. However, using 3D images to train AI models is computationally challenging because they consist of tens or hundreds of times more pixels than their 2D counterparts. To train with high-resolution 3D images, convolutional neural networks typically resort to downsampling them or projecting them to two dimensions. In this work, we propose an effective alternative, a novel neural network architecture that enables computationally efficient classification of 3D medical images in their full resolution. Compared to off-the-shelf convolutional neural networks, 3D-GMIC uses 77.98%-90.05% less GPU memory and 91.23%-96.02% less computation. While our network is trained only with image-level labels, without segmentation labels, it explains its classification predictions by providing pixel-level saliency maps. On a dataset collected at NYU Langone Health, including 85,526 patients with full-field 2D mammography (FFDM), synthetic 2D mammography, and 3D mammography (DBT), our model, the 3D Globally-Aware Multiple Instance Classifier (3D-GMIC), achieves a breast-wise AUC of 0.831 (95% CI: 0.769-0.887) in classifying breasts with malignant findings using DBT images. As DBT and 2D mammography capture different information, averaging predictions on 2D and 3D mammography together leads to a diverse ensemble with an improved breast-wise AUC of 0.841 (95% CI: 0.768-0.895). Our model generalizes well to an external dataset from Duke University Hospital, achieving an image-wise AUC of 0.848 (95% CI: 0.798-0.896) in classifying DBT images with malignant findings.
Characterizing and overcoming the greedy nature of learning in multi-modal deep neural networks
Feb 10, 2022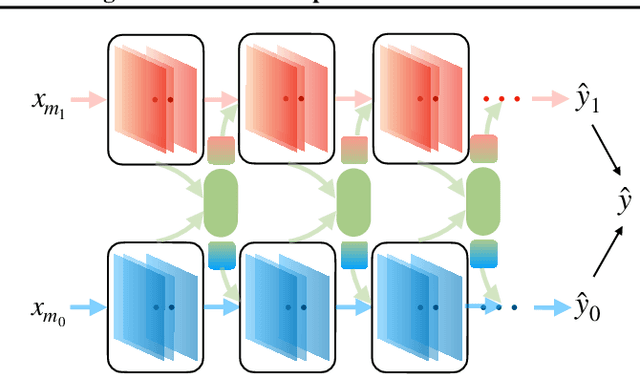
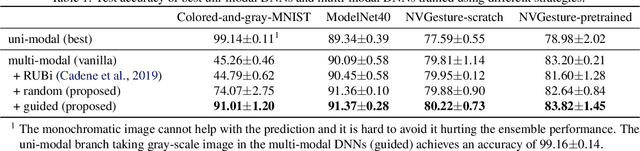
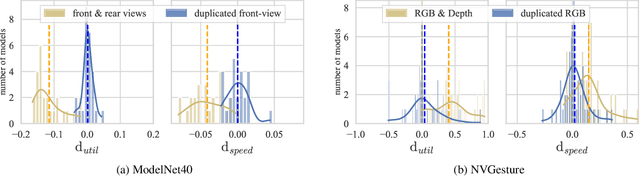
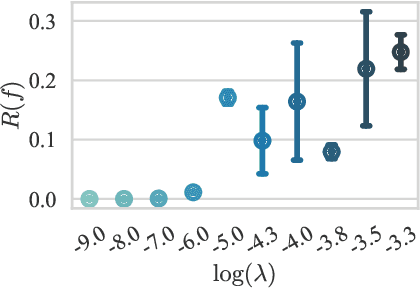
Abstract:We hypothesize that due to the greedy nature of learning in multi-modal deep neural networks, these models tend to rely on just one modality while under-fitting the other modalities. Such behavior is counter-intuitive and hurts the models' generalization, as we observe empirically. To estimate the model's dependence on each modality, we compute the gain on the accuracy when the model has access to it in addition to another modality. We refer to this gain as the conditional utilization rate. In the experiments, we consistently observe an imbalance in conditional utilization rates between modalities, across multiple tasks and architectures. Since conditional utilization rate cannot be computed efficiently during training, we introduce a proxy for it based on the pace at which the model learns from each modality, which we refer to as the conditional learning speed. We propose an algorithm to balance the conditional learning speeds between modalities during training and demonstrate that it indeed addresses the issue of greedy learning. The proposed algorithm improves the model's generalization on three datasets: Colored MNIST, Princeton ModelNet40, and NVIDIA Dynamic Hand Gesture.
Relative Molecule Self-Attention Transformer
Oct 12, 2021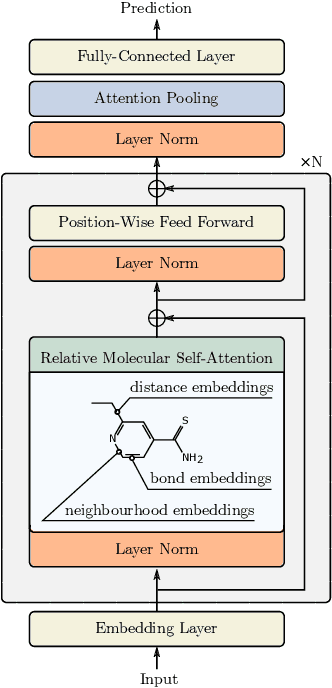
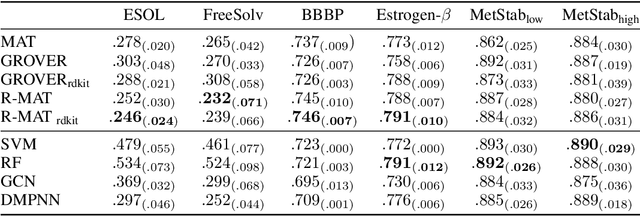
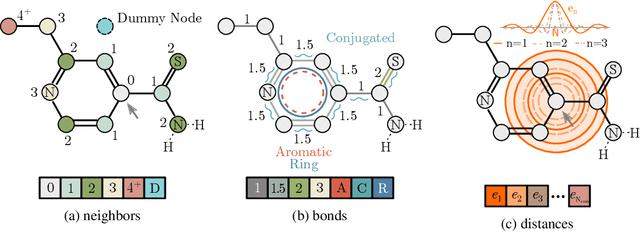
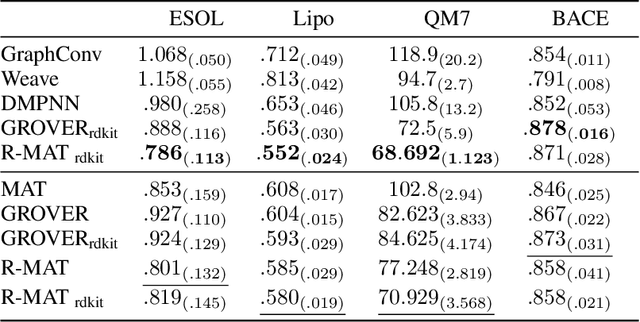
Abstract:Self-supervised learning holds promise to revolutionize molecule property prediction - a central task to drug discovery and many more industries - by enabling data efficient learning from scarce experimental data. Despite significant progress, non-pretrained methods can be still competitive in certain settings. We reason that architecture might be a key bottleneck. In particular, enriching the backbone architecture with domain-specific inductive biases has been key for the success of self-supervised learning in other domains. In this spirit, we methodologically explore the design space of the self-attention mechanism tailored to molecular data. We identify a novel variant of self-attention adapted to processing molecules, inspired by the relative self-attention layer, which involves fusing embedded graph and distance relationships between atoms. Our main contribution is Relative Molecule Attention Transformer (R-MAT): a novel Transformer-based model based on the developed self-attention layer that achieves state-of-the-art or very competitive results across a~wide range of molecule property prediction tasks.
RetroGNN: Approximating Retrosynthesis by Graph Neural Networks for De Novo Drug Design
Nov 25, 2020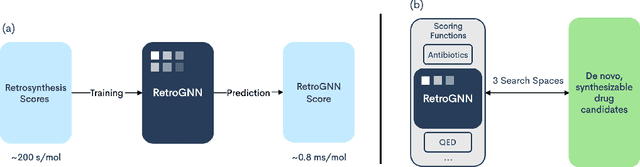
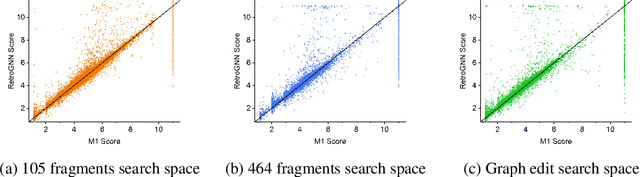
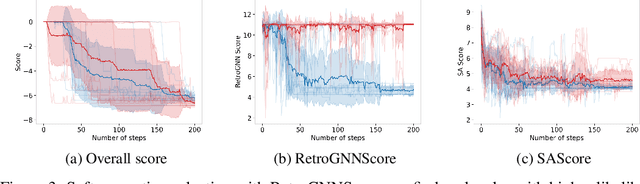
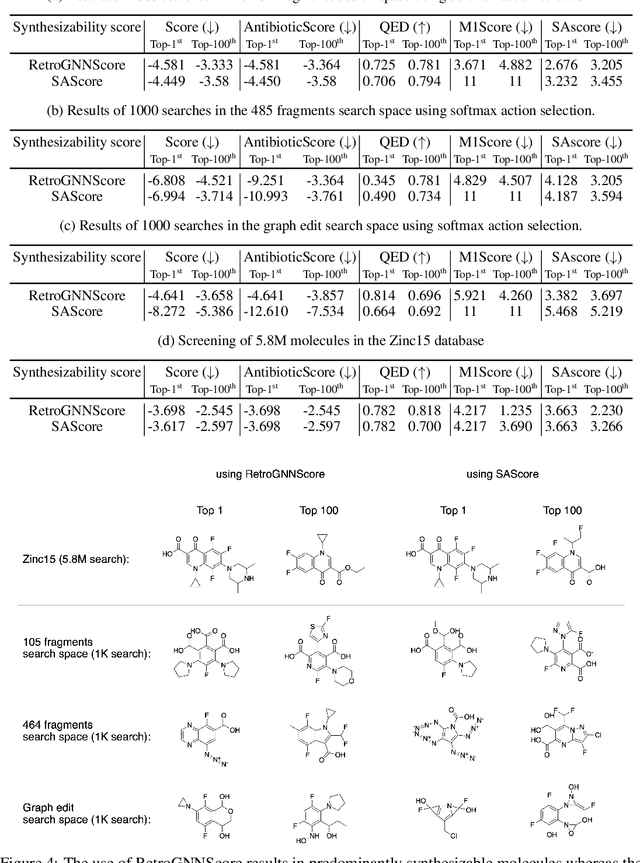
Abstract:De novo molecule generation often results in chemically unfeasible molecules. A natural idea to mitigate this problem is to bias the search process towards more easily synthesizable molecules using a proxy for synthetic accessibility. However, using currently available proxies still results in highly unrealistic compounds. We investigate the feasibility of training deep graph neural networks to approximate the outputs of a retrosynthesis planning software, and their use to bias the search process. We evaluate our method on a benchmark involving searching for drug-like molecules with antibiotic properties. Compared to enumerating over five million existing molecules from the ZINC database, our approach finds molecules predicted to be more likely to be antibiotics while maintaining good drug-like properties and being easily synthesizable. Importantly, our deep neural network can successfully filter out hard to synthesize molecules while achieving a $10^5$ times speed-up over using the retrosynthesis planning software.
Latent Adversarial Debiasing: Mitigating Collider Bias in Deep Neural Networks
Nov 19, 2020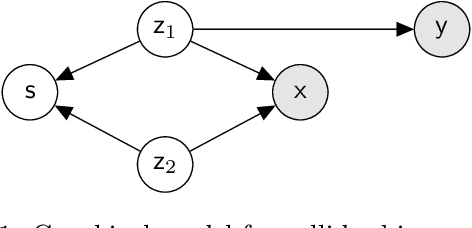
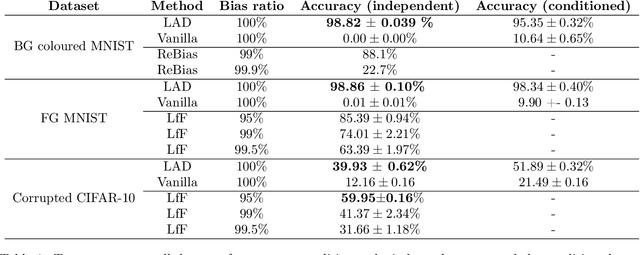
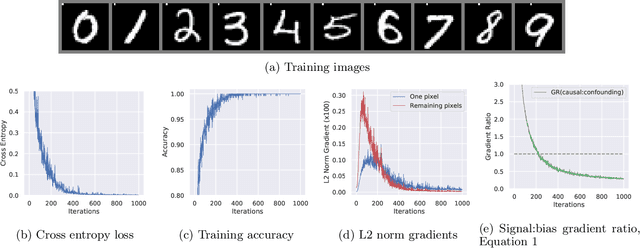
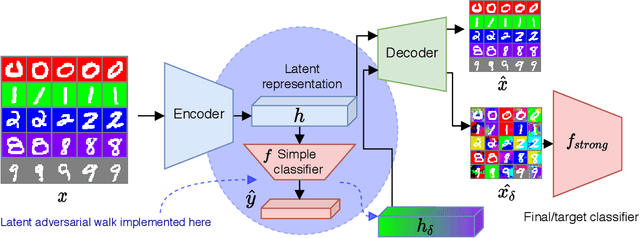
Abstract:Collider bias is a harmful form of sample selection bias that neural networks are ill-equipped to handle. This bias manifests itself when the underlying causal signal is strongly correlated with other confounding signals due to the training data collection procedure. In the situation where the confounding signal is easy-to-learn, deep neural networks will latch onto this and the resulting model will generalise poorly to in-the-wild test scenarios. We argue herein that the cause of failure is a combination of the deep structure of neural networks and the greedy gradient-driven learning process used - one that prefers easy-to-compute signals when available. We show it is possible to mitigate against this by generating bias-decoupled training data using latent adversarial debiasing (LAD), even when the confounding signal is present in 100% of the training data. By training neural networks on these adversarial examples,we can improve their generalisation in collider bias settings. Experiments show state-of-the-art performance of LAD in label-free debiasing with gains of 76.12% on background coloured MNIST, 35.47% on fore-ground coloured MNIST, and 8.27% on corrupted CIFAR-10.
An artificial intelligence system for predicting the deterioration of COVID-19 patients in the emergency department
Aug 04, 2020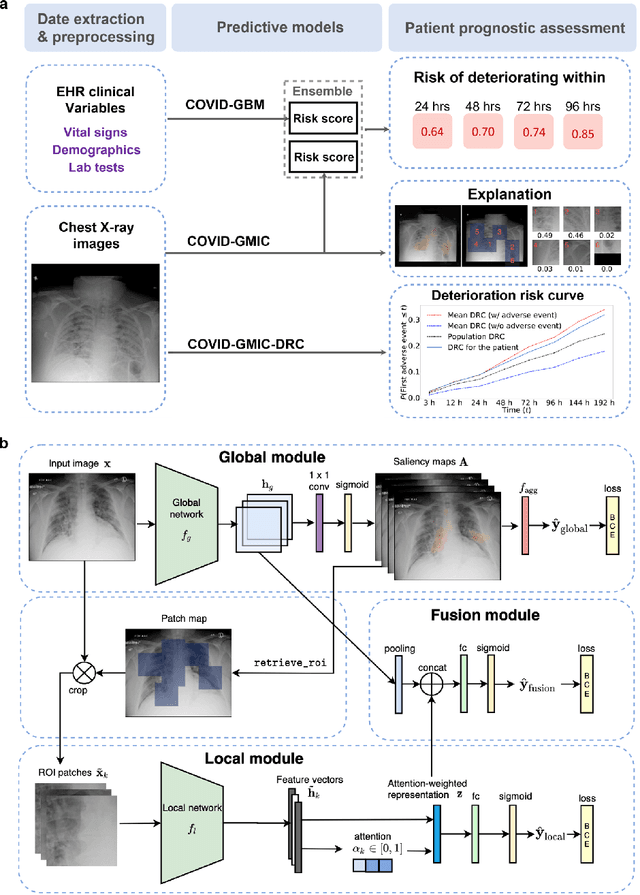
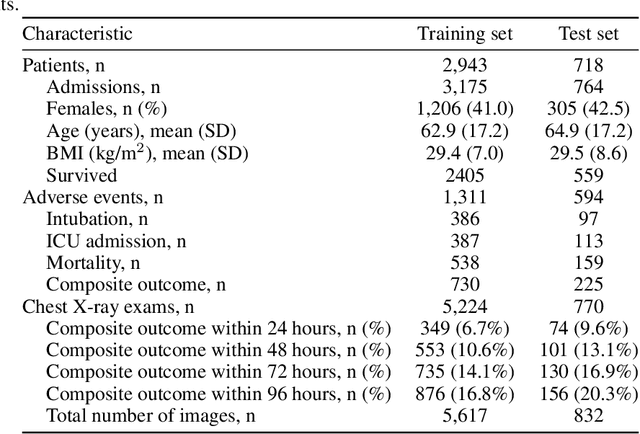
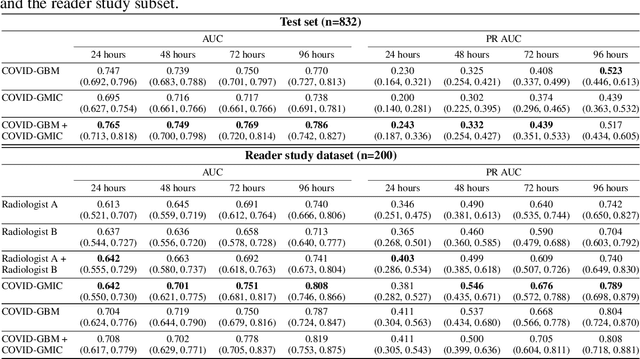
Abstract:During the COVID-19 pandemic, rapid and accurate triage of patients at the emergency department is critical to inform decision-making. We propose a data-driven approach for automatic prediction of deterioration risk using a deep neural network that learns from chest X-ray images, and a gradient boosting model that learns from routine clinical variables. Our AI prognosis system, trained using data from 3,661 patients, achieves an AUC of 0.786 (95% CI: 0.742-0.827) when predicting deterioration within 96 hours. The deep neural network extracts informative areas of chest X-ray images to assist clinicians in interpreting the predictions, and performs comparably to two radiologists in a reader study. In order to verify performance in a real clinical setting, we silently deployed a preliminary version of the deep neural network at NYU Langone Health during the first wave of the pandemic, which produced accurate predictions in real-time. In summary, our findings demonstrate the potential of the proposed system for assisting front-line physicians in the triage of COVID-19 patients.
Molecule Edit Graph Attention Network: Modeling Chemical Reactions as Sequences of Graph Edits
Jun 27, 2020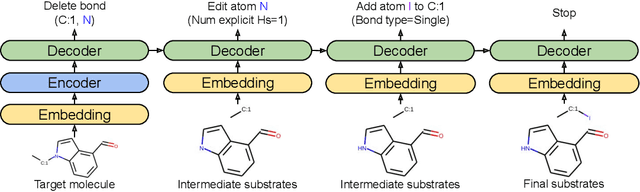
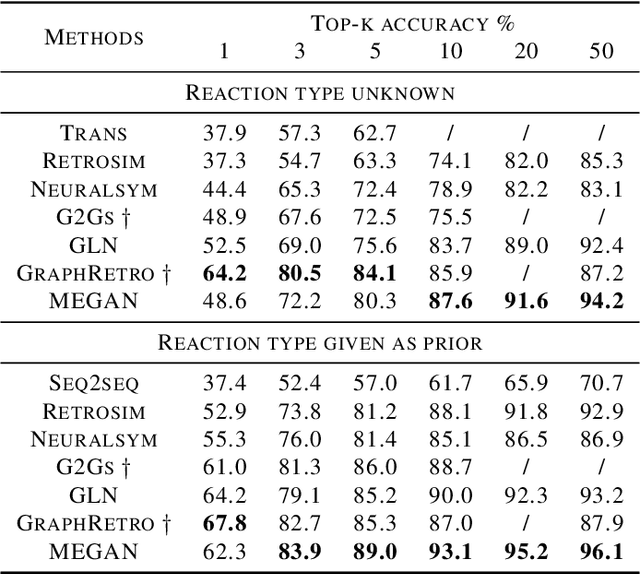

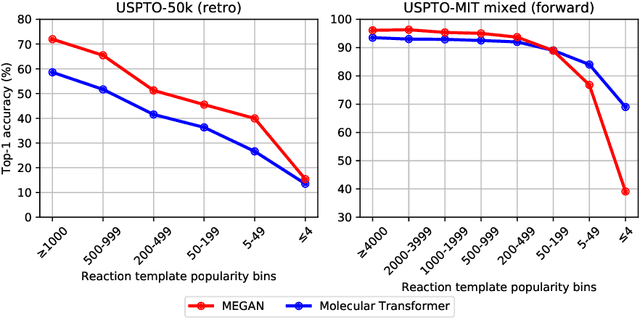
Abstract:One of the key challenges in automated synthesis planning is to generate diverse and reliable chemical reactions. Many reactions can be naturally represented using graph transformation rules referred broadly to as reaction templates. Using reaction templates enables accurate and interpretable predictions but can suffer from limited coverage of the reaction space. On the other hand, template-free methods can increase the coverage but can be prone to making trivial mistakes and are challenging to interpret. A promising idea for constructing more interpretable template-free models is to model a reaction as a sequence of graph edits of the substrates. We extend this idea to retrosynthesis and scale it up to large datasets. We propose Molecule Edit Graph Attention Network (MEGAN), a template-free neural model that encodes reaction as a sequence of graph edits. We achieve competitive performance on both retrosynthesis and forward synthesis and in particular state-of-the-art top-k accuracy for larger K values. Crucially, the latter shows excellent coverage of the reaction space of our model. In summary, MEGAN brings together the strong elements of template-free and template-based models and can be applied to both retro and forward synthesis tasks.
Understanding the robustness of deep neural network classifiers for breast cancer screening
Mar 23, 2020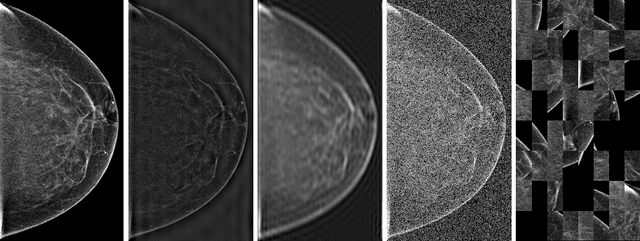
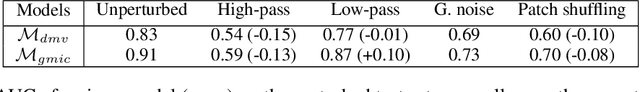
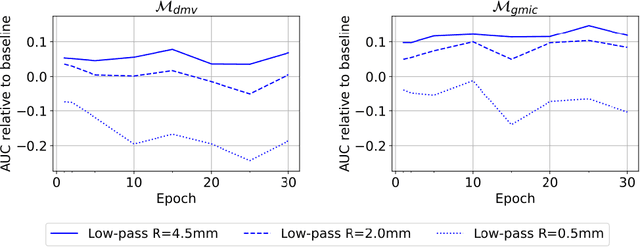
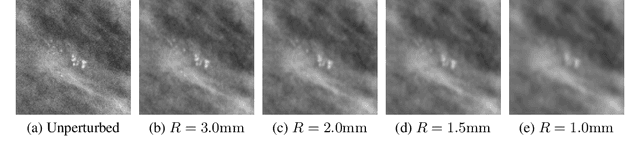
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) show promise in breast cancer screening, but their robustness to input perturbations must be better understood before they can be clinically implemented. There exists extensive literature on this subject in the context of natural images that can potentially be built upon. However, it cannot be assumed that conclusions about robustness will transfer from natural images to mammogram images, due to significant differences between the two image modalities. In order to determine whether conclusions will transfer, we measure the sensitivity of a radiologist-level screening mammogram image classifier to four commonly studied input perturbations that natural image classifiers are sensitive to. We find that mammogram image classifiers are also sensitive to these perturbations, which suggests that we can build on the existing literature. We also perform a detailed analysis on the effects of low-pass filtering, and find that it degrades the visibility of clinically meaningful features called microcalcifications. Since low-pass filtering removes semantically meaningful information that is predictive of breast cancer, we argue that it is undesirable for mammogram image classifiers to be invariant to it. This is in contrast to natural images, where we do not want DNNs to be sensitive to low-pass filtering due to its tendency to remove information that is human-incomprehensible.
Molecule Attention Transformer
Feb 19, 2020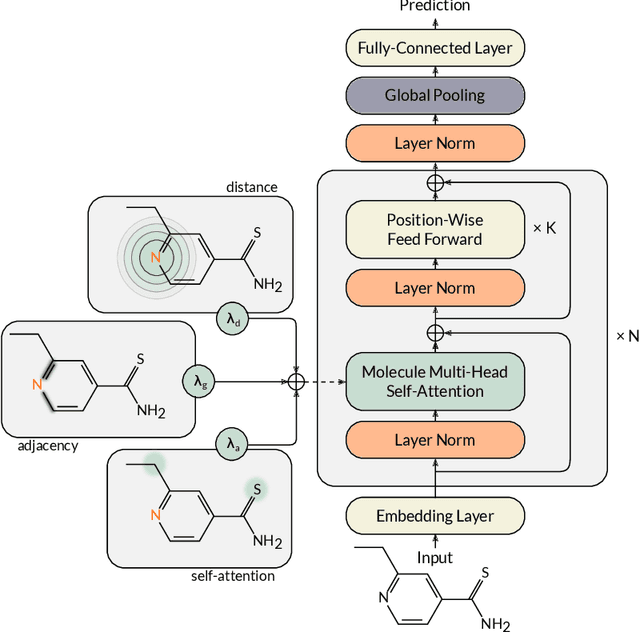
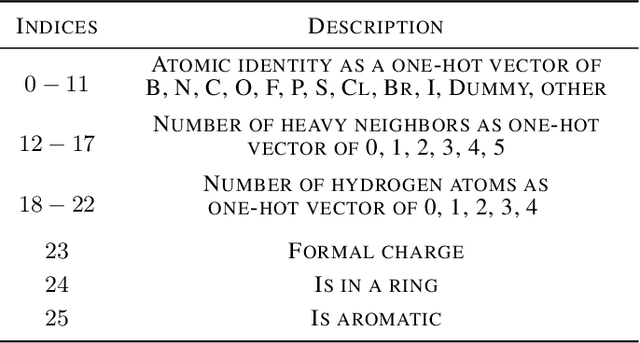
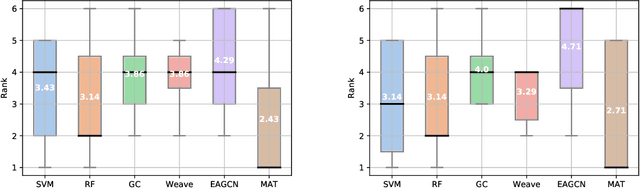

Abstract:Designing a single neural network architecture that performs competitively across a range of molecule property prediction tasks remains largely an open challenge, and its solution may unlock a widespread use of deep learning in the drug discovery industry. To move towards this goal, we propose Molecule Attention Transformer (MAT). Our key innovation is to augment the attention mechanism in Transformer using inter-atomic distances and the molecular graph structure. Experiments show that MAT performs competitively on a diverse set of molecular prediction tasks. Most importantly, with a simple self-supervised pretraining, MAT requires tuning of only a few hyperparameter values to achieve state-of-the-art performance on downstream tasks. Finally, we show that attention weights learned by MAT are interpretable from the chemical point of view.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge